A basic CLI lookup tool. Describe a bash command and it outputs sample line(s) by quering LLMs. It can make use of OpenAI (GPT 3.5) or Llama.cpp models.
Try a few commands
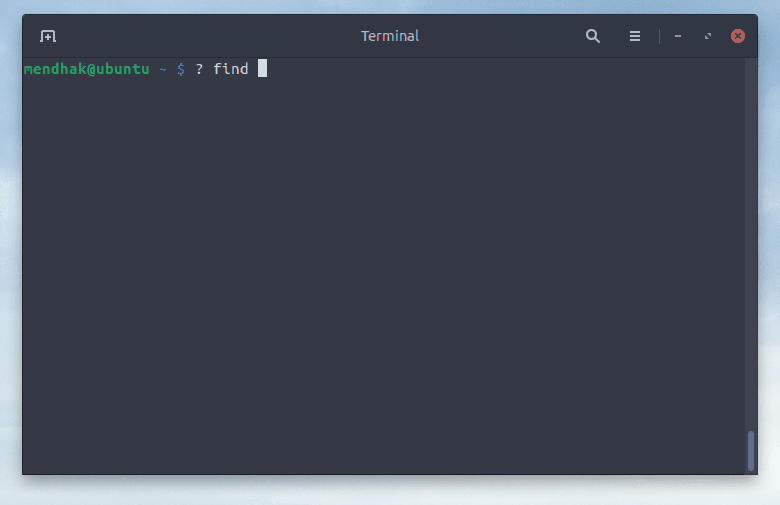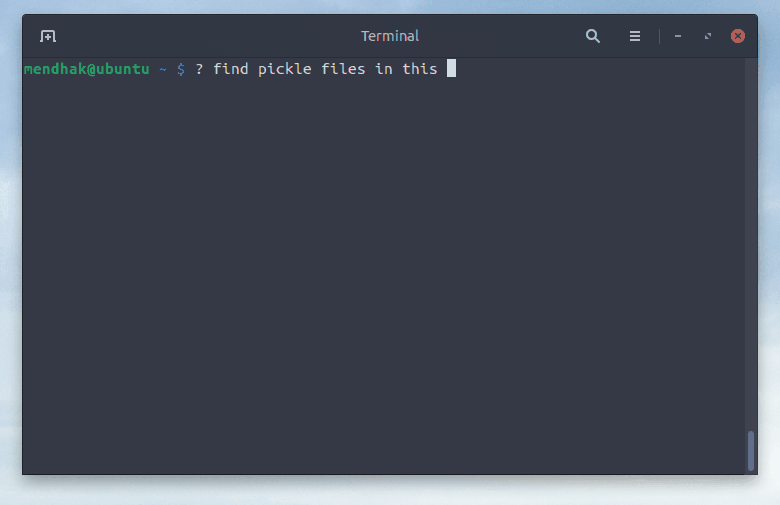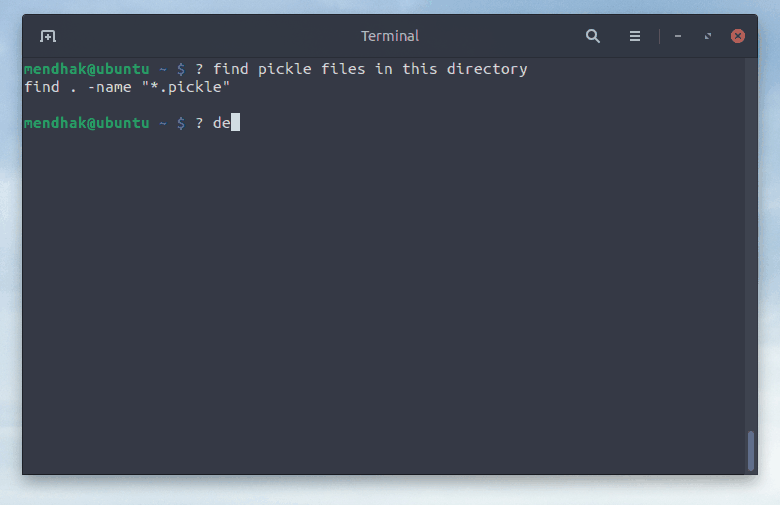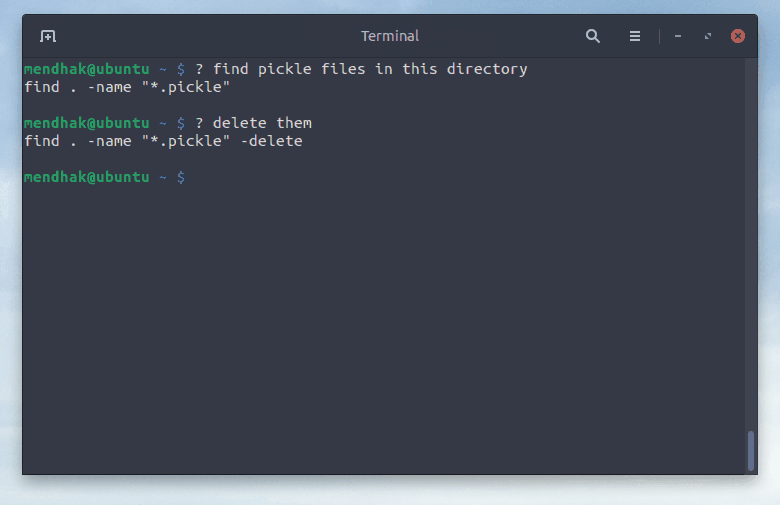
$ ? how much disk space
df -h
$ ? show top processes by CPU usage
top -o %CPU
There is a history, so the next question can be a follow up. Example:
$ ? find .pickle files in this directory
find . -type f -name "*.pickle"
$ ? delete them
find . -type f -name "*.pickle" -deleteAnother example, I didn't like the first output so asked for nc instead.
$ ? check if port 443 on example.com is open
echo | telnet example.com 443
$ ? using nc
nc -zv example.com 443Set up dependencies
python3 -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txtMake a copy of the .env.sample file and call it .env
Get an API key from your OpenAI account. Place it in the .env file
OPENAI_API_KEY="......................................."
There is a small cost associated with OpenAI calls, so it's a good idea to set monthly limits on usage.
The application is best used as an alias called ?. Add it to ~/.bashrc like so:
# add alias
echo alias ?="\"$(pwd)/.venv/bin/python3 $(realpath openai.clihelper.py)\"" >> ~/.bashrc
# reload bash
exec bashNow start using ?
Llama.cpp is a fast way of running local LLMs on your own computer. It is very fast with GPUs which will be my focus. It is free to use.
First, ensure that CUDA Toolkit is installed. After installing Cuda, add it to your path and reload bash:
echo 'export PATH="/usr/local/cuda/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.bashrc
exec bash
# test that it worked:
nvcc --versionNext install the cmake and Python dependencies, and build one specific package with GPU support.
sudo apt install make cmake
python3 -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txt
CMAKE_ARGS="-DLLAMA_CUBLAS=on" FORCE_CMAKE=1 pip install llama-cpp-python --force --no-cacheBecause Llama is open, there are many Llama models you can choose from. Llama.cpp requires models to be in the GGML format. Here are some I tested with:
TheBloke/Llama-2-7B-Chat-GGML - llama-2-7b-chat.ggmlv3.q4_0.bin
TheBloke/StableBeluga-7B-GGML - stablebeluga-7b.ggmlv3.q4_0.bin
Download these then set the path to the model in the .env file. Example:
LLAMA_MODEL_PATH="./models/7B/stablebeluga-7b.ggmlv3.q4_0.bin"
The application is best used as an alias called ?. Add it to ~/.bashrc like so:
# add alias
echo alias ?="\"$(pwd)/.venv/bin/python3 $(realpath llamacpp.clihelper.py)\"" >> ~/.bashrc
# reload bash
exec bashNow start using ?
This was made using langchain, a library that helps make calls to large language models (LLMs) and process its output.
In this case I did a 'few shot', which is a way of showing the LLM a few examples of questions and the kind of answers to generate.
I chose the gpt-3.5-turbo model which is the cheapest on OpenAI currently.