This is an unofficial implementation of the paper "Deep Image Homography Estimation", by Daniel DeTone, Tomasz Malisiewicz, and Andrew Rabinovich: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1606.03798.pdf
Traditional homography estimators are based on finding feature correspondences in images. The most common algorithms used
for this task make the use of point feature correspondences as well as other features and they are based on corner
estimation and robust homography estimation. This work is based on the paper “Deep Image Homography Estimation” by Daniel
DeTone, Tomasz Malisiewicz and Andrew Rabnovich, in which the authors present a deep convolutional neural network to
estimate a homography mapping between a pair of images without the need for feature detection and processing. The
network is trained end-to-end using MS-COCO dataset images.
MS-COCO 2017 dataset is a relatively big dataset (118,287 (18GB) of training samples). As described by the authors, we trained the network on 90000 iterations for 48 epochs. We used NVIDIA tesla p4 GPU, the training took approximately 7 hours. During training, we used stochastic gradient descent (SGD) with momentum of 0.9 and a learning rate of 0.005 and dropout enabled in the last convolutional layer and the first fully connected layer. We evaluated the model on MS-COCO 2017 validation set. The performance of the model is based on the L2 loss values omitted by the network.
Due to the specification of the task that requires a new way of organizing the data that will be fed into the network, we have implemented a costumized Dataset class in Pytorch so that the data loader can produce iterable samples of data knowing the sample X (2 batches A and B) and the corresponding label Y (H 4 points).
To train the network from scratch on MS-COCO dataset we needed a powerful GPU. Fortunately, Google Cloud Platform (GCP) provides different types of GPU’s on the cloud in deep learning instances, so we have used a google compute engine with the following characteristics:
• High memory machine type with 8 vCPUs and 52 GB of memory.
• 200 GB disk.
• NVIDIA tesla p4 GPU:
GPU Architecture | NVIDIA Pascal™
Single-Precision Performance | 5.5 TeraFLOPSInteger Operations (INT8)22 TOPS (Tera-Operations per Second)
GPU Memory | 8 GB
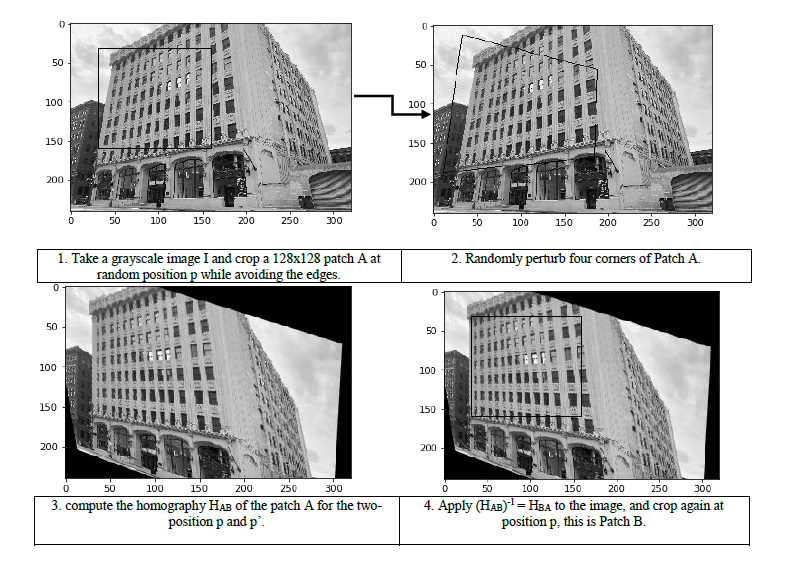
The authors have generated a large amount of image data and ground truth homographies from the MS-COCO dataset by applying random projective transformations to generate image pairs as well as the corresponding homography in 4 steps:
Finally, Stack Patch A and Patch B channel-wise and feed into the network. Set HAB as the target vector.