Android Based Implementation of Acoustic Data Transmission System
This project contains the working repository for the Android Studio based project for an acoustic data transmission app.
The application developed was built for Android 6 and used 16-FSK with a symbol duration of 0.5 seconds per symbol to transmit strings of 80 bits.
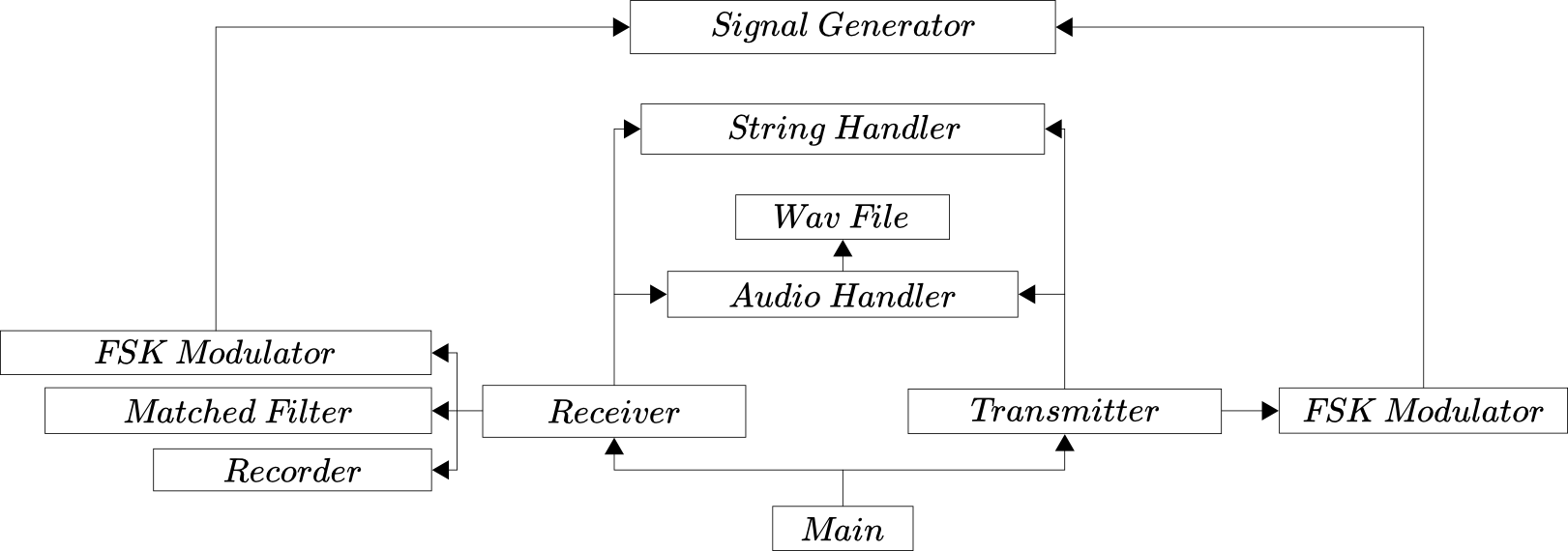
As shown by the diagram a simplified model of the implemented system may be segmented into two subsystems, the transmitter and receiver. These two subsystems are then interfaced with and controlled by the main class.
Simply put, the transmitter collects the user defined strings and converts them to a binary representation. This binary data is then modulated using FSK and saved as a wav-file, the transmitter interface then allows for the user to play this waveform, thereby transmitting it to the receiver.
The receiver offers an interface for recording the transmitted waveform and saves it to file. This waveform is then synchronized using a matched filter, and the recovered modulated signal is concatenated and saved to file. Then the waveform is demodulated and the resulting binary data is converted back to a string.
The transmitter object is a class that deals with the high-level algorithmic process of generating the modulated waveform. This is achieved by first initializing the parameters required for effective modulation, these being sample rate, symbol duration, the number of carriers and source string.
Then the the transmitter class initializes the FSK modulator object and requests the FSK modulated waveform from the it. This modulated data is then passed to the wavfile object which writes the .wav file to storage. This process may be seen in the block diagram shown in the diagram below.
The receiver object is a a class that deals with the high-level algorithmic process of demodulating the received waveform. This is achieved by first initializing the parameters required for demodulation and synchronization. A thread is then started to record the modulated waveform of known length, once completed the thread writes the recorded waveform to file to be analysed.
This analysis consists of first concatenating the recording so that so that the number of samples is a power of two. This was done to increase speed of the synchronization algorithm in the frequency domain. For the FFT algorithms are considerably faster when applying them to data that is of length 2^n . The synchronization mechanism used was the matched filter previously designed, which ensured accurate symbol recovery.
This synchronized waveform was then demodulated using a correlation based FSK demodulation algorithm. Finally the resultant binary signal as converted back into a UTF-16. This process may be see in the block diagram shown below.
The infrastructure of Android based implementation is that of objects used by both the transmitter and receiver objects. These objects are the string handler, audio handler and signal generator. The system was designed to increase modularity and portability, as per the Java based object orientation specifications.
The string handler was used to convert both the user entered characters into UTF-16 binary arrays, and the demodulated binary arrays from UTF-16 to Java based strings. The conversion from characters to UTF-16 was done by finding the UTF-16 value of each character in the user entered string and the conversion from UTF-16 to characters was done through the use of Java based StringBuilder object.
The audio handler essentially worked as an interface for the wave-file library. It was able to take in modulated data streams and call the wav-file library to write them to storage. In order to do this, the audio handler checked permissions and created files and directories accordingly. Furthermore, the audio handler enabled reading the recorded wav-files from storage through the use of the wav-file library.
The signal generator object was used to populate ArrayLists for the carriers and synchronization signals. The carrier generation was achieved by iteratively populating the ArrayList with a sinusoidal waveform sampled at 44100Hz.
Build the project, it is compatible on Android 5.0 and above.