RTKBase
An easy to use and easy to install web frontend with bash scripts and services for a simple headless gnss base station.
FrontEnd:
Frontend's main features are:
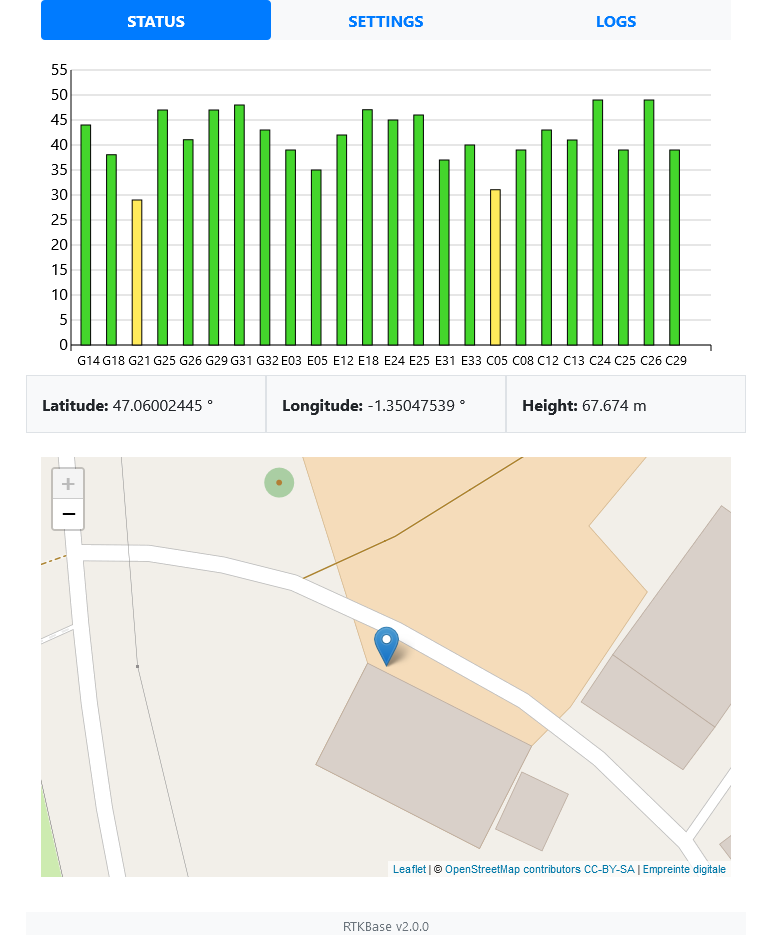
- View the satellites signal levels
- View the base location on a map
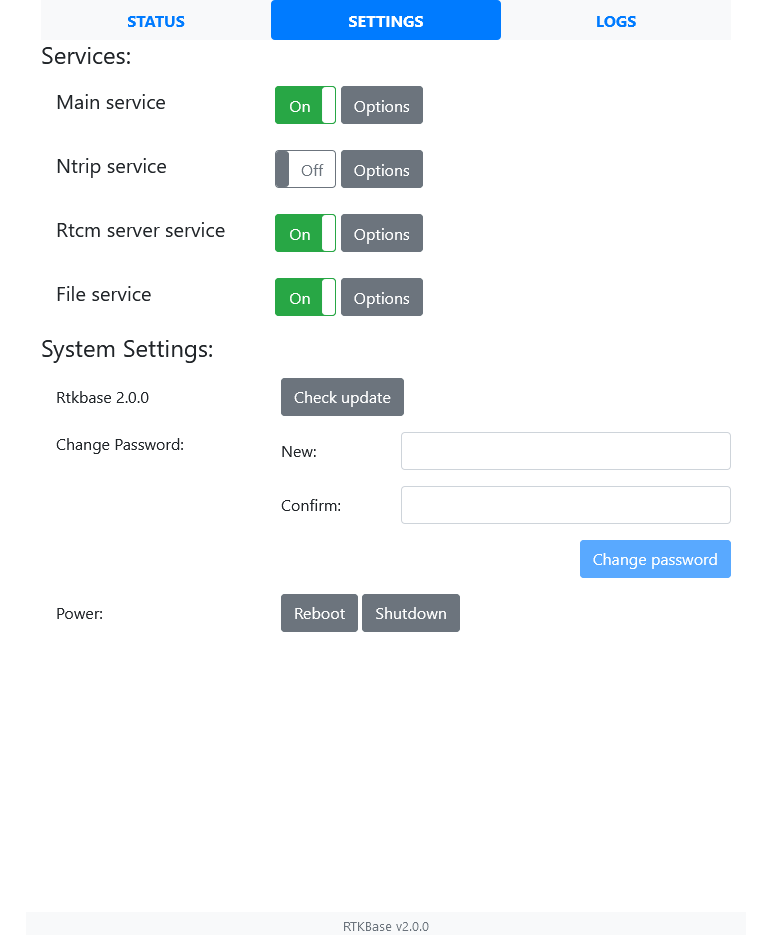
- Start/stop various services (Sending data to a Ntrip caster, Ntrip caster, Rtcm server, Sending Rtcm stream on a radio link, Log raw data to files)
- Edit the services settings
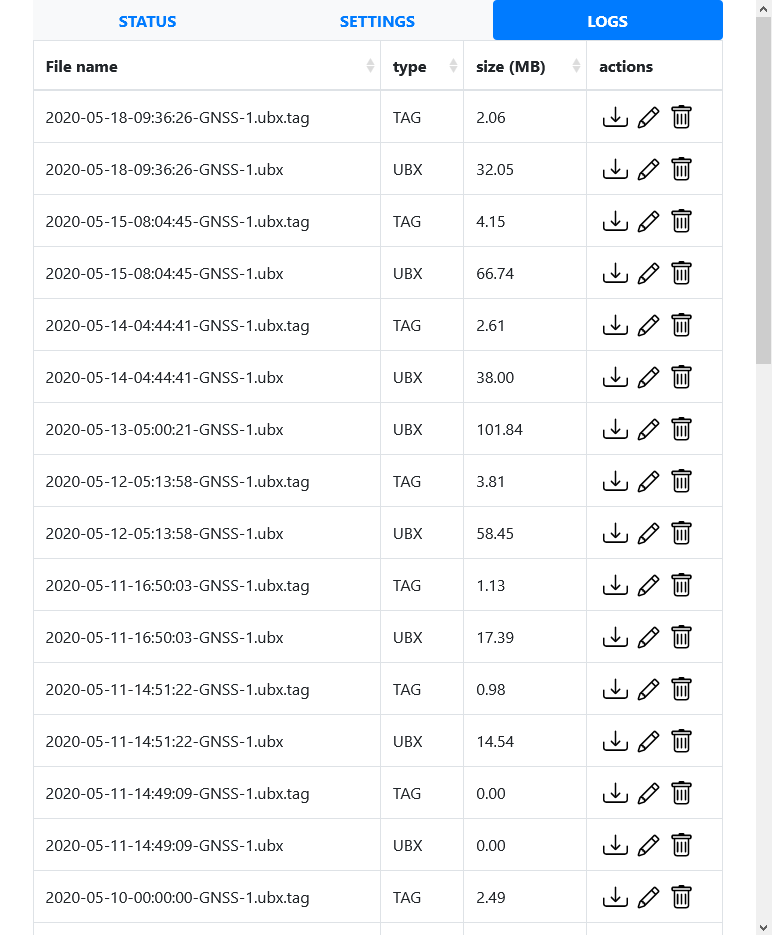
- Download/delete raw data
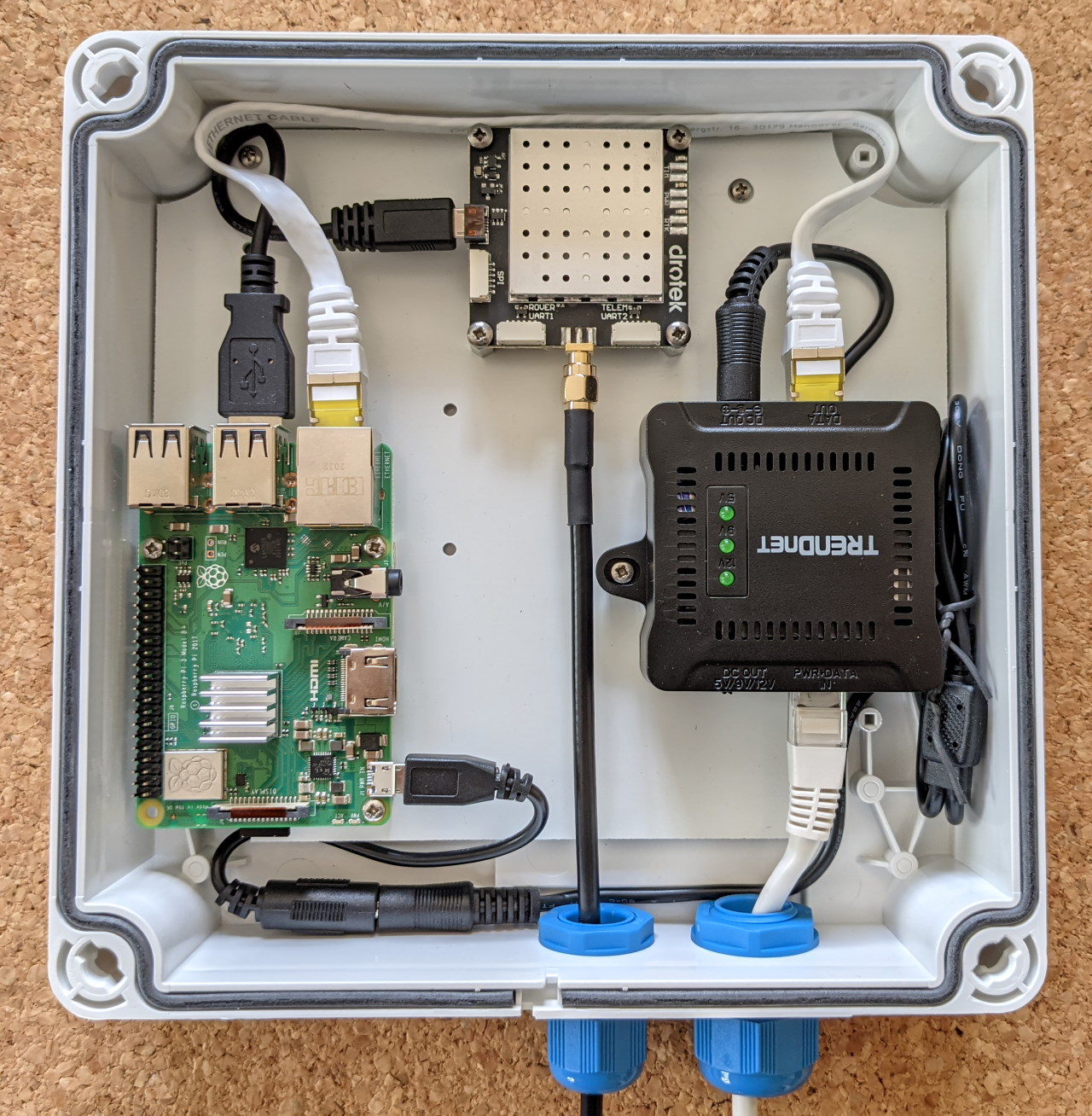
Base example:
- Enclosure: GentleBOX JE-200 (waterproof, cable glands for antenna and ethernet cable)
- SBC: Raspberry Pi 3 / Orange Pi Zero (512MB)
- Gnss Receiver: U-Blox ZED-F9P (from Drotek)
- Antenna: DA910 (Gps L1/L2, Glonass L1/L2, Beidou B1/B2/B3 and Galileo E1/E5b/E6) + sma (male) to TNC (male) outdoor cable.
- Power: Trendnet TPE-115GI POE+ injector + Trendnet POE TPE-104GS Extractor/Splitter + DC Barrel to Micro Usb adapter
Other images are available in the ./images folder.
Ready to flash release:
If you use a Raspberry Pi, thanks to jancelin, you can download a ready to flash iso file here.
Easy installation:
-
Connect your gnss receiver to your raspberry pi/orange pi/....
-
Open a terminal and:
$ cd ~ $ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Stefal/rtkbase/master/tools/install.sh -O install.sh $ chmod +x install.sh $ sudo ./install.sh --all
-
Go grab a coffee, it's gonna take a while. The script will install the needed software, and if you use a Usb-connected U-Blox ZED-F9P receiver, it'll be detected and set to work as a base station. If you don't use a F9P, you will have to configure your receiver manually (see step 7 in manual installation), and choose the correct port from the settings page.
-
Open a web browser to
http://ip_of_your_sbc(the script will try to show you this ip address). Default password isadmin. The settings page allows you to enter your own settings for the base coordinates, ntrip credentials and so on...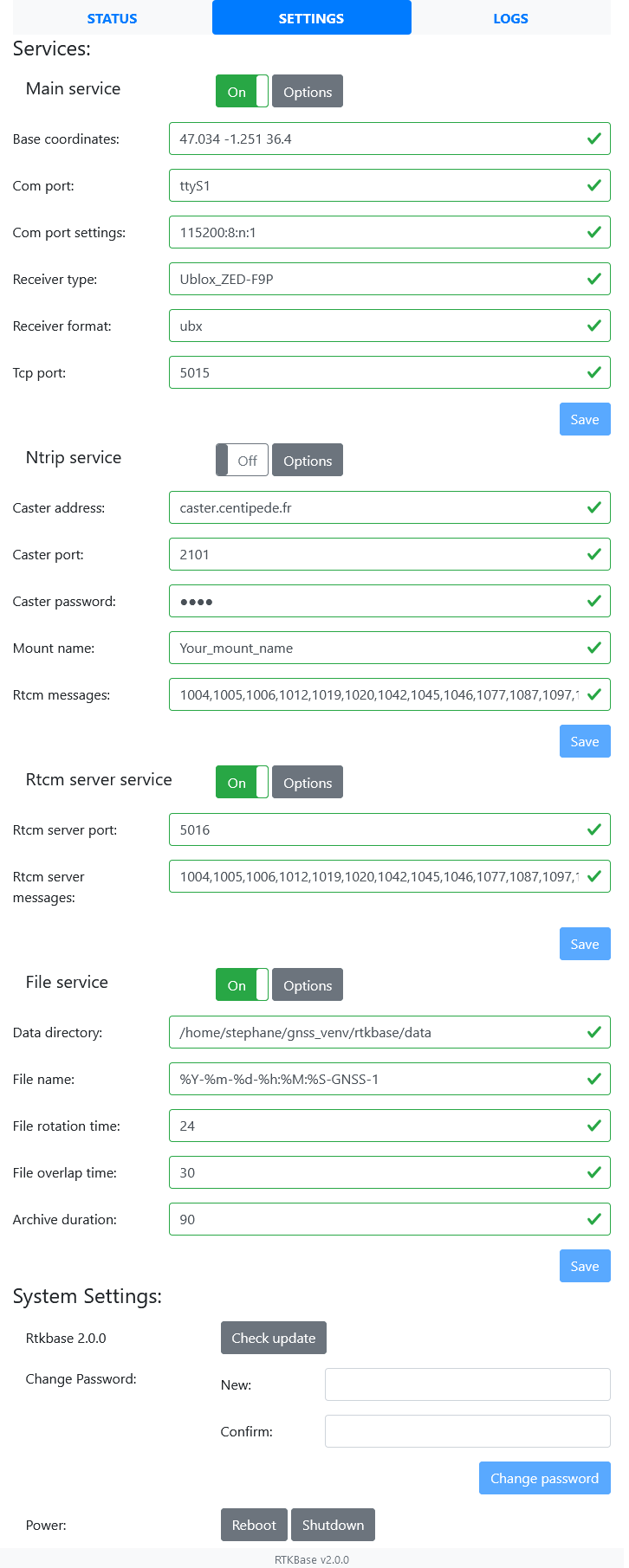
If you don't already know your base precise coordinates, it's time to read one of these tutorials:
Manual installation:
The install.sh script can be used without the --all option to split the installation process into several different steps:
$ ./install.sh --help
################################
RTKBASE INSTALLATION HELP
################################
Bash script to install a simple gnss base station with a web frontend.
* Before install, connect your gnss receiver to raspberry pi/orange pi/.... with usb or uart.
* Running install script with sudo
sudo ./install.sh
Options:
--all
Install all dependencies, Rtklib, last release of Rtkbase, gpsd, chrony, services,
crontab jobs, detect your GNSS receiver and configure it.
--dependencies
Install all dependencies like git build-essential python3-pip ...
--rtklib
Clone RTKlib 2.4.3 from github and compile it.
https://github.com/tomojitakasu/RTKLIB/tree/rtklib_2.4.3
--rtkbase-release
Get last release of RTKBASE:
https://github.com/Stefal/rtkbase/releases
--rtkbase-repo
Clone RTKBASE from github:
https://github.com/Stefal/rtkbase/tree/web_gui
--unit-files
Deploy services.
--gpsd-chrony
Install gpsd and chrony to set date and time
from the gnss receiver.
--detect-usb-gnss
Detect your GNSS receiver.
--configure-gnss
Configure your GNSS receiver.
--start-services
Start services (rtkbase_web, str2str_tcp, gpsd, chrony)
So, if you really want it, let's go for a manual installation with some explanations:
-
Install dependencies with
sudo ./install.sh --dependencies, or do it manually with:$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install -y git build-essential python3-pip python3-dev python3-setuptools python3-wheel libsystemd-dev bc dos2unix socat
-
Install RTKLIB with
sudo ./install.sh --rtklib, or:-
clone RTKlib
$ cd ~ $ git clone -b rtklib_2.4.3 --single-branch https://github.com/tomojitakasu/RTKLIB
-
compile and install str2str:
Optionally, you can edit the CTARGET line in makefile in RTKLIB/app/str2str/gcc
$ cd RTKLIB/app/str2str/gcc $ nano makefileFor an Orange Pi Zero SBC, i use:
CTARGET = -mcpu=cortex-a7 -mfpu=neon-vfpv4 -funsafe-math-optimizationsThen you can compile and install str2str:
$ make $ sudo make install
-
Compile/install
rtkrcvandconvbinthe same way asstr2str.
-
-
Get latest rtkbase release
sudo ./install.sh --rtkbase-release, or:$ wget https://github.com/stefal/rtkbase/releases/latest/download/rtkbase.tar.gz -O rtkbase.tar.gz $ tar -xvf rtkbase.tar.gz
If you prefer, you can clone this repository to get the latest code.
-
Install the rtkbase requirements:
$ python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip setuptools wheel --extra-index-url https://www.piwheels.org/simple $ python3 -m pip install -r rtkbase/web_app/requirements.txt --extra-index-url https://www.piwheels.org/simple
-
Install the systemd services with
sudo ./install.sh --unit-files, or do it manually with:- Edit them (
rtkbase/unit/) to replace{user}with your username. - If you log the raw data inside the base station, you may want to compress these data and delete the too old archives.
archive_and_clean.shwill do it for you. The default settings compress the previous day data and delete all archives older than 90 days. To automate these 2 tasks, enable thertkbase_archive.timer. The default value runs the script every day at 04H00. - Copy these services to
/etc/systemd/system/then enable the web server, str2str_tcp and rtkbase_archive.timer:
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload $ sudo systemctl enable rtkbase_web $ sudo systemctl enable str2str_tcp $ sudo systemctl enable rtkbase_archive.timer
- Edit them (
-
Install and configure chrony and gpsd with
sudo ./install.sh --gpsd-chrony, or:-
Install chrony with
sudo apt install chronythen add this parameter in the chrony conf file (/etc/chrony/chrony.conf):refclock SHM 0 refid GPS precision 1e-1 offset 0.2 delay 0.2Edit the chrony unit file. You should set
After=gpsd.service -
Install a gpsd release >= 3.2 or it won't work with a F9P. Its conf file should contains:
# Devices gpsd should connect to at boot time. # They need to be read/writeable, either by user gpsd or the group dialout. DEVICES="tcp://127.0.0.1:5015" # Other options you want to pass to gpsd GPSD_OPTIONS="-n -b"Edit the gpsd unit file. You should have something like this in the "[Unit]" section:
[Unit] Description=GPS (Global Positioning System) Daemon Requires=gpsd.socket BindsTo=str2str_tcp.service After=str2str_tcp.service- Reload the services and enable them:
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload $ sudo systemctl enable chrony $ sudo systemctl enable gpsd
-
-
Connect your gnss receiver to raspberry pi/orange pi/.... with usb or uart, and check which com port it uses (ttyS1, ttyAMA0, something else...). If it's a U-Blox usb receiver, you can use
sudo ./install.sh --detect-usb-gnss. Write down the result, you may need it later. -
If you didn't have already configure your gnss receiver, you must set it to output raw data:
If it's a U-Blox ZED-F9P (usb), you can use
$ sudo ./install.sh -detect-usb-gnss --configure-gnss
If it's a U-Blox ZED-F9P (uart), you can use this command (change the ttyS1 and 115200 value if needed)):
$ rtkbase/tools/set_zed-f9p.sh /dev/ttyS1 115200 rtkbase/receiver_cfg/U-Blox_ZED-F9P_rtkbase.cfg
If you need to use a config tool from another computer (like U-center), you can use
socat:$ sudo socat tcp-listen:128,reuseaddr /dev/ttyS1,b115200,raw,echo=0
Change the ttyS1 and 115200 value if needed. Then you can use a network connection in U-center with the base station ip address and the port n°128.
-
Now you can start the services with
sudo ./install.sh --start-services, or:$ sudo systemctl start rtkbase_web $ sudo systemctl start str2str_tcp $ sudo systemctl start gpsd $ sudo systemctl start chrony $ sudo systemctl start rtkbase_archive.timer
Everything should be ready, now you can open a web browser to your base station ip address.
How it works:
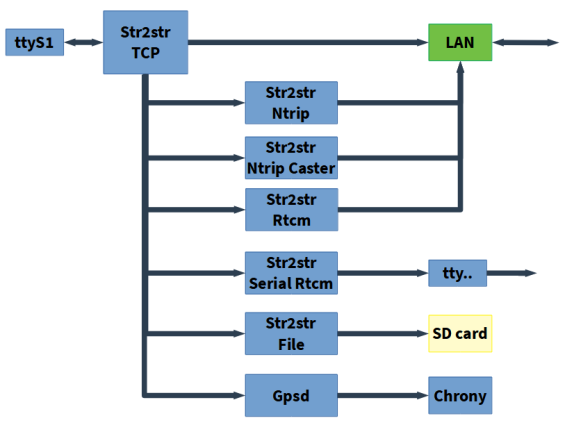
RTKBase use several RTKLIB str2str instances started with run_cast.sh as systemd services. run_cast.sh gets its settings from settings.conf
str2str_tcp.serviceis the main instance. It is connected to the gnss receiver and broadcast the raw data on TCP for all the others services.str2str_ntrip.serviceget the data from the main instance, convert the data to rtcm and stream them to a Ntrip caster.str2str_local_ntrip_caster.serviceget the data from the main instance, convert the data to rtcm, and act as a local Ntrip caster.str2str_rtcm_svr.serviceget the data from the main instance, convert the data to rtcm and stream them to clientsstr2str_rtcm_serial.serviceget the data from the main instance, convert the data to rtcm and stream them to a serial port (radio link, or other peripherals)str2str_file.serviceget the data from the main instance, and log the data to files.
The web GUI is available when the rtkbase_web service is running.
Advanced:
-
Aerial images: The default map background is OpenStreetMap, but you can switch to a worldwide aerial layer if you have a Maptiler key. To enable this layer, create a free account on Maptiler, create a key and add it to
settings.confinside the[general]section:maptiler_key=your_key -
Receiver options: str2str accept some receiver dependent options. If you use a U-Blox, the
-TADJ=1parameter is recommended as a workaround to non-rounded second values in Rtcm and Ntrip outputs. You can enter this parameter inside the settings forms. More information here and here.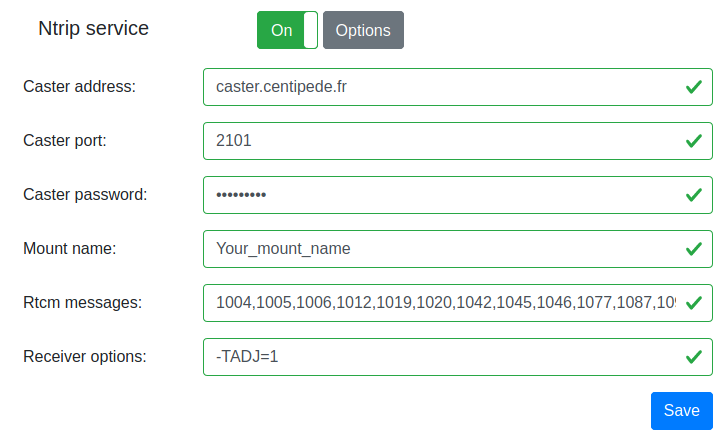
Development release:
If you want to install RTKBase from the dev branch, you can do it with these commands:
$ cd ~
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Stefal/rtkbase/dev/tools/install.sh -O install.sh
$ chmod +x install.sh
$ sudo ./install.sh --alldevOther usages:
A gnss receiver with a timepulse output is a very accurate stratum 0 clock thus, your gnss base station could act as a stratum 1 ntp peer for your local network and/or the ntp pool. There are a few steps to do this:
-
Connect the timepulse output + GND to some GPIO inputs on your SBC.
-
Configure this input as PPS in your operating system.
-
Raspberry Pi example:
- Inside /boot/config.txt, add
dtoverlay=pps-gpio,gpiopin=18on a new line. '18' is the input used for timepulse. - Inside /etc/modules, add
pps-gpioon a new line, if it is not already present.
- Inside /boot/config.txt, add
-
Orange Pi Zero example, inside /boot/armbianEnv.txt:
- Add
pps-gpioto theoverlaysline. - One a new line, add
param_pps_pin=PA19<- change 'PA19' to your input.
- Add
-
-
Set gpsd and chrony to use PPS
-
gpsd: comment the
DEVICEline in/etc/defaut/gpsdand uncomment#DEVICES="tcp:\\127.0.0.1:5015 \dev\pps0 -
chrony: inside
/etc/chrony/chrony.confuncomment the refclock pps line and add noselect to the 'refclock SHM 0`. You should have something like this:
refclock SHM 0 refid GPS precision 1e-1 offset 0 delay 0.2 noselect refclock PPS /dev/pps0 refid PPS lock GPS- reboot your sbc and check the result of
chronyc sources -vYou should read something like this, notice the '*' before 'PPS':
basegnss@orangepizero:~$ chronyc sources -v 210 Number of sources = 6 .-- Source mode '^' = server, '=' = peer, '#' = local clock. / .- Source state '*' = current synced, '+' = combined , '-' = not combined, | / '?' = unreachable, 'x' = time may be in error, '~' = time too variable. || .- xxxx [ yyyy ] +/- zzzz || Reachability register (octal) -. | xxxx = adjusted offset, || Log2(Polling interval) --. | | yyyy = measured offset, || \ | | zzzz = estimated error. || | | \ MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample =============================================================================== #? GPS 0 4 377 17 +64ms[ +64ms] +/- 200ms #* PPS 0 4 377 14 +363ns[ +506ns] +/- 1790ns ^- ntp0.dillydally.fr 2 6 177 16 -12ms[ -12ms] +/- 50ms ^? 2a01:e35:2fba:7c00::21 0 6 0 - +0ns[ +0ns] +/- 0ns ^- 62-210-213-21.rev.poneyt> 2 6 177 17 -6488us[-6487us] +/- 67ms ^- kalimantan.ordimatic.net 3 6 177 16 -27ms[ -27ms] +/- 64ms -
History:
See the changelog
License:
RTKBase is licensed under AGPL 3 (see LICENSE file).
RTKBase uses some parts of other software:
- RTKLIB (BSD-2-Clause)
- ReachView (GPL v3)
- Flask Jinja Werkzeug (BSD-3-Clause)
- Flask SocketIO (MIT)
- Bootstrap Bootstrap Flask Bootstrap 4 Toggle Bootstrap Table (MIT)
- wtforms (BSD-3-Clause) Flask WTF (BSD)
- pystemd (L-GPL 2.1)
- gpsd (BSD-2-Clause)
RTKBase uses OpenStreetMap tiles, courtesy of Empreinte digitale.