This is a repository of resources for React Fiber.
React Fiber is a new React reconciler algorithm, which is used from v16.
You can try React Fiber asynchronous rendering by the following ways.
Inside a ReactDOM.unstable_deferredUpdates callback, the updates are treated as Low Priority.
ReactDOM.unstable_deferredUpdates(() => {
ReactDOM.render(<App />. container);
// or
instance.setState(() => newState);
});React.unstable_AsyncMode is a Component to make updates in child components asynchronous, which means the updates are treated as Low Priority.
const AsyncMode = React.unstable_AsyncMode;
<AsyncMode>
<App /> // Low Priority by default
</AsyncMode>If you'd like to use synchronous updates inside the component, you can use ReactDOM.flushSync(cb).
Inside of the ReactDOM.flushSync callback, the updates are treated as Sync Priority, which is the default priority of v16.
ReactDOM.flushSync(() => {
// Sync Priority for use input or an animation etc
});You can try the React Fiber's time slicing feature in the following example. In the example, you would realize that low priorities updates don't block sync priority updates. If you can't get any diferrence between Async mode and Sync mode, you should use CPU throttling on Chrome 😄
If you are not familiar with React internals, I recommend you to read the documentations, which are very helpful.
- React Fiber Architecture
- Fiber Principles: Contributing To Fiber #7942
- How React Fiber Works
- React Internals
- Capability of React Fiber
- A look inside React Fiber - how work will get done
- Build your own React Fiber
- Dan Abramov: Beyond React 16
- Andrew Clark: Roadmap for React Fiber and Beyond
- The Evolution of React and GraphQL at Facebook and Beyond
- Lin Clark - A Cartoon Intro to Fiber - React Conf 2017
- Sebastian Markbåge - React Performance End to End (React Fiber)
- Andrew Clark: What's Next for React — ReactNext 2016
- Why, What, and How of React Fiber with Dan Abramov and Andrew Clark
- A tiny Fiber renderer
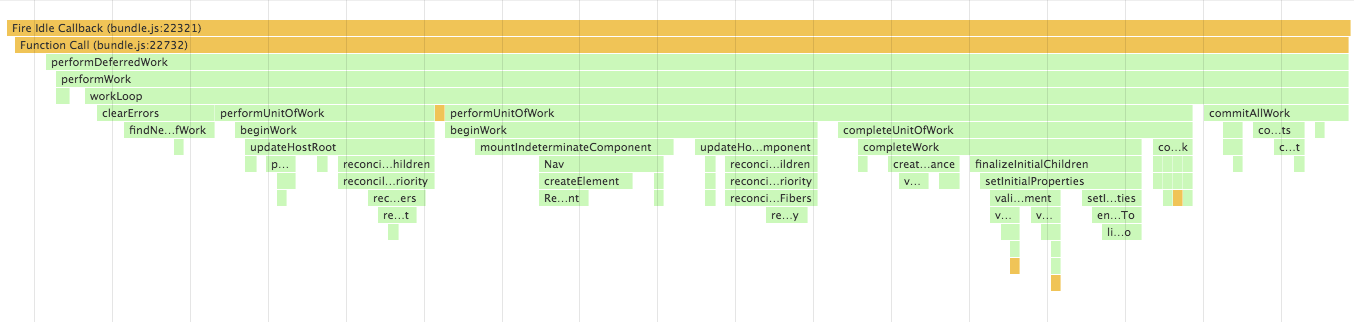
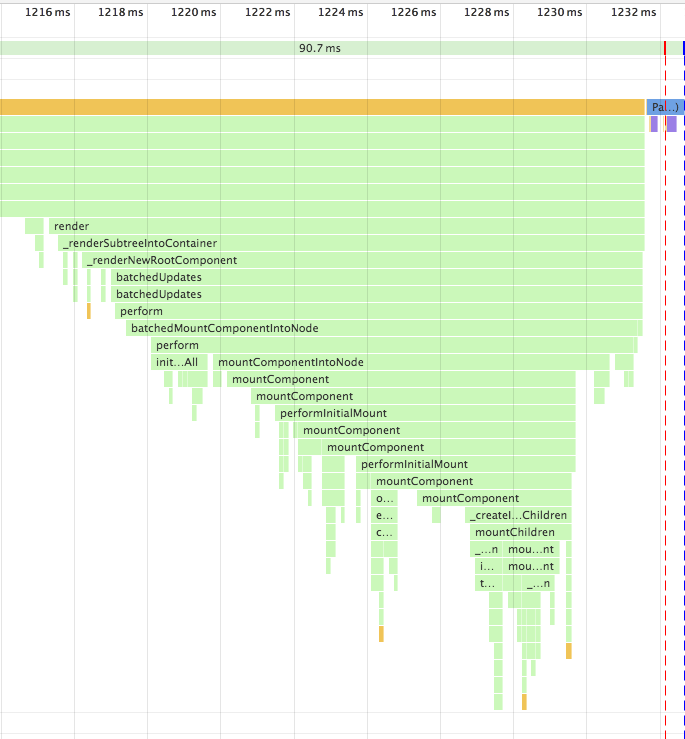
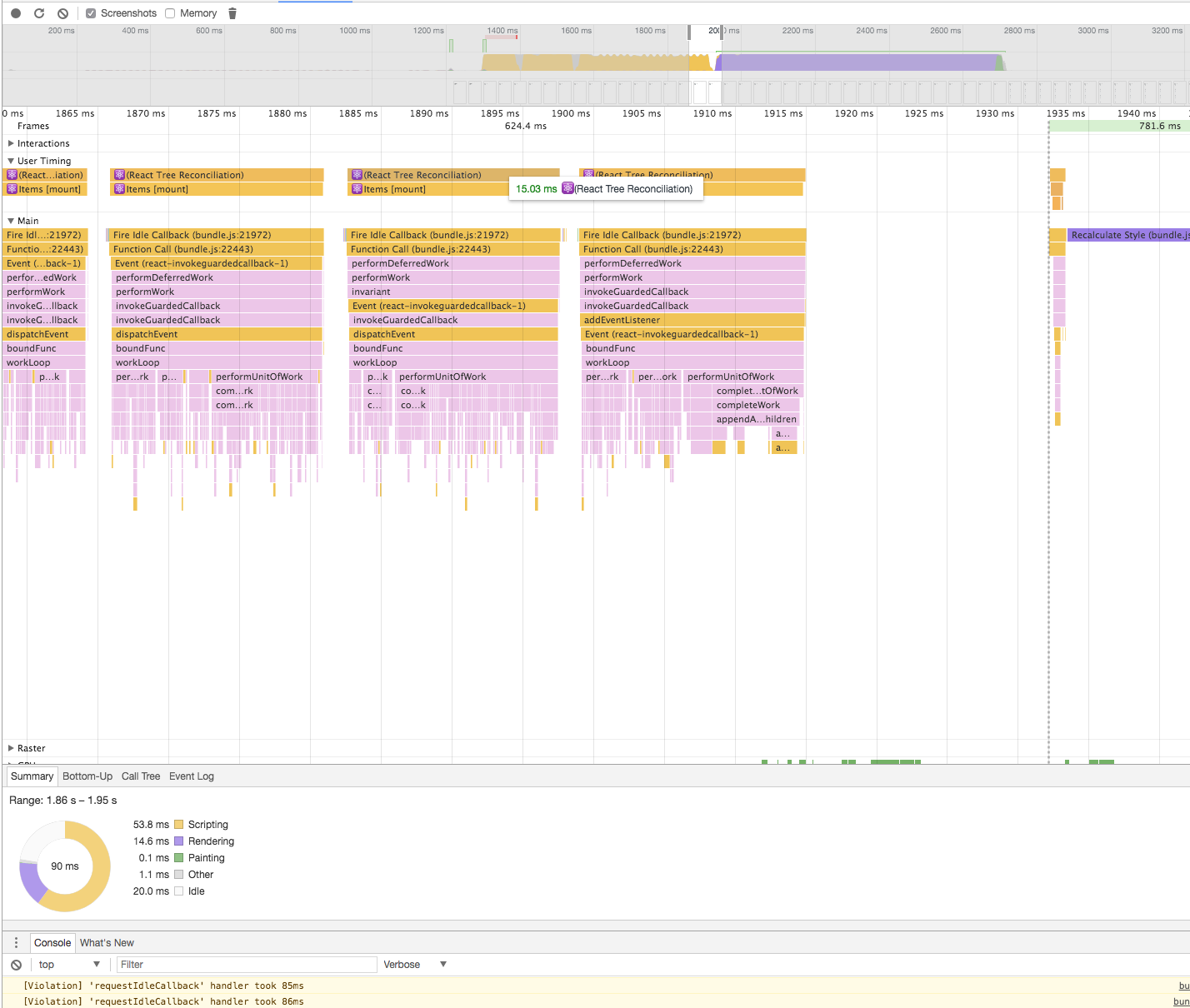
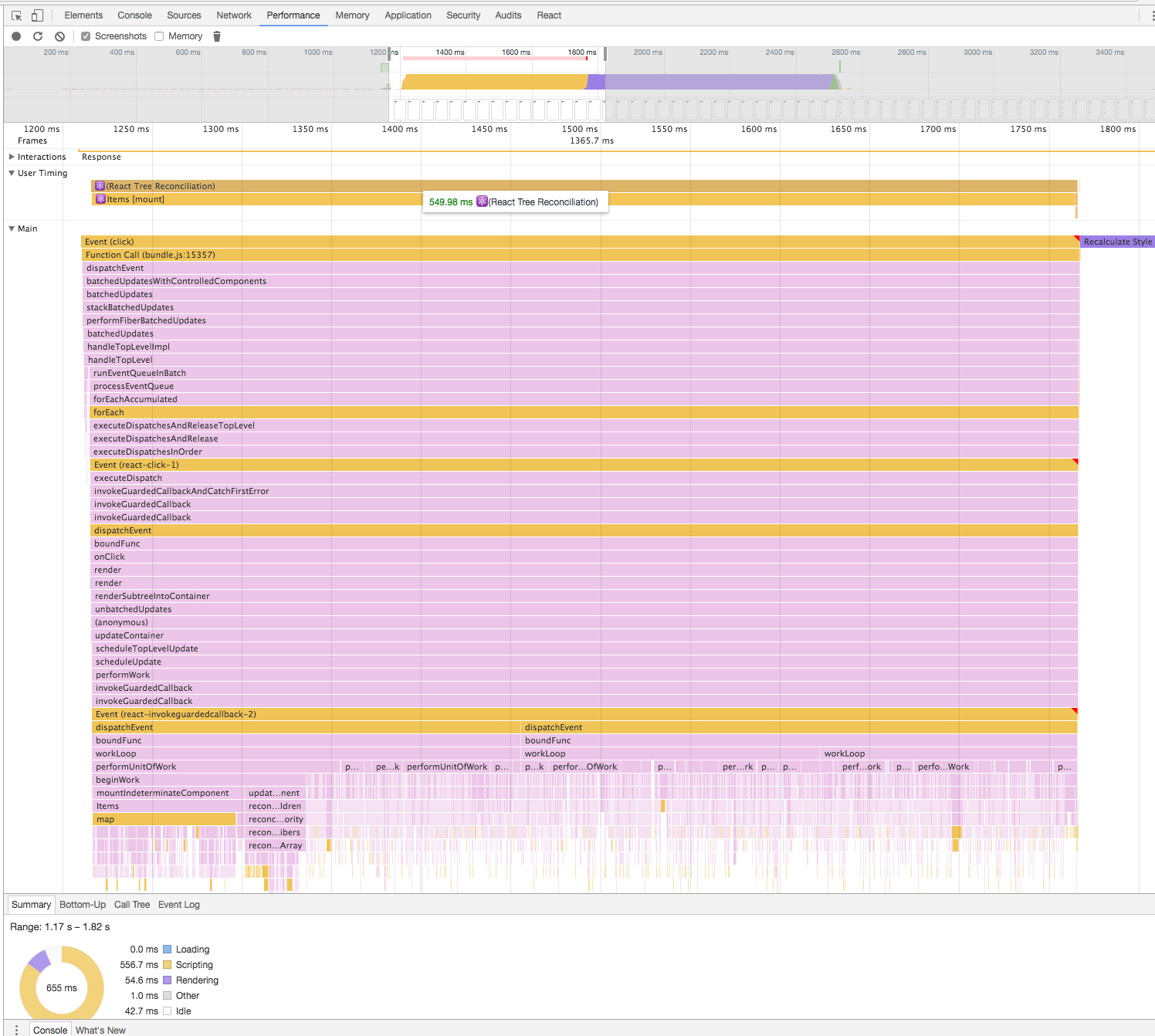
[Note] React Fiber now behaves as synchronous by default. See #8127. This call stacks are results in the time when it behaved as asynchronous.
--- working asynchronously using requestIdleCallback -------------------------------------------------
| ------- Fiber --------------- ------- Fiber --------------- ------ Fiber --------------- |
| | beginWork -> completeWork | -> | beginWork -> completeWork | -> |beginWork -> completeWork | ... |
| ----------------------------- ------------------------------ ---------------------------- |
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
↓↓↓
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
| commitAllWork(flush side effects computed in the above to the host) |
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
- Fiber
- Call Stack
- Coroutine
- Continuation
- Algebraic Effects
You should implement the following interface when create a custom fiber renderer.
- https://github.com/facebook/react/tree/master/packages/react-reconciler
- https://github.com/facebook/react/blob/master/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberReconciler.js
ReactConsole.render(
<>
<red>Hello</red>
<yellow>World</yellow>
<cyan>React</cyan>
<rainbow>Custom Renderer!</rainbow>
</>,
() => console.log(colors.inverse('##### Update ######'))
);
ReactConsole.render(
<>
<green>Hello</green>
<yellow>World2</yellow>
<cyan>React</cyan>
</>
);- Voice Renderer
ReactVoice.render(
<>
<alex>Hello</alex>
<victoria>React Fiber</victoria>
</>
);ReactNoop is a renderer for React Fiber, which is using for testing and debugging. It is very useful to understand React Fiber renderer!! 👀
Bonus: You should watch ReactIncremental-test.internal.js, which helps to understand what React Fiber makes it possible