Credit card companies need to have the ability to recognize fraudulent credit card transactions so that customers are not charged for items that they did not purchase.
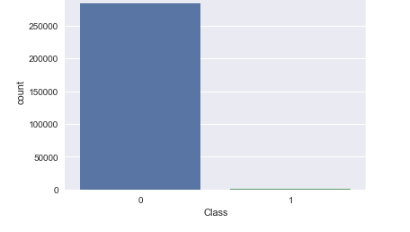
Datasets contains transactions made by credit cards in September 2013 by european cardholders. This dataset presents transactions that occurred in two days, where we have 492 frauds out of 284,807 transactions. The dataset is highly unbalanced, the positive class (frauds) account for 0.172% of all transactions.
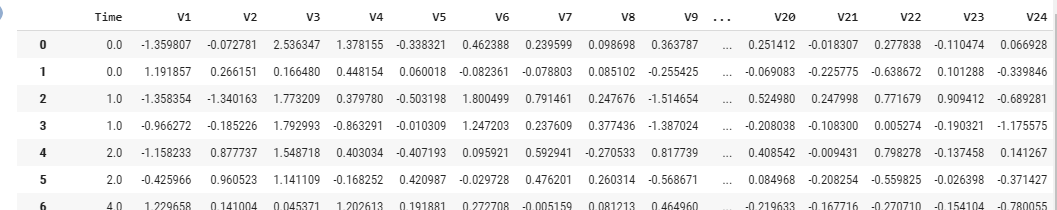
The data contains only numerical input variables which are the result of a PCA transformation. Unfortunately, due to confidentiality issues, we cannot provide the original features and more background information about the data.
-
Input Features: V1, V2, ... V28 are the principal components obtained with PCA, the only features which have not been transformed with PCA are 'Time' and 'Amount'.
-
Feature 'Time' contains the seconds elapsed between each transaction and the first transaction in the dataset.
-
The feature 'Amount' is the transaction Amount, this feature can be used for example-dependant cost-senstive learning.
-
Output: 1 in case of fraud and 0 otherwise.
-
Link to the dataset: https://www.kaggle.com/mlg-ulb/creditcardfraud/home
- Import the data set
- Transform the data
- Split the data in Train and Test
- Train and Test the model in the data set
- Visualize data points
- Get best accuracy
- Improve model as needed
- Discover if there is a potentialy risk of fraud
Open Google Colab https://colab.research.google.com/
- File
- Upload Notebook
- Run the Cells
Import the data set and visualize the data
- Data set
- Describe the data
Creating 2 variables
- negative, no fraud
- positive, fraud
Visualize the Count of Fraud and NoFraud
- Find out that the data is very unbalanced
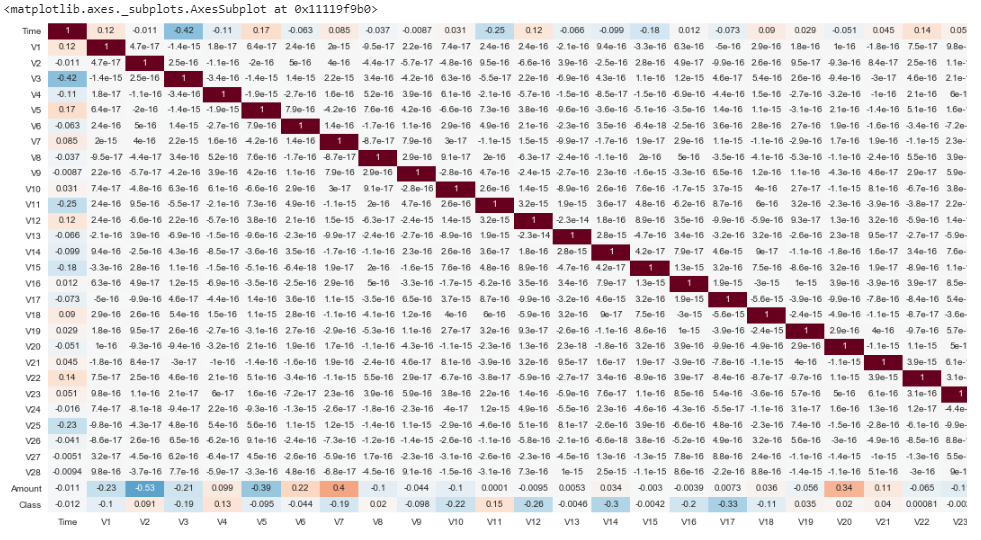
Heat Map
Kernel density estimation (KDE) is a non-parametric way to estimate the probability density function of a random variable.
- Re-shaping the values
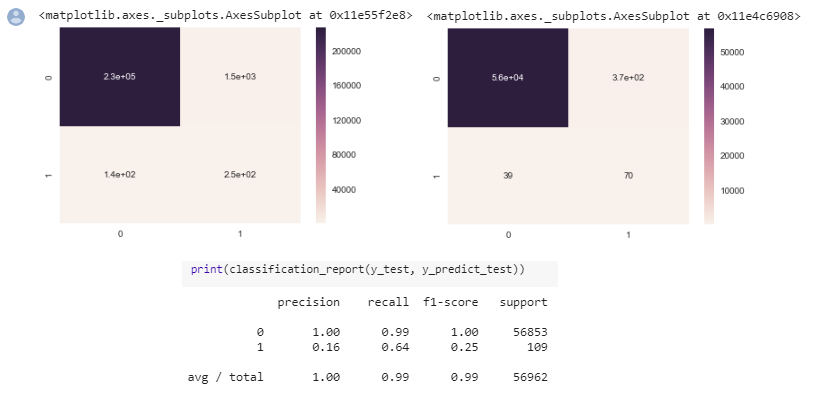
- Evaluating the Model
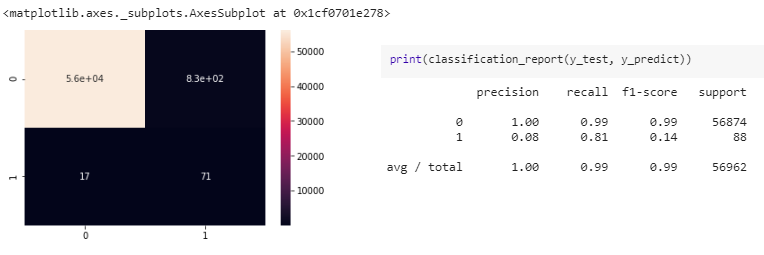
Final Model represented by Confunsion Matrix