PyTorch Implementation + Code Templates
The approach implemented here aims to maximize the performance of machine learning classifiers by relying on optimal low-dimensional embeddings learned from a deep-learning based clustering network.
This repository is only intended to help researchers understand and learn to use the approach presented in our paper: Adaptive Clustering-based Malicious Traffic Classification at the Network Edge. It is therefore important to note that the architectures of the neural networks used, as well as the hyper-parameters, can be subject to change depending on the task at hand.
In this basic implementation, only feed-forward networks are employed.
These instructions will get you a copy of the project up and running on your local machine for development and testing purposes.
Clone the project to have a copy in your desired local repository
git clone https://github.com/Mobile-Intelligence-Lab/ACID.git [LOCAL_DIRECTORY_PATH]
Use pip installation to install dependencies from requirements.txt
pip install -r requirements.txt
(Default architecture)
from core.models.network import AdaptiveClustering
from torch.optim import Adam
import numpy as np
...
model = AdaptiveClustering(
encoder_dims=[100, 50, 10], # neurons per hidden layer (for mlp)
n_kernels=NUM_CLASSES,
kernel_size=EMBEDDIMG_DIMENSION
)
# Training...
optimizer = None
for _ in range(NUM_EPOCHS):
for _, (x, y) in enumerate(data_loader):
model.zero_grad()
outputs = model(x, y)
if optimizer is None:
optimizer = Adam(model.parameters(), lr=LEARNING_RATE)
loss = model.loss()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
...
# Inference...
outputs = model(x).max(dim=1).indices.squeeze().tolist()
# Embeddings...
encoded_repr = np.stack([model.sub_nets[output_class].encoder(x[i]).tolist()
for i, output_class in enumerate(outputs)]).squeeze()
# Cluster centers...
cluster_centers = np.asarray([model.sub_nets[i].kernel_weights.squeeze().tolist()
for i in range(model.n_kernels_)])(Clustering experiments)
- Adaptive Clustering Network:
python demo/clustering/acnet.py [-h]
- Baseline methods:
- k-Means
python demo/clustering/kmeans.py [-h] - DBSCAN
python demo/clustering/dbscan.py [-h] - Spectral Clustering
python demo/clustering/spectral.py [-h]
- k-Means
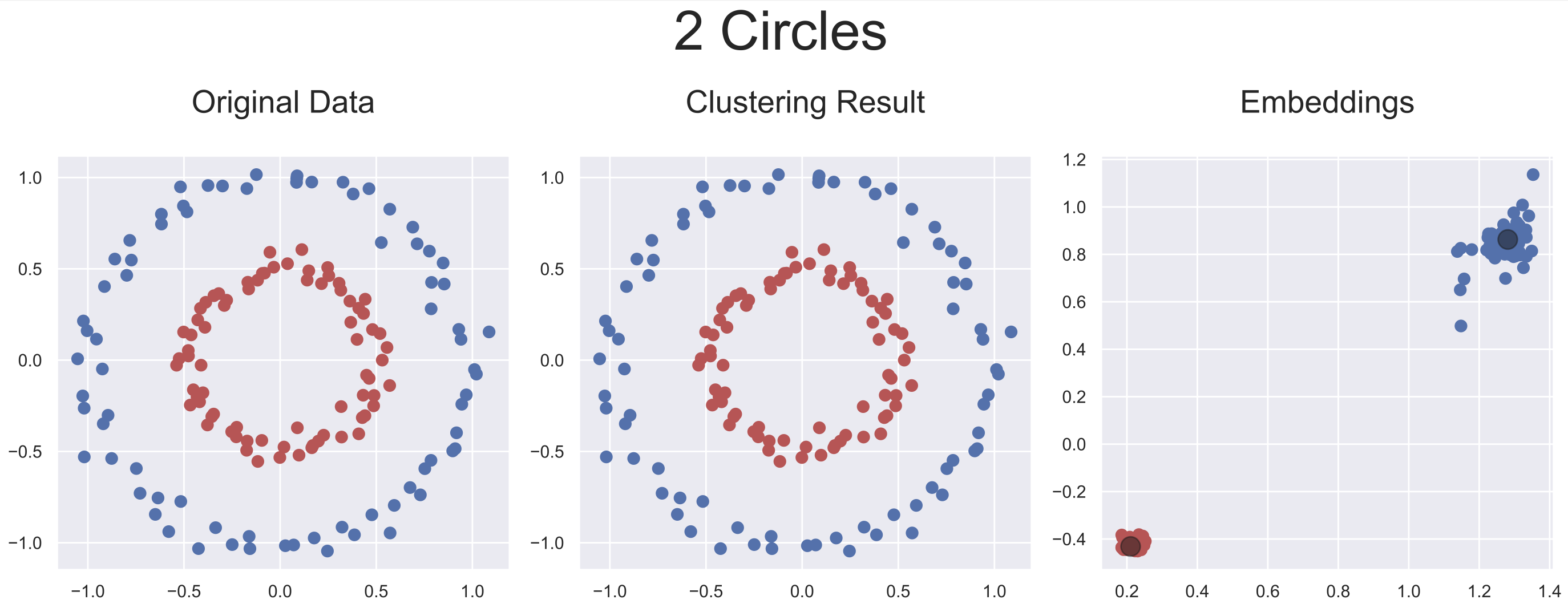
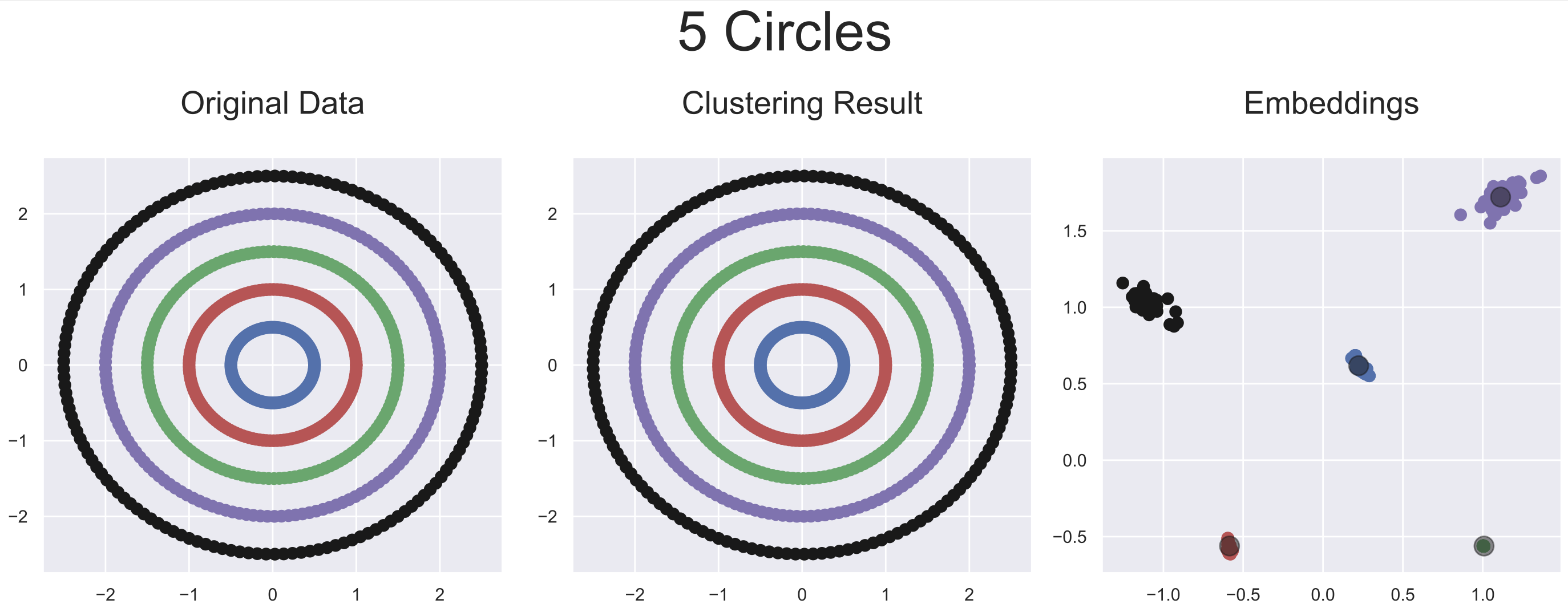
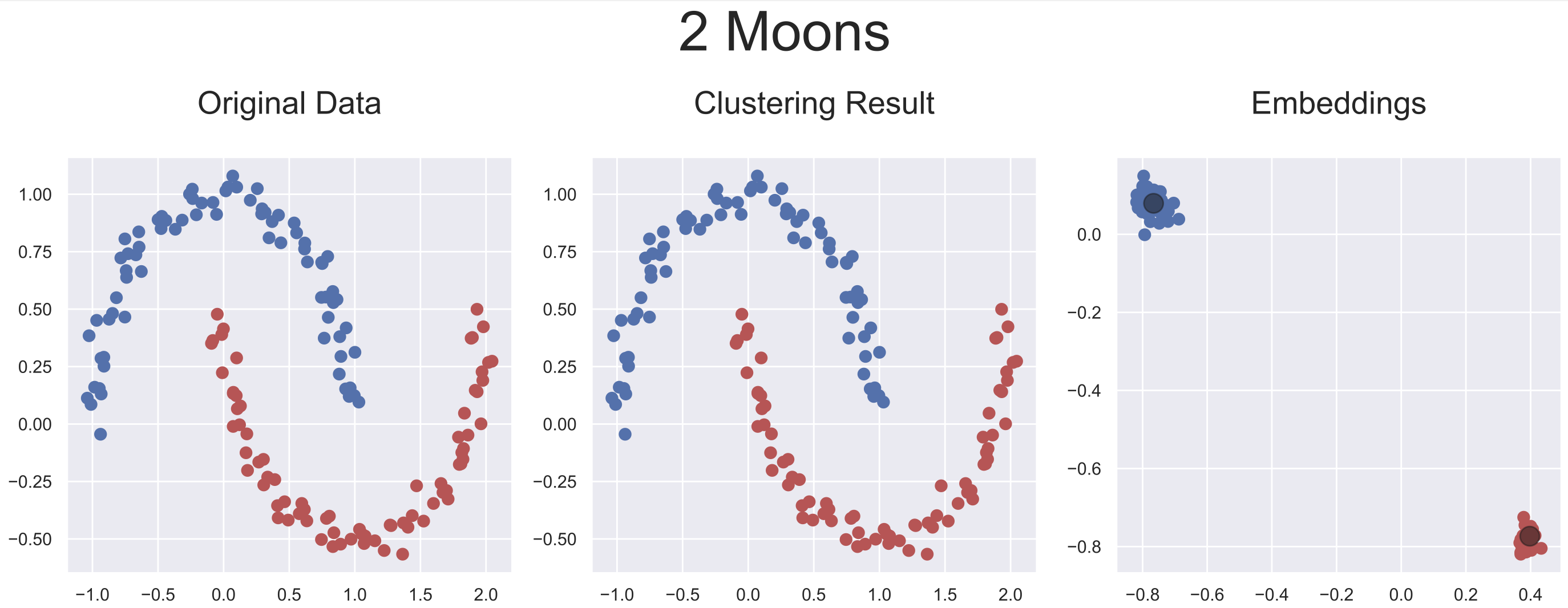
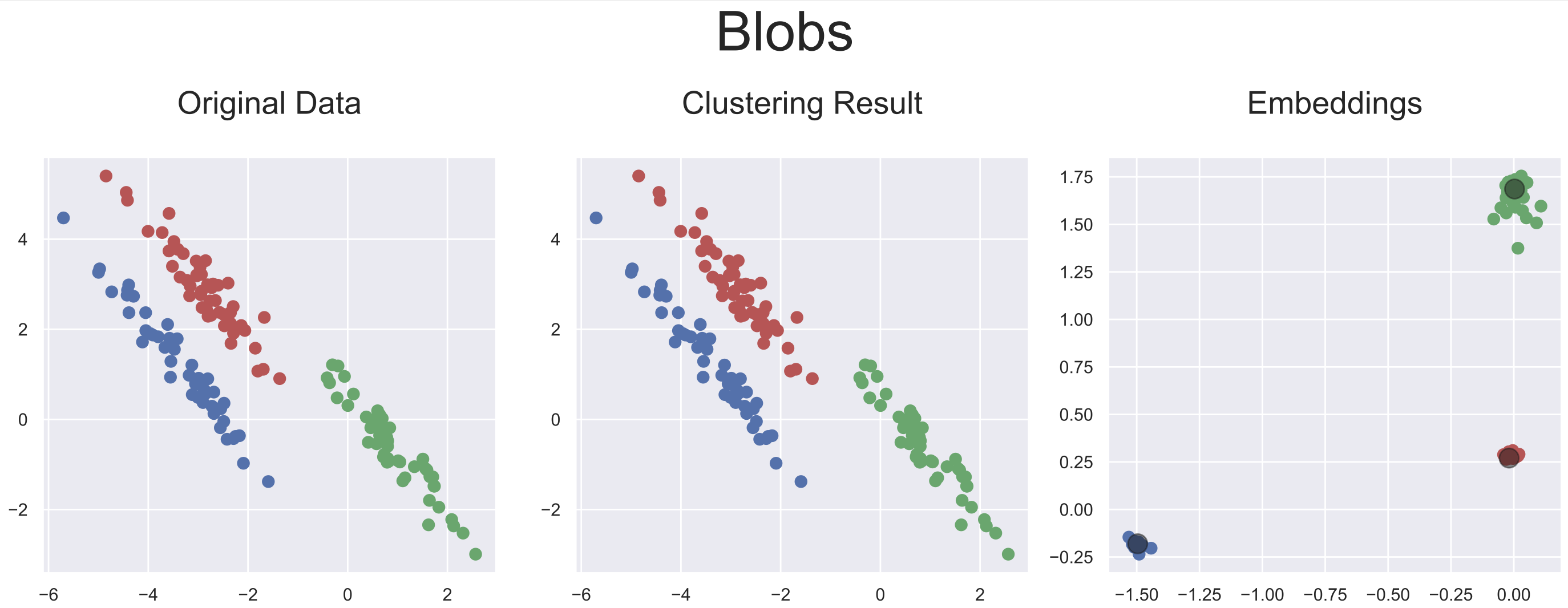
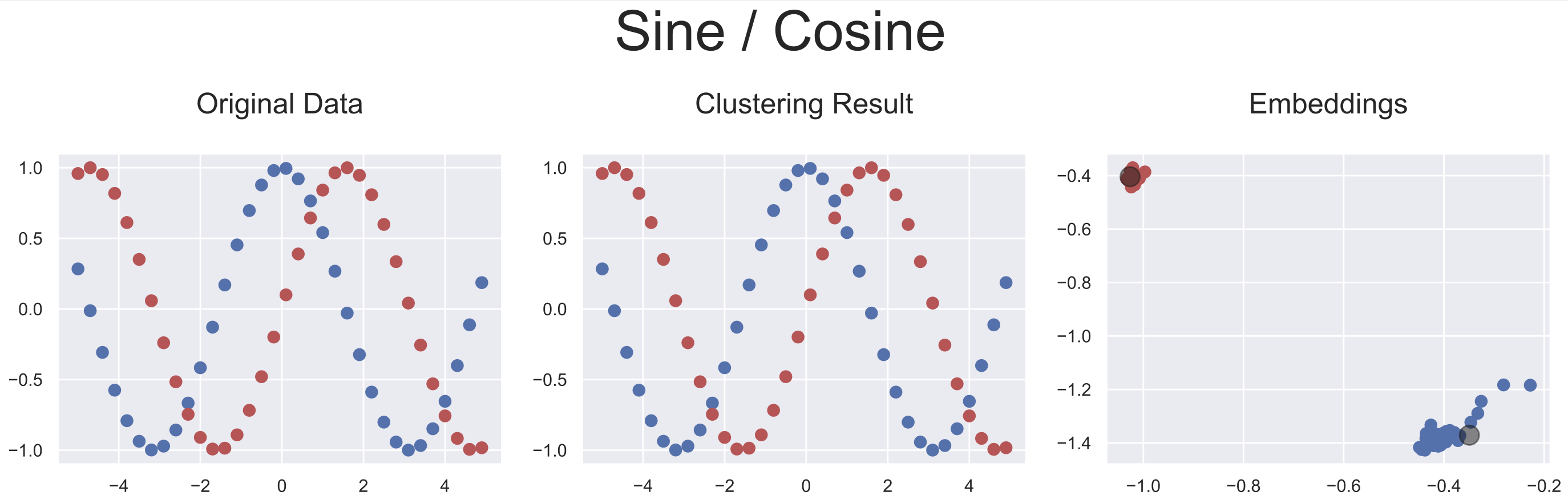
Five artificially generated datasets were used to evaluate the adaptability of this approach to different ranges of data configuration. As our approach provides latent representations of the inputs, it is rather simple to visualize each step of the inputs' transformations leading to the optimal latent representations obtained by AC-Net.
Below are plotted the final embeddings obtained with the artificial datasets used in the paper.
The source codes for reproducing these results, as well as the baseline methods' can be found here.
python demo/clustering/acnet.py --2-circles
python demo/clustering/acnet.py --5-circles
python demo/clustering/acnet.py --2-moons
python demo/clustering/acnet.py --blobs
python demo/clustering/acnet.py --sine-cosine
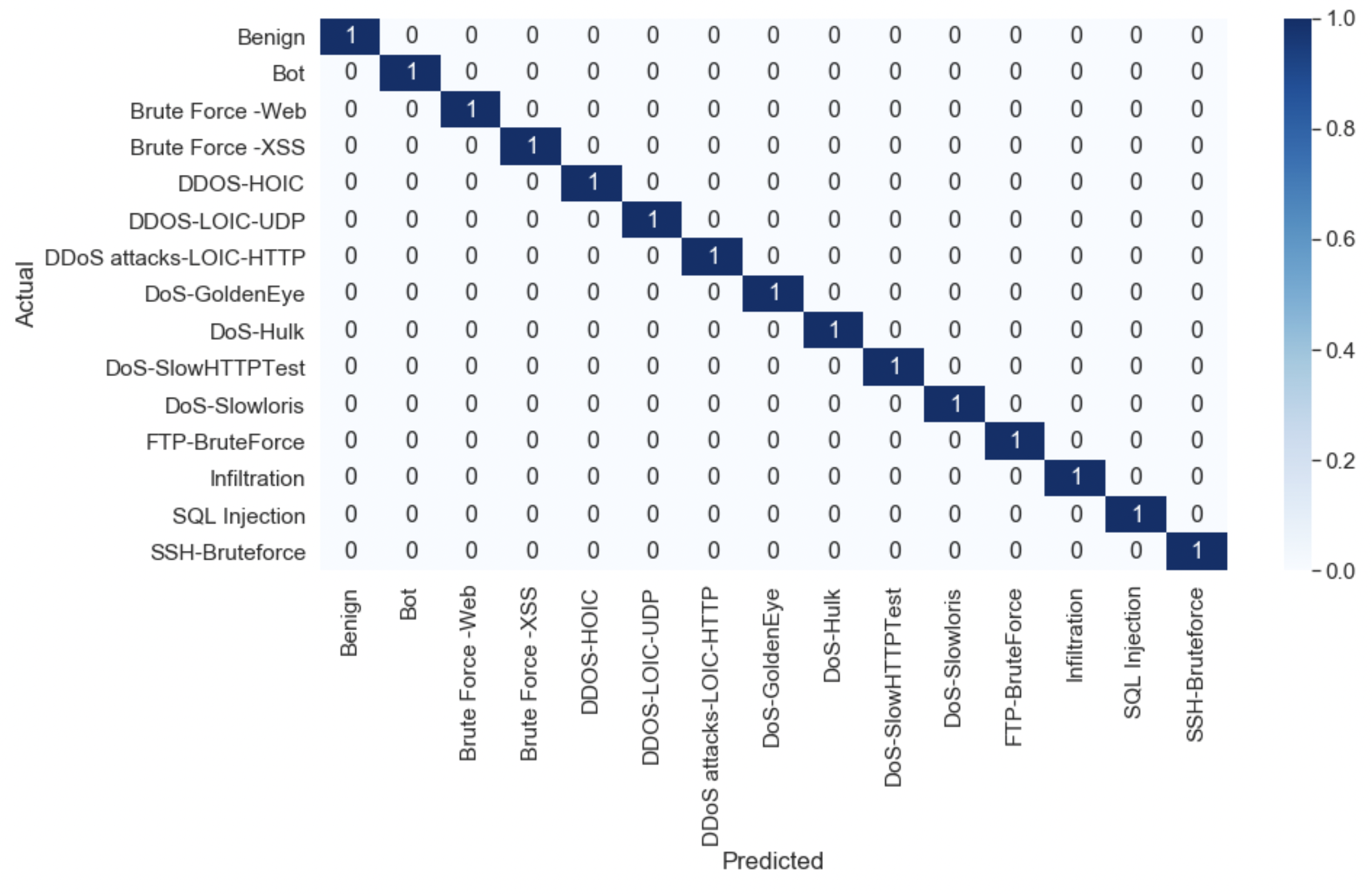
As practical use-cases, AC-Net was used on three network intrusion detection datasets: KDD Cup’99 [1], ISCX-IDS 2012 [2], and CSE-CIC-IDS 2018 [3].
(Dataset extended with "payload features" as mentioned in the paper)
A notebook including a step-by-step tutorial is provided here: .ipynb | .html (with traces).
@inproceedings{,
author = {Alec F. Diallo and Paul Patras},
title = {Adaptive Clustering for Lightweight Malicious Traffic Classification at the Edge},
booktitle = "IEEE INFOCOM 2021",
year = {2021},
month = {05}
}[1] http://kdd.ics.uci.edu/databases/kddcup99/kddcup99.html