LLM tools are
... a unified interface to access LLMs, both remote (such as OpenAI models) and self-hosted (on our Slurm cluster).
... a starter skript to easily start the models on Slurm.
... helpers to interact with the LLMs.
Clone the repository. Use an example slurm starter skript from the llm models table. Then make the starter skript executable and execute it (replace PATH with your installation directory)
chmod +x __PATH__/src/slurm/run_llm.sh
./usrun.sh -p A100-40GB --gpus=1 --time 08:00:00 --mem 100GB __PATH__/src/slurm/run_llm.sh vicuna7b
Finding out the URL of the API or the user interface is currently a bit fiddly. On the slurm cluster, run
$ squeue |grep YOUR_USER_NAME
709485_3 batch G_w2 YOUR_USER_NAME R 12:03:17 1 serv-9209
It shows a list of all your runnig slurm jobs. On the right you can see your host name. Ping it to get the IP address:
$ ping serv-9209
PING serv-9209.kl.dfki.de (192.168.92.189) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from serv-9209.kl.dfki.de (192.168.92.189): icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=0.137 ms
Here you can see your nodes IP address. The web UI and the API run on this IP address on port 5000, in the example http://192.168.92.189:5000.
- Create a virtual environment, e.g. with Conda. We recommend Python 3.9.6.
- Install the requirements:
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
You can start the command line tool to do a oneshot interaction with the LLM. Or you can start an HTTP API. Here are some examples:
Get help
$ python3 -m llm.run --help
usage: LLM Tools [-h] --wrapper LLM [--input_str INPUT_STR] [--mode {http_api,oneshot}]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--wrapper LLM Specify which LLM you want to load.
--input_str INPUT_STR
Specify input document. For mode=oneshot.
--mode {http_api,oneshot}
One shot interaction with the Dummy LLM
python3 -m llm.run --wrapper dummy_llm --mode oneshot --input_str="hallo"
Start the HTTP API with the Dummy LLM
python3 -m llm.run --mode http_api --wrapper dummy_llm
Send a post request to the Dummy LLM:
curl -X POST -d '{"doc": "hello world"}' -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://localhost:5000/api/generate
Call the dummy LLM from a remote LLM:
python3 -m llm.run --wrapper http --mode oneshot --input_str="hallo" --api_url "http://localhost:5000/api/generate"
HTTP API interaction with OpenAI Davinci
export OPENAI_API_KEY=...
python3 -m llm.run --wrapper openai --model text-davinci-003 --mode http_api
Adding a new LLM to llm_tools
Inside llm_registry.py file, add a new entry to the llm_registry dictionary,
mapping a unique name for your LLM to a lambda function that creates an instance of your LLM class.
Inside my_llm.py, define a class that inherits from the LLMWrapper abstract class.
This class will represent your LLM implementation.
You have successfully added a new LLM to the llm_tools.
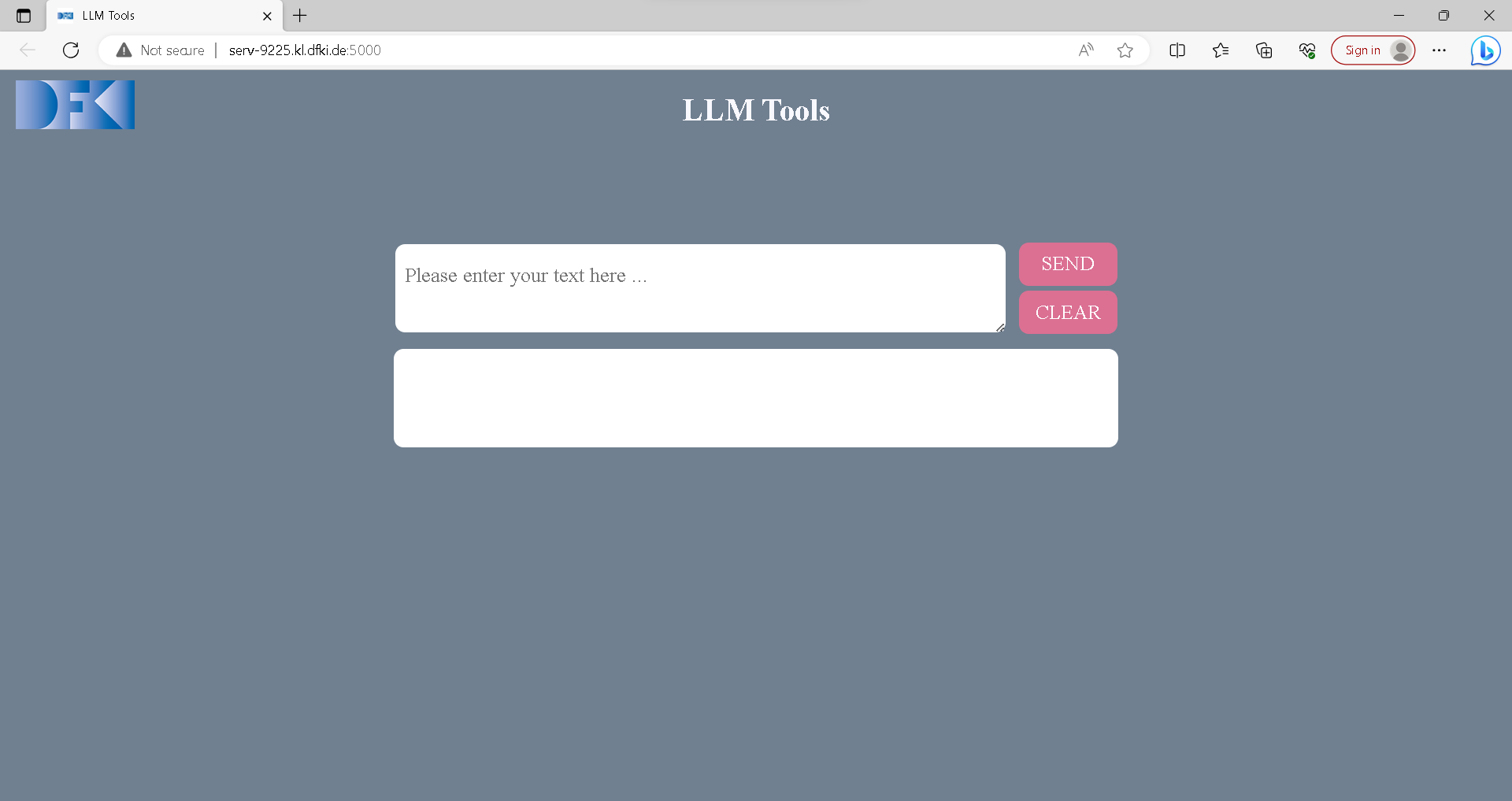
There is a Web user interface available to interact with llm.
Start the HTTP API with any desired llm using the --http_api parameter. This will also start the service of web interface.
You can open web UI through your browser using local IP (127.0.0.1:5000).
You can type in any text in the textbox that you want to sent to llm and press send.
The result will be displayed in the lower white box.
Tool for processing CSV files with llm.
Help:
$ python batch_processor.py -h
usage: batch_processor [-h] [--api API] [-i INPUT_FILE] [-o OUTPUT_FILE] [-ic INPUT_COLUMN] [-oc OUTPUT_COLUMN] [--max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS] [--temperature TEMPERATURE]
Process a csv data in api
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--api API API URL; defaults to 'http://localhost:5000/api/generate'
-i INPUT_FILE, --input_file INPUT_FILE
input file path; defaults to 'input.csv'
-o OUTPUT_FILE, --output_file OUTPUT_FILE
output file path; defaults to 'output.csv'
-ic INPUT_COLUMN, --input_column INPUT_COLUMN
name of the input data column; defaults to 'input'
-oc OUTPUT_COLUMN, --output_column OUTPUT_COLUMN
name of the output data column; defaults to 'output'
--max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS
maximum model return size in tokens; defaults to 100
--temperature TEMPERATURE
model output temperature between 0 and 2, defines how random is output; defaults to 1
Each entry in an INPUT_COLUMN of INPUT_FILE will be sent to API.
OUTPUT_FILE is a copy of an input file with a new column OUTPUT_COLUMN (default = 'output') which contains API responses.
Make sure to set MAX_NEW_TOKENS as needed. 100 Tokens is only 1 paragraph maximum.
If input file already has an 'output' column - only rows with empty output will be processed. Processing may be interrupted(via CTRL+C in UNIX) at any point and continued later by using an output file as an input.
Example usage
$ python3.11 batch_processor.py -i output.csv
processing output.csv: 100%|########################################| 60/60 [00:00<00:00, 673.91rows/s]
Processed 60 rows in 0.08912 seconds. (673.3 rows/second)
Saved results into output.csv