Implementation of Alphafold 3 in Pytorch
You can chat with other researchers about this work here
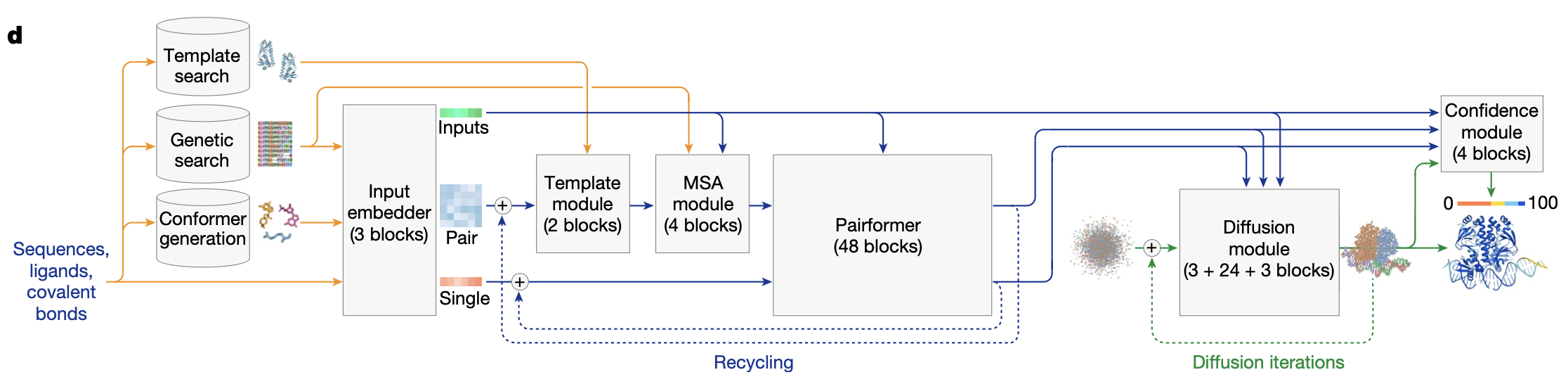
Illustrated guide by Elana P. Simon
A fork with full Lightning + Hydra support is being maintained by Alex at this repository
-
Joseph for contributing the Relative Positional Encoding and the Smooth LDDT Loss!
-
Felipe for contributing Weighted Rigid Align, Express Coordinates In Frame, Compute Alignment Error, and Centre Random Augmentation modules!
-
Alex for fixing various issues in the transcribed algorithms
-
Heng for pointing out inconsistencies with the paper and pull requesting the solutions
-
Heng for finding an issue with the molecular atom indices for the distogram loss
-
Wei Lu for catching a few erroneous hyperparameters
-
Alex for the PDB dataset preparation script!
-
Milot for optimizing the PDB dataset clustering script!
-
Patrick for jaxtyping, Florian for einx, and of course, Alex for einops
$ pip install alphafold3-pytorchimport torch
from alphafold3_pytorch import Alphafold3
alphafold3 = Alphafold3(
dim_atom_inputs = 77,
dim_template_feats = 44
)
# mock inputs
seq_len = 16
molecule_atom_lens = torch.randint(1, 3, (2, seq_len))
atom_seq_len = molecule_atom_lens.sum(dim = -1).amax()
atom_inputs = torch.randn(2, atom_seq_len, 77)
atompair_inputs = torch.randn(2, atom_seq_len, atom_seq_len, 5)
additional_molecule_feats = torch.randint(0, 2, (2, seq_len, 5))
additional_token_feats = torch.randn(2, seq_len, 2)
is_molecule_types = torch.randint(0, 2, (2, seq_len, 4)).bool()
molecule_ids = torch.randint(0, 32, (2, seq_len))
template_feats = torch.randn(2, 2, seq_len, seq_len, 44)
template_mask = torch.ones((2, 2)).bool()
msa = torch.randn(2, 7, seq_len, 64)
msa_mask = torch.ones((2, 7)).bool()
# required for training, but omitted on inference
atom_pos = torch.randn(2, atom_seq_len, 3)
molecule_atom_indices = molecule_atom_lens - 1 # last atom, as an example
distance_labels = torch.randint(0, 37, (2, seq_len, seq_len))
pae_labels = torch.randint(0, 64, (2, seq_len, seq_len))
pde_labels = torch.randint(0, 64, (2, seq_len, seq_len))
plddt_labels = torch.randint(0, 50, (2, seq_len))
resolved_labels = torch.randint(0, 2, (2, seq_len))
# train
loss = alphafold3(
num_recycling_steps = 2,
atom_inputs = atom_inputs,
atompair_inputs = atompair_inputs,
molecule_ids = molecule_ids,
molecule_atom_lens = molecule_atom_lens,
additional_molecule_feats = additional_molecule_feats,
additional_token_feats = additional_token_feats,
is_molecule_types = is_molecule_types,
msa = msa,
msa_mask = msa_mask,
templates = template_feats,
template_mask = template_mask,
atom_pos = atom_pos,
molecule_atom_indices = molecule_atom_indices,
distance_labels = distance_labels,
pae_labels = pae_labels,
pde_labels = pde_labels,
plddt_labels = plddt_labels,
resolved_labels = resolved_labels
)
loss.backward()
# after much training ...
sampled_atom_pos = alphafold3(
num_recycling_steps = 4,
num_sample_steps = 16,
atom_inputs = atom_inputs,
atompair_inputs = atompair_inputs,
molecule_ids = molecule_ids,
molecule_atom_lens = molecule_atom_lens,
additional_molecule_feats = additional_molecule_feats,
additional_token_feats = additional_token_feats,
is_molecule_types = is_molecule_types,
msa = msa,
msa_mask = msa_mask,
templates = template_feats,
template_mask = template_mask
)
sampled_atom_pos.shape # (2, <atom_seqlen>, 3)An example with molecule level input handling
import torch
from alphafold3_pytorch import (
Alphafold3,
Alphafold3Input,
alphafold3_inputs_to_batched_atom_input
)
contrived_protein = 'AG'
mock_atompos = [
torch.randn(6, 3), # alanine has 6 non-hydrogen atoms
torch.randn(5, 3) # glycine has 5 non-hydrogen atoms
]
train_alphafold3_input = Alphafold3Input(
proteins = [contrived_protein],
atom_pos = mock_atompos
)
eval_alphafold3_input = Alphafold3Input(
proteins = [contrived_protein]
)
batched_atom_input = alphafold3_inputs_to_batched_atom_input(train_alphafold3_input, atoms_per_window = 27)
# training
alphafold3 = Alphafold3(
dim_atom_inputs = 3,
dim_atompair_inputs = 1,
atoms_per_window = 27,
dim_template_feats = 44,
num_dist_bins = 38,
confidence_head_kwargs = dict(
pairformer_depth = 1
),
template_embedder_kwargs = dict(
pairformer_stack_depth = 1
),
msa_module_kwargs = dict(
depth = 1
),
pairformer_stack = dict(
depth = 2
),
diffusion_module_kwargs = dict(
atom_encoder_depth = 1,
token_transformer_depth = 1,
atom_decoder_depth = 1,
)
)
loss = alphafold3(**batched_atom_input.dict())
loss.backward()
# sampling
batched_eval_atom_input = alphafold3_inputs_to_batched_atom_input(eval_alphafold3_input, atoms_per_window = 27)
alphafold3.eval()
sampled_atom_pos = alphafold3(**batched_eval_atom_input.dict())
assert sampled_atom_pos.shape == (1, (6 + 5), 3)To acquire the AlphaFold 3 PDB dataset, first download all first-assembly (and asymmetric unit) complexes in the Protein Data Bank (PDB), and then preprocess them with the script referenced below. The PDB can be downloaded from the RCSB: https://www.wwpdb.org/ftp/pdb-ftp-sites#rcsbpdb. The two Python scripts below (i.e., filter_pdb_mmcifs.py and cluster_pdb_mmcifs.py) assume you have downloaded the PDB in the mmCIF file format, placing its first-assembly and asymmetric unit mmCIF files at data/pdb_data/unfiltered_assembly_mmcifs/ and data/pdb_data/unfiltered_asym_mmcifs/, respectively.
For reproducibility, we recommend downloading the PDB using AWS snapshots (e.g., 20240101). To do so, refer to AWS's documentation to set up the AWS CLI locally. Alternatively, on the RCSB website, navigate down to "Download Protocols", and follow the download instructions depending on your location.
For example, one can use the following commands to download the PDB as two collections of mmCIF files:
# For `assembly1` complexes, use the PDB's `20240101` AWS snapshot:
aws s3 sync s3://pdbsnapshots/20240101/pub/pdb/data/assemblies/mmCIF/divided/ ./data/pdb_data/unfiltered_assembly_mmcifs
# Or as a fallback, use rsync:
rsync -rlpt -v -z --delete --port=33444 \
rsync.rcsb.org::ftp_data/assemblies/mmCIF/divided/ ./data/pdb_data/unfiltered_assembly_mmcifs/
# For asymmetric unit complexes, also use the PDB's `20240101` AWS snapshot:
aws s3 sync s3://pdbsnapshots/20240101/pub/pdb/data/structures/divided/mmCIF/ ./data/pdb_data/unfiltered_asym_mmcifs
# Or as a fallback, use rsync:
rsync -rlpt -v -z --delete --port=33444 \
rsync.rcsb.org::ftp_data/structures/divided/mmCIF/ ./data/pdb_data/unfiltered_asym_mmcifs/WARNING: Downloading the PDB can take up to 700GB of space.
NOTE: The PDB hosts all available AWS snapshots here: https://pdbsnapshots.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/index.html.
After downloading, you should have two directories formatted like this: https://files.rcsb.org/pub/pdb/data/assemblies/mmCIF/divided/ & https://files.rcsb.org/pub/pdb/data/structures/divided/mmCIF/
00/
01/
02/
..
zz/For these directories, unzip all the files:
find ./data/pdb_data/unfiltered_assembly_mmcifs/ -type f -name "*.gz" -exec gzip -d {} \;
find ./data/pdb_data/unfiltered_asym_mmcifs/ -type f -name "*.gz" -exec gzip -d {} \;Next run the commands
wget -P ./data/ccd_data/ https://files.wwpdb.org/pub/pdb/data/monomers/components.cif.gz
wget -P ./data/ccd_data/ https://files.wwpdb.org/pub/pdb/data/component-models/complete/chem_comp_model.cif.gzfrom the project's root directory to download the latest version of the PDB's Chemical Component Dictionary (CCD) and its structural models. Extract each of these files using the following command:
find data/ccd_data/ -type f -name "*.gz" -exec gzip -d {} \;Then run the following with pdb_assembly_dir, pdb_asym_dir, ccd_dir, and mmcif_output_dir replaced with the locations of your local copies of the first-assembly PDB, asymmetric unit PDB, CCD, and your desired dataset output directory (i.e., ./data/pdb_data/unfiltered_assembly_mmcifs/, ./data/pdb_data/unfiltered_asym_mmcifs/, ./data/ccd_data/, and ./data/pdb_data/mmcifs/).
python scripts/filter_pdb_mmcifs.py --mmcif_assembly_dir <pdb_assembly_dir> --mmcif_asym_dir <pdb_asym_dir> --ccd_dir <ccd_dir> --output_dir <mmcif_output_dir>See the script for more options. Each first-assembly mmCIF that successfully passes
all processing steps will be written to mmcif_output_dir within a subdirectory
named according to the mmCIF's second and third PDB ID characters (e.g. 5c).
Next, run the following with mmcif_dir and clustering_output_dir replaced, respectively, with your local output directory created using the dataset filtering script above and with your desired clustering output directory (i.e., ./data/pdb_data/mmcifs/ and ./data/pdb_data/data_caches/clusterings/):
python scripts/cluster_pdb_mmcifs.py --mmcif_dir <mmcif_dir> --output_dir <clustering_output_dir> --clustering_filtered_pdb_datasetNote: The --clustering_filtered_pdb_dataset flag is recommended when clustering the filtered PDB dataset as curated using the script above, as this flag will enable faster runtimes in this context (since filtering leaves each chain's residue IDs 1-based). However, this flag must not be provided when clustering other (i.e., non-PDB) datasets of mmCIF files. Otherwise, interface clustering may be performed incorrectly, as these datasets' mmCIF files may not use strict 1-based residue indexing for each chain.
Note: One can also download preprocessed (i.e., filtered) mmCIF files (~20GB, comprising 148k complexes) and chain/interface clustering files (~1GB) for the PDB's 20240101 AWS snapshot via a shared OneDrive folder.
At the project root, run
$ sh ./contribute.shThen, add your module to alphafold3_pytorch/alphafold3.py, add your tests to tests/test_af3.py, and submit a pull request. You can run the tests locally with
$ pytest tests/The included Dockerfile contains the required dependencies to run the package and to train/inference using PyTorch with GPUs.
The default base image is pytorch/pytorch:2.3.0-cuda12.1-cudnn8-runtime and installs the latest version of this package from the main GitHub branch.
## Build Docker Container
docker build -t af3 .Alternatively, use build arguments to rebuild the image with different software versions:
PYTORCH_TAG: Changes the base image and thus builds with different PyTorch, CUDA, and/or cuDNN versions.GIT_TAG: Changes the tag of this repo to clone and install the package.
For example:
## Use build argument to change versions
docker build --build-arg "PYTORCH_TAG=2.2.1-cuda12.1-cudnn8-devel" --build-arg "GIT_TAG=0.1.15" -t af3 .Then, run the container with GPUs and mount a local volume (for training) using the following command:
## Run Container
docker run -v .:/data --gpus all -it af3@article{Abramson2024-fj,
title = "Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with
{AlphaFold} 3",
author = "Abramson, Josh and Adler, Jonas and Dunger, Jack and Evans,
Richard and Green, Tim and Pritzel, Alexander and Ronneberger,
Olaf and Willmore, Lindsay and Ballard, Andrew J and Bambrick,
Joshua and Bodenstein, Sebastian W and Evans, David A and Hung,
Chia-Chun and O'Neill, Michael and Reiman, David and
Tunyasuvunakool, Kathryn and Wu, Zachary and {\v Z}emgulyt{\.e},
Akvil{\.e} and Arvaniti, Eirini and Beattie, Charles and
Bertolli, Ottavia and Bridgland, Alex and Cherepanov, Alexey and
Congreve, Miles and Cowen-Rivers, Alexander I and Cowie, Andrew
and Figurnov, Michael and Fuchs, Fabian B and Gladman, Hannah and
Jain, Rishub and Khan, Yousuf A and Low, Caroline M R and Perlin,
Kuba and Potapenko, Anna and Savy, Pascal and Singh, Sukhdeep and
Stecula, Adrian and Thillaisundaram, Ashok and Tong, Catherine
and Yakneen, Sergei and Zhong, Ellen D and Zielinski, Michal and
{\v Z}{\'\i}dek, Augustin and Bapst, Victor and Kohli, Pushmeet
and Jaderberg, Max and Hassabis, Demis and Jumper, John M",
journal = "Nature",
month = "May",
year = 2024
}@inproceedings{Darcet2023VisionTN,
title = {Vision Transformers Need Registers},
author = {Timoth'ee Darcet and Maxime Oquab and Julien Mairal and Piotr Bojanowski},
year = {2023},
url = {https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:263134283}
}@article{Arora2024SimpleLA,
title = {Simple linear attention language models balance the recall-throughput tradeoff},
author = {Simran Arora and Sabri Eyuboglu and Michael Zhang and Aman Timalsina and Silas Alberti and Dylan Zinsley and James Zou and Atri Rudra and Christopher R'e},
journal = {ArXiv},
year = {2024},
volume = {abs/2402.18668},
url = {https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:268063190}
}@article{Puny2021FrameAF,
title = {Frame Averaging for Invariant and Equivariant Network Design},
author = {Omri Puny and Matan Atzmon and Heli Ben-Hamu and Edward James Smith and Ishan Misra and Aditya Grover and Yaron Lipman},
journal = {ArXiv},
year = {2021},
volume = {abs/2110.03336},
url = {https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:238419638}
}@article{Duval2023FAENetFA,
title = {FAENet: Frame Averaging Equivariant GNN for Materials Modeling},
author = {Alexandre Duval and Victor Schmidt and Alex Hernandez Garcia and Santiago Miret and Fragkiskos D. Malliaros and Yoshua Bengio and David Rolnick},
journal = {ArXiv},
year = {2023},
volume = {abs/2305.05577},
url = {https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:258564608}
}@article{Wang2022DeepNetST,
title = {DeepNet: Scaling Transformers to 1, 000 Layers},
author = {Hongyu Wang and Shuming Ma and Li Dong and Shaohan Huang and Dongdong Zhang and Furu Wei},
journal = {ArXiv},
year = {2022},
volume = {abs/2203.00555},
url = {https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:247187905}
}@inproceedings{Ainslie2023CoLT5FL,
title = {CoLT5: Faster Long-Range Transformers with Conditional Computation},
author = {Joshua Ainslie and Tao Lei and Michiel de Jong and Santiago Ontan'on and Siddhartha Brahma and Yury Zemlyanskiy and David Uthus and Mandy Guo and James Lee-Thorp and Yi Tay and Yun-Hsuan Sung and Sumit Sanghai},
year = {2023}
}