Kangaroo [http://mehikmat.github.io/Kangaroo/]
Cloud-based android mobile phone contact backup system. Secures your contacts and get from anywhere.
The x86 based android virtual device emulator is recomended for faster emulation then (arm based emulation). Linux-based systems support virtual machine acceleration through the KVM software package. so it needs to be installed.
$> yum install kvm
If you use another virtualization technology in your Linux platform,
unload its kernel driver before running the x86 emulator.
For example, the VirtualBox driver program is vboxdrv
To run an x86-based emulator with VM acceleration:
$> $ANDROID_HOME/tools/emulator -avd <avd_name> -qemu -m 512 -enable-kvm
OR
Run from Android Studio with cmd option `-qemu -m 512 -enable-kvm`
That's all for setting up AVD to test/debug applications.
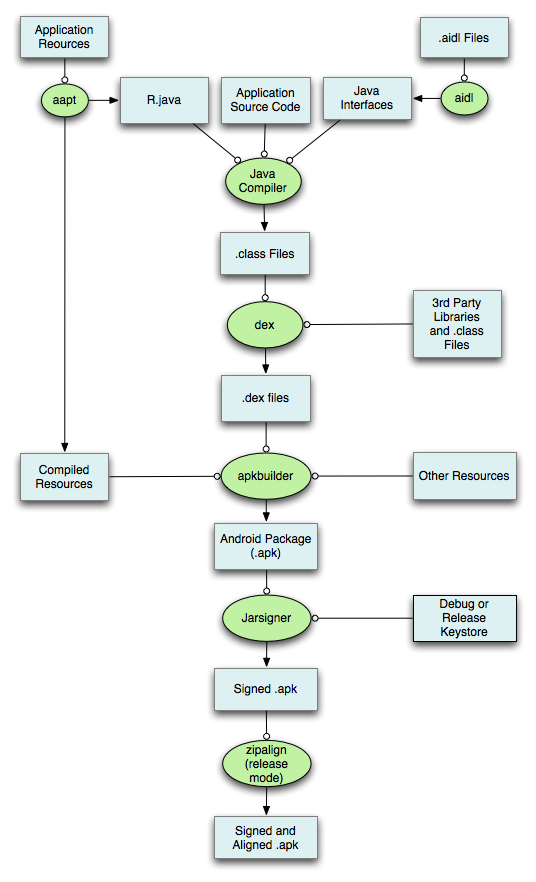
This document shows you how to use Android Studio to build an application .apk for testing or release and how to run your application on an emulator or a real device.
- Select Build-->Make Project
- View log on Gradle Console
###Build a release version### You can now build the release version of your application for distribution. To build it from Android Studio:
- Click Gradle on the right side of the IDE window.
- On the All tasks section of the sidebar that appears, expand
- double-click assembleRelease.
And there will be for example, app-full-release.apk and app-demo-debug.apk.
- To run (or debug) your application, select Run > Run (or Run > debug)
Reference:> https://developer.android.com/tools/building/building-studio.html
- The Android build system consists of an Android plugin for Gradle.
- Gradle is an advanced build toolkit that manages dependencies and allows you to define custom build logic.
- Android Studio uses a Gradle wrapper to fully integrate the Android plugin for Gradle
The build configuration for your project is defined inside build.gradle files,
- Build variants. The build system can generate multiple APKs with different product and build configurations for the same module.
- Dependencies. The build system manages project dependencies and supports dependencies from your local filesystem and from remote repositories.
- Manifest entries. The build system enables you to specify values for some elements of the manifest file in the build variant configuration
- Signing. The build system enables you to specify signing settings in the build configuration, and it can sign your APKs during the build process.
- ProGuard. The build system enables you to specify a different ProGuard rules file for each build variant.
- Testing. For most templates, the build system creates a test directory, androidTest and generates a test APK from the test sources in your project, so you do not have to create a separate test project.
The Android Studio build system defines a hierarchical set of build tasks: the top-level or anchor tasks invoke dependent tasks to produce their collective build outcomes. The top-level build tasks are:
- assemble :Builds the project output.
- check :Runs checks and tests.
- build :Runs both assemble and check.
- clean :Performs the clean.
Reference:> https://developer.android.com/tools/building/plugin-for-gradle.html
Android Studio projects contain the Gradle wrapper, which consists of:
- A JAR file
- A properties file
- A shell script for Windows platforms
- A shell script for Mac and Linux platforms
######Note: You should submit all of these files to your source control system.###### Using the Gradle wrapper (instead of the local Gradle installation) ensures that you always run the version of Gradle defined in the local.properties file. To configure your project to use a newer version of Gradle, edit the properties file and specify the new version there