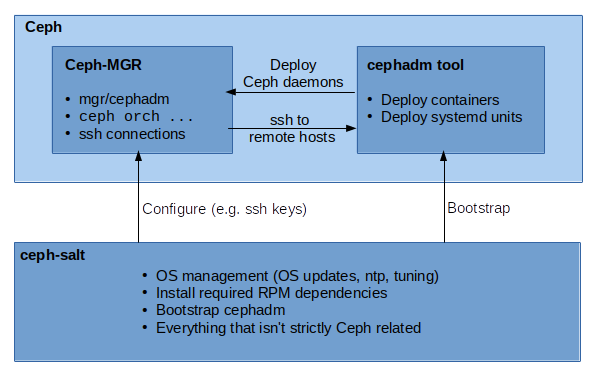
This project provides tools for deploying Ceph clusters managed by cephadm using Salt. It delivers missing pieces to fully manage a Ceph cluster with cephadm:
- OS management (performing OS updates, ntp, tuning)
- Install required RPM dependencies
- Bootstrap cephadm
- Enhanced bootstrapping by defining roles for Salt minions
This repository contains two components:
ceph-salt-formulais a Salt Formula using Salt Highstates to manage Ceph minions.ceph-saltis a CLI tool to manage the Salt Formula.
In order to use ceph-salt, you need a working Salt cluster and minion IDs
must be resolvable to IP addresses (e.g. host <minion_id>).
Now, install ceph-salt on your Salt Master from the openSUSE
repositories:
zypper in ceph-salt
Afterwards, reload the salt-master daemon:
systemctl restart salt-master
salt \* saltutil.sync_all
To deploy a Ceph cluster, first run config to start the configuration shell to
set the initial deployment of your cluster:
ceph-salt config
This opens a shell where you can manipulate ceph-salt's configuration. Each
configuration option is present under a configuration group. You can navigate
through the groups and options using the familiar ls and cd commands
similar to a regular shell. In each path you can type help to see the
available commands. Different options might have different commands available.
First step of configuration is to add the salt-minions that should be managed
byceph-salt.
The add command under /ceph_cluster/minions option supports autocomplete
and glob expressions:
/ceph_cluster/minions add *
Then we must specify which minions will be used to deploy Ceph. Those minions will be Ceph nodes controlled by cephadm:
/ceph_cluster/roles/cephadm add *
And which of them will have admin "keyring" installed:
/ceph_cluster/roles/admin add *
Next step is to specify which minion should be used to run cephadm bootstrap ....
This minion will be the Ceph cluster's first Mon and Mgr.
/ceph_cluster/roles/bootstrap set node1.test.com
Now we need to set the SSH key pair to be used by the Ceph orchestrator. The SSH key can be generated by ceph-salt with the following command:
/ssh generate
Alternatively, you can import existing keys by providing the path to the private and public key files:
/ssh/private_key import /root/.ssh/id_rsa
/ssh/public_key import /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
(Just be aware that ceph-salt does not support SSH private keys that are protected with a password)
In the typical ("storage appliance") case, one node of the cluster (typically the "admin node") will be designated as the "time server host". This node will sync its clock against one or more external servers (e.g. "pool.ntp.org"), and all other nodes in the cluster will sync their clocks against this node:
/time_server/servers add <minion id of the admin node>
/time_server/external_servers add pool.ntp.org
Ceph-salt can also configure all nodes to sync against an arbitrary host - this can be useful when setting up a cluster at a site that already has a single source of time:
/time_server/servers add <hostname>
(In this case, the on-site time server is assumed to be already configured and ceph-salt will make no attempt to manage it.)
ceph-salt can also be told not to touch the time sync configuration:
/time_server disable
In this case, it is up to the user to ensure that some form of time syncing is
configured and running on all machines in the cluster before triggering
ceph-salt apply. This is because cephadm will refuse to run without it.
Finally we need to set the Ceph container image path:
/cephadm_bootstrap/ceph_image_path set registry.opensuse.org/filesystems/ceph/octopus/images/ceph/ceph
Afterwards, you can exit the ceph-salt configuration shell by typing exit
or pressing [Ctrl]+[d]. Now use the apply command to start the
ceph-salt-formula and execute the deployment:
ceph-salt apply
Check man page for a full list of available commands:
man ceph-salt