The ESP8266 is a low-cost Wi-Fi chip with full TCP/IP stack and MCU (Micro Controller Unit) capability produced by Espressif Systems.
The ESP8266 RTOS SDK version v1.5 is based on FreeRTOS. This repo integrates ESP8266 RTOS SDK version 1.5 commit bbdf366 with the Azure IoT C SDK version 1.1.3 to stream data from ESP8266 to Azure IoT using MQTT protocol.
Get Build Environment:
- Follow this guide
- Under section 3.3. ESP8266 Toolkit, download VirtualBox and the lubuntu image.
- Make sure to share a local folder with the VM
Get esptool.py on your host machine:
- Follow this guide
Clone this repo within the shared folder on your host:
git clone https://github.com/ritazh/ESP8266-Azure-IOT
To stream data to Azure IoT, you need to provision an Azure IoT Hub and an IoT Hub device. Follow this guide. Once you have completed this step, make sure to copy the device-specific connection string for testing later.
Update the following files within this solution:
/examples/project_template/user/user_main.c
Update these values with your own wifi ssid and password for ESP8266 to connect to
uint8 ssid[] =
uint8 password[] =
/examples/project_template/gen_misc4.sh
Update these variables to the path of the shared folder on the VM
export SDK_PATH=~/ESP8266-Azure-IOT
export BIN_PATH=~/ESP8266-Azure-IOT/bin
/examples/project_template/user/iothub_client_sample_mqtt.c
Update the connectionString variable to the device-specific connection string you got earlier from the Setup Azure IoT step:
static const char* connectionString = '[azure connection string]'
The azure connection string contains Hostname, DeviceId, and SharedAccessKey in the format:
"HostName=<host_name>;DeviceId=<device_id>;SharedAccessKey=<device_key>"
Now you are ready to compile From the VM, run the following command from a terminal:
./gen_misc4.sh
Once compliation is completed successfully, you should see something that looks like the following:
bin crc: 1a38d19
Support boot_v1.4 and +
Generate user1.4096.new.6.bin successully in BIN_PATH
boot.bin------------>0x00000
user1.4096.new.6.bin--->0x01000
!!!
Now you are ready to flash the binaries to your ESP8266. From your host machine, cd into /bin.
Run the following command on the host to flash the binaries to ESP8266 using:
esptool.py --port /dev/cu.SLAB_USBtoUART write_flash --flash_freq 40m --flash_mode qio --flash_size 32m-c1 0x1000 ./upgrade/user1.4096.new.6.bin 0x0 ./boot_v1.5.bin 0x3FC000 ./esp_init_data_default.bin 0x3FE000 ./blank.bin
To test that the sample application is streaming data to Azure IoT, download the iothub-explorer on your computer. Use the device-specific connection string you got earlier from the Setup Azure IoT section to get messages received by Azure IoT. Run the following from terminal:
iothub-explorer '[azure connection string]' monitor-events [DeviceId]
The azure connection string contains Hostname, DeviceId, and SharedAccessKey in the format:
"HostName=<host_name>;DeviceId=<device_id>;SharedAccessKey=<device_key>"
To view logs generated by the application, you can install ESPlorer. Note: make sure to set the baud rate to 115200 within the ESPlorer tool.
To customize this sample solution for your own use, update /examples/project_template/user/iothub_client_sample_mqtt.c with your own data to stream and your own logic.
In the mqtt sample, it continues to send messages to Azure, until cloud sends a "quit" message to end the program. Before the program ends, you can send any message to the device by using the iothub-explorer like the following:
To send a message to a device named "RitaIoT":
iothub-explorer send RitaIoT "hello3" --ack=full
To quit the sample:
iothub-explorer send RitaIoT "quit" --ack=full
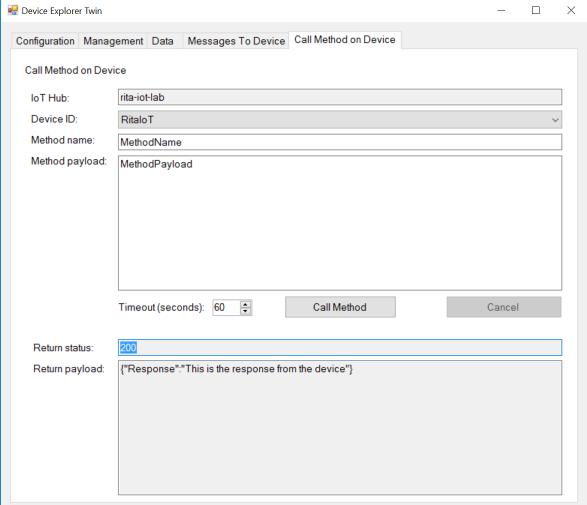
You can also send a direct method request to invoke a direct method on the device. For example, using Device Explorer to call a method and the method will return a payload:
Licensed as MIT - please see LICENSE for details.