rsgeo is an interface to the Rust libraries geo-types and geo.
geo-types implements pure rust geometry primitives. The geo library
adds additional algorithm functionalities on top of geo-types. This
package lets you harness the speed, safety, and memory efficiency of
these libraries. geo-types does not support Z or M dimensions. There
is no support for CRS at this moment.
# remotes::install_github("josiahparry/rsgeo")
library(rsgeo)
#>
#> Attaching package: 'rsgeo'
#> The following object is masked from 'package:base':
#>
#> withinCreate geometries from sf objects
# get geometry from sf
data(guerry, package = "sfdep")
polys <- guerry[["geometry"]] |>
sf::st_cast("POLYGON")
# cast to rust geo-types
rs_polys <- as_rsgeom(polys)
head(rs_polys)
#> <rs_POLYGON[6]>
#> [1] (Polygon { exterior: LineString([Coord { x: 801150.0, y: 2092615.0 }, Coor...
#> [2] (Polygon { exterior: LineString([Coord { x: 729326.0, y: 2521619.0 }, Coor...
#> [3] (Polygon { exterior: LineString([Coord { x: 710830.0, y: 2137350.0 }, Coor...
#> [4] (Polygon { exterior: LineString([Coord { x: 882701.0, y: 1920024.0 }, Coor...
#> [5] (Polygon { exterior: LineString([Coord { x: 886504.0, y: 1922890.0 }, Coor...
#> [6] (Polygon { exterior: LineString([Coord { x: 747008.0, y: 1925789.0 }, Coor...Cast geometries to sf
sf::st_as_sfc(rs_polys)
#> Geometry set for 116 features
#> Geometry type: POLYGON
#> Dimension: XY
#> Bounding box: xmin: 47680 ymin: 1703258 xmax: 1031401 ymax: 2677441
#> CRS: NA
#> First 5 geometries:
#> POLYGON ((801150 2092615, 800669 2093190, 80068...
#> POLYGON ((729326 2521619, 729320 2521230, 72928...
#> POLYGON ((710830 2137350, 711746 2136617, 71243...
#> POLYGON ((882701 1920024, 882408 1920733, 88177...
#> POLYGON ((886504 1922890, 885733 1922978, 88547...Calculate the unsigned area of polygons.
bench::mark(
rust = unsigned_area(rs_polys),
sf = sf::st_area(polys),
check = FALSE
)
#> # A tibble: 2 × 6
#> expression min median `itr/sec` mem_alloc `gc/sec`
#> <bch:expr> <bch:tm> <bch:tm> <dbl> <bch:byt> <dbl>
#> 1 rust 83.27µs 87.7µs 11213. 3.82KB 0
#> 2 sf 1.31ms 1.38ms 721. 745.35KB 10.6Find centroids
bench::mark(
centroids(rs_polys),
sf::st_centroid(polys),
check = FALSE
)
#> # A tibble: 2 × 6
#> expression min median `itr/sec` mem_alloc `gc/sec`
#> <bch:expr> <bch:tm> <bch:tm> <dbl> <bch:byt> <dbl>
#> 1 centroids(rs_polys) 200.6µs 245.71µs 3741. 3.82KB 15.1
#> 2 sf::st_centroid(polys) 2.4ms 2.49ms 396. 756.52KB 6.38Extract points as matrix
rs_polys |>
centroids() |>
as.matrix() |>
head()
#> [,1] [,2]
#> [1,] 832852.3 2126601
#> [2,] 688485.6 2507622
#> [3,] 665510.1 2155203
#> [4,] 912995.8 1908303
#> [5,] 911433.9 1970312
#> [6,] 765421.3 1974521Plot the polygons and their centroids
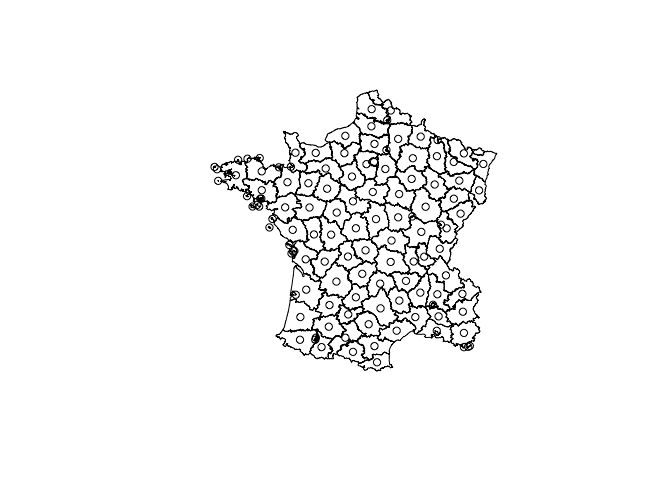
plot(rs_polys)
plot(centroids(rs_polys), add = TRUE)Calculate a distance matrix
pnts <- centroids(rs_polys)
pnts_sf <- sf::st_as_sfc(pnts)
bench::mark(
rust = euclidean_distance_matrix(pnts, pnts),
sf = sf::st_distance(pnts_sf, pnts_sf)
)
#> # A tibble: 2 × 6
#> expression min median `itr/sec` mem_alloc `gc/sec`
#> <bch:expr> <bch:tm> <bch:tm> <dbl> <bch:byt> <dbl>
#> 1 rust 165.48µs 181.63µs 5464. 108KB 12.6
#> 2 sf 2.83ms 2.88ms 344. 352KB 2.02Simplify a geometry
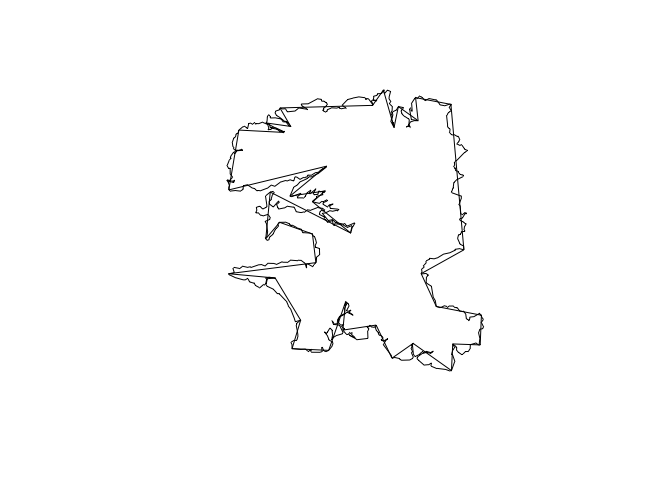
x <- rs_polys[[37]]
x_simple <- simplify_geom(x, 5000)
plot(x)
plot(x_simple, add = TRUE)bench::mark(
rust = simplify_geoms(rs_polys, 500),
sf = sf::st_simplify(polys, FALSE, 500),
check = FALSE
)
#> # A tibble: 2 × 6
#> expression min median `itr/sec` mem_alloc `gc/sec`
#> <bch:expr> <bch:tm> <bch:tm> <dbl> <bch:byt> <dbl>
#> 1 rust 3.61ms 3.82ms 262. 4KB 0
#> 2 sf 7.75ms 8.05ms 124. 1.23MB 2.07Union geometries with union_geoms()
plot(union_geoms(rs_polys))Find the closest point to a geometry
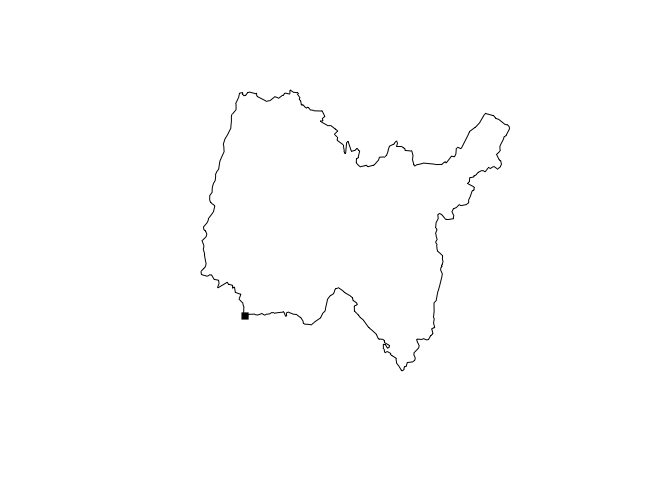
close_pnt <- closest_point(
rs_polys[[1]],
geom_point(800000, 2090000)
)
plot(rs_polys[[1]])
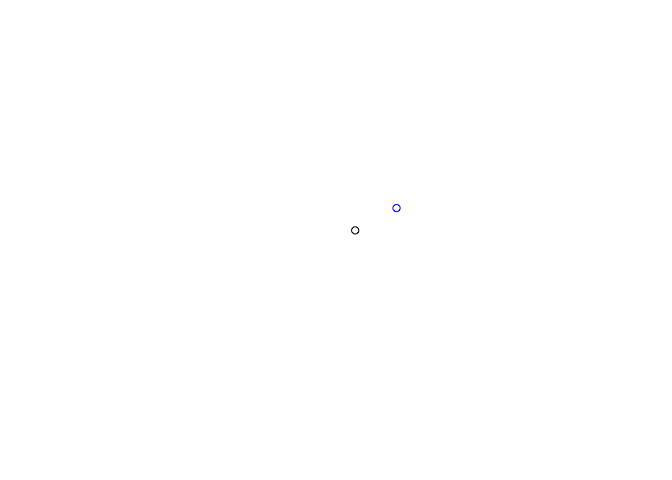
plot(close_pnt, pch = 15, add = TRUE)Find the haversine destination of a point, bearing, and distance.
bench::mark(
rust = haversine_destination(geom_point(10, 10), 45, 10000),
Cpp = geosphere::destPoint(c(10, 10), 45, 10000),
check = FALSE
)
#> # A tibble: 2 × 6
#> expression min median `itr/sec` mem_alloc `gc/sec`
#> <bch:expr> <bch:tm> <bch:tm> <dbl> <bch:byt> <dbl>
#> 1 rust 2.34µs 3.03µs 307755. 3.23KB 0
#> 2 Cpp 15.66µs 17.38µs 51943. 11.45MB 46.8origin <- geom_point(10, 10)
destination <- haversine_destination(origin, 45, 10000)
plot(origin)
plot(destination, col = "blue", add = TRUE)Find intermediate point.
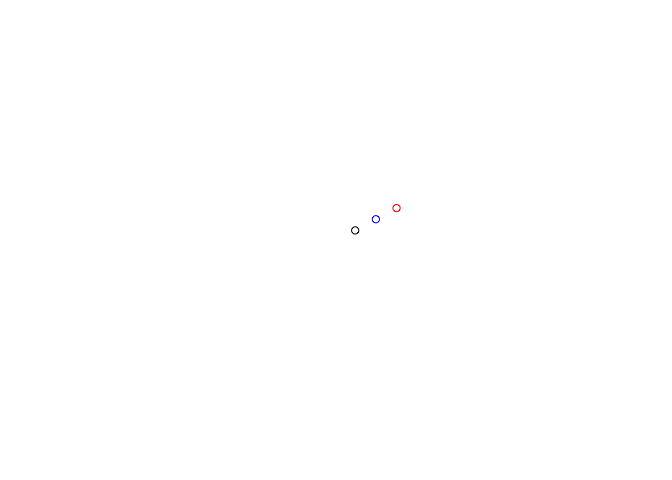
middle <- haversine_intermediate(origin, destination, 1/2)
plot(origin)
plot(destination, add = TRUE, col = "red")
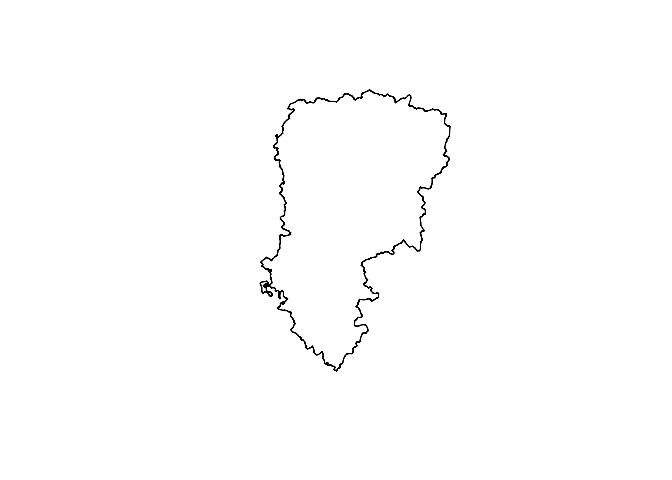
plot(middle, add = TRUE, col = "blue")Utilize the chaikin smoothing algorithm with 5 iterations.
region <- rs_polys[[2]]
plot(chaikin_smoothing(region, 5))Find extreme coordinates with extreme_coords()
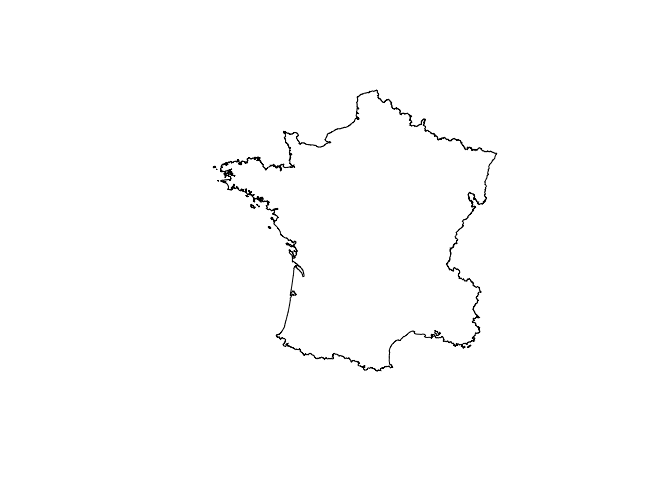
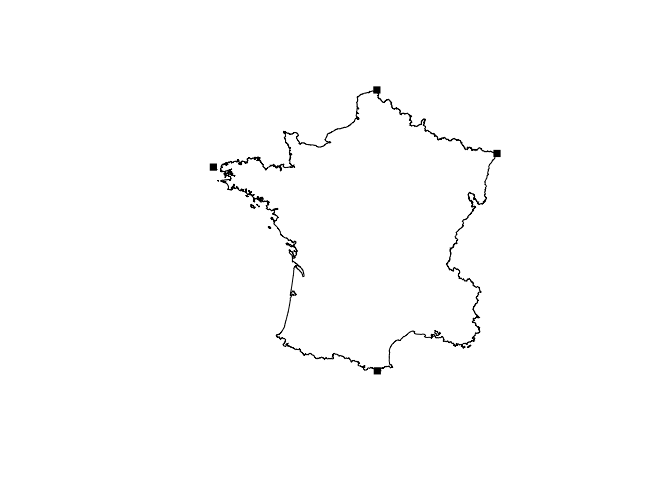
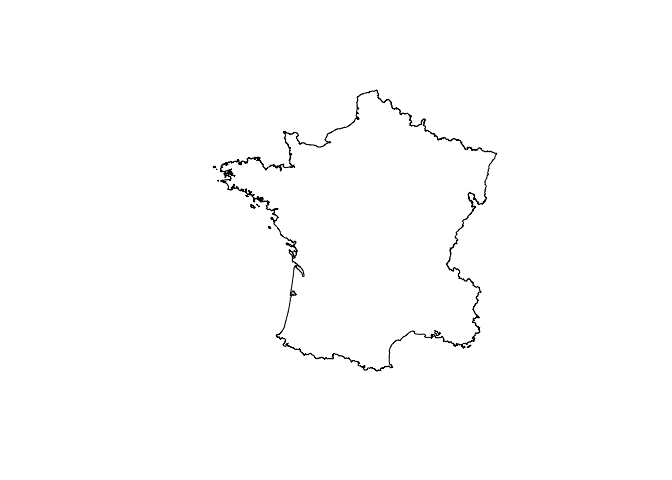
france <- union_geoms(rs_polys)
plot(france)
plot(extreme_coords(france[[1]]), add = TRUE, pch = 15)Get bounding rectangles
rects <- bounding_rectangles(rs_polys)
plot(rects)Convext hulls
convex_hulls(rs_polys) |>
plot()Cast geometries
lns <- cast_geoms(rs_polys, "linestring")
head(lns)
#> <rs_LINESTRING[6]>
#> [1] (LineString([Coord { x: 801150.0, y: 2092615.0 }, Coord { x: 800669.0, y: ...
#> [2] (LineString([Coord { x: 729326.0, y: 2521619.0 }, Coord { x: 729320.0, y: ...
#> [3] (LineString([Coord { x: 710830.0, y: 2137350.0 }, Coord { x: 711746.0, y: ...
#> [4] (LineString([Coord { x: 882701.0, y: 1920024.0 }, Coord { x: 882408.0, y: ...
#> [5] (LineString([Coord { x: 886504.0, y: 1922890.0 }, Coord { x: 885733.0, y: ...
#> [6] (LineString([Coord { x: 747008.0, y: 1925789.0 }, Coord { x: 746630.0, y: ...Expand into constituent geometries.
expand_geoms(rs_polys, flat = TRUE) |>
head()
#> <rs_LINESTRING[6]>
#> [1] (LineString([Coord { x: 801150.0, y: 2092615.0 }, Coord { x: 800669.0, y: ...
#> [2] (LineString([Coord { x: 729326.0, y: 2521619.0 }, Coord { x: 729320.0, y: ...
#> [3] (LineString([Coord { x: 647667.0, y: 2468296.0 }, Coord { x: 647777.0, y: ...
#> [4] (LineString([Coord { x: 710830.0, y: 2137350.0 }, Coord { x: 711746.0, y: ...
#> [5] (LineString([Coord { x: 882701.0, y: 1920024.0 }, Coord { x: 882408.0, y: ...
#> [6] (LineString([Coord { x: 886504.0, y: 1922890.0 }, Coord { x: 885733.0, y: ...Combine geometries into a single geometry
combine_geoms(lns)
#> <rs_MULTILINESTRING[1]>
#> [1] (MultiLineString([LineString([Coord { x: 801150.0, y: 2092615.0 }, Coord {...Union geometries
plot(union_geoms(rs_polys))Spatial predicates
x <- rs_polys[1:5]
intersects_sparse(x, rs_polys)
#> [[1]]
#> [1] 94 50 1 92 48
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] 63 2 7 80 98 78 81 101
#>
#> [[3]]
#> [1] 77 84 3 20 94 27 53
#>
#> [[4]]
#> [1] 4 5 30 109 107
#>
#> [[5]]
#> [1] 4 5 48 30Convert to and from wkb and wkt
wkt <- wkt_from_geoms(x)
wkt_to_geoms(wkt)
#> <rs_POLYGON[5]>
#> [1] (Polygon { exterior: LineString([Coord { x: 801150.0, y: 2092615.0 }, Coor...
#> [2] (Polygon { exterior: LineString([Coord { x: 729326.0, y: 2521619.0 }, Coor...
#> [3] (Polygon { exterior: LineString([Coord { x: 710830.0, y: 2137350.0 }, Coor...
#> [4] (Polygon { exterior: LineString([Coord { x: 882701.0, y: 1920024.0 }, Coor...
#> [5] (Polygon { exterior: LineString([Coord { x: 886504.0, y: 1922890.0 }, Coor...wkb <- wkb_from_geoms(x)
head(wkb[[1]])
#> [1] 01 03 00 00 00 01
wkb_to_geoms(wkb)
#> <rs_POLYGON[5]>
#> [1] (Polygon { exterior: LineString([Coord { x: 801150.0, y: 2092615.0 }, Coor...
#> [2] (Polygon { exterior: LineString([Coord { x: 729326.0, y: 2521619.0 }, Coor...
#> [3] (Polygon { exterior: LineString([Coord { x: 710830.0, y: 2137350.0 }, Coor...
#> [4] (Polygon { exterior: LineString([Coord { x: 882701.0, y: 1920024.0 }, Coor...
#> [5] (Polygon { exterior: LineString([Coord { x: 886504.0, y: 1922890.0 }, Coor...Right now plotting is done using sf by first casting into R native
objects and then assigned the appropriate sf class. That object is then
plotted by sf