- Release: v2.3.2
- Author: Corrado Gerbaldo - IU1BOW.
- Mail: corrado.gerbaldo@gmail.com
- Licensing: Gpl V3.0 see "LICENSE" file.
- Languages: This application is written in Python/flask,Javascript and HTML
DXSpider is a great DX Cluster software that has a usefull telnet interface. I wrote this application in order to add a web user interface to DXSpider and show the spots collected. The user could see 50 spots at time and filter them by band, spotter continent and spotted continent.
For this application I've used:
- Bootstrap for stylesheet CSS
- jQuery In the header you can find the link to MS link
- qrz.com For each callsing found you can click on lens and you'll see him on qrz.com
- flag-icon-css https://github.com/lipis/flag-icon-css I used it for show the country flags
- ng3k.com ng3k.com I used to get information about "Announced Dx Operations". Thanks to Bill/NG3K !!!
You can find my web site at https://www.iu1bow.it
see file "CHANGELOG.md"
1) DXSpider First of all you have to installed [DXspider] (http://www.dxcluster.org/) and connected with some other cluster nodes.
2) MariaDB / MySQL
Then you have to install MariaDB on your web server, on the same server where DXSpider is running and configure DXSpider to use it: in your spider folder edit local/DXVars.pm adding these lines:
# the SQL database DBI dsn
$dsn = "dbi:mysql:dxcluster:localhost:3306";
$dbuser = "your-user";
$dbpass = "your-password"; If you would change some MariaDB parameters, then you can find them in /etc/mysql/my.cnf or /etc/my.cnf, depending on your distro.
If the database will not be created automatically, please see "DB_ISSUES.md"
3) Python modules
You could install python modules using automatic or manual way.
3.1) Automatic modules install
after downloaded spiderweb move in the main folder and install using requirements.txt file
foo@bar:~$ cd spiderweb
foo@bar:~$ pip install -r requirements.txt3.2) Manual modules install
First of all you have to install the python3 pip installer
foo@bar:~$ sudo apt install python3-pipThis application is based on Flask To install Flask:
foo@bar:~$ pip install flask
foo@bar:~$ pip install Flask-minify
foo@bar:~$ pip install staticjinja
foo@bar:~$ pip install flask_wtfThen you have to install mysql libraries**:
foo@bar:~$ pip install mysql-connector-python
foo@bar:~$ pip install --upgrade mysql-connector-python==8.0.12
Finally you have to install matplotlib and pandas in order to plots some graphics
foo@bar:~$ pip3 install matplotlib
foo@bar:~$ pip3 install statsmodels
foo@bar:~$ pip3 install geopandas
foo@bar:~$ pip3 install shapely
or
foo@bar:~$ sudo -H pip3 install matplotlib --system
foo@bar:~$ sudo -H pip3 install statsmodels --system
foo@bar:~$ sudo -H pip3 install geopandas --system
foo@bar:~$ sudo -H pip3 install shapely --system In the path spiderweb/cfg/ rename config.json.template in config.json:
foo@bar:~$ mv config.json.template config.jsonthen edit it and set the user and password of your database, the menu items, and other stuffs (callsign, mail address...). There is also a specific parameter, named "enable_cq_filter" used to enable the CQ Zone filtering.
Othewhise, if you prefer, you could use an utility for edit your configuration and menu. Go in "script" folder and run ./config.sh
foo@bar:~$ cd scripts
foo@bar:~$ ./config.sh
*** DxSpider configuration ***
Configuration file loaded from: ../cfg/config.json
h: help
vc: view config.
ec: edit config.
vm: view menu
em: edit menu
s: save
t: load config. from template
x: exit
Make your choiche:
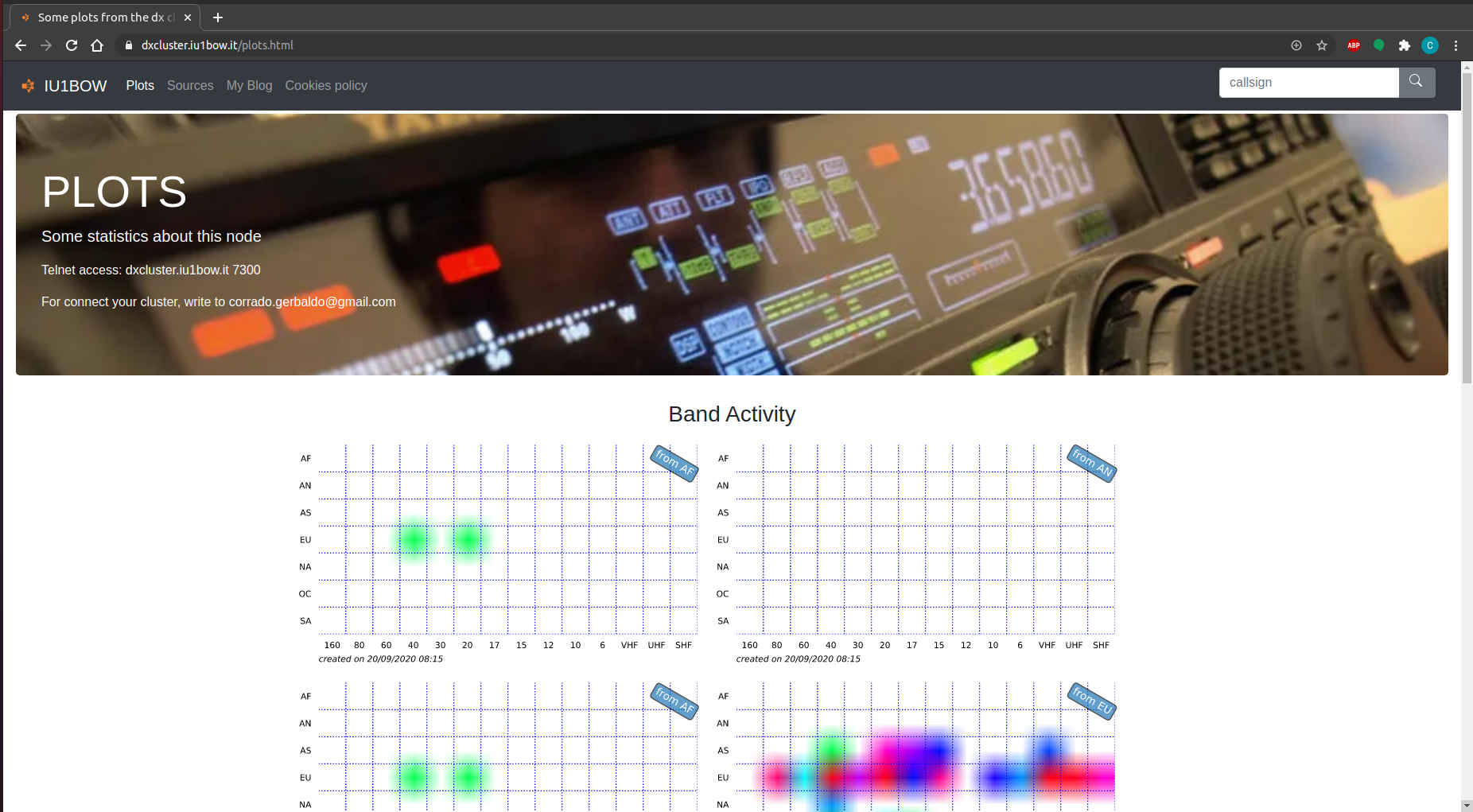
In order to show the right plots, you have to generate them! To do so you have to run .sh files inside scripts folders, or the better way is to schedule them with your crontab
foo@bar:~$ crontab -ethen edit it in a manner like this:
0 22 * * * /home/web/spiderweb/scripts/qso_world_map.sh > /dev/null 2>&1
0 23 * * * /home/web/spiderweb/scripts/qso_months.sh > /dev/null 2>&1
*/15 * * * * /home/web/spiderweb/scripts/propagation_heatmaps.sh > /dev/null 2>&1
0 1 * * * /home/web/spiderweb/scripts/qso_trend.sh > /dev/null 2>&1
*/30 * * * * /home/web/spiderweb/scripts/qso_hour_band.sh > /dev/null 2>&1
39 * * * * /home/web/spiderweb/scripts/monitor.sh> /dev/null 2>&1
__Now you can run your web application with the following command:
foo@bar:~$ python3 webapp.pyThe flask default port is 5000, so you can see your web app, typing http://localhost:5000 in your web browser.
Keep in mind that the flask web server, usually is used as a test server.
There are some ways to use it in production.
My configuration is: Cloudflare + Nginx + Bjoern
Bjoern is a lightweight WSGI for python.
for install it:
foo@bar:~$ sudo apt install libev-dev libevdev2
foo@bar:~$ pip3 install bjoernIf you want you can make it as a daemon service. Create and edit a file named for example spiderweb.service (in the systemd folder)
foo@bar:~$ sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/spiderweb.serviceBelow an example of configuration:
[Unit]
Description=bjoern instance spiderweb
After=network.target
After=multi-user.target
[Service]
User=web
Group=www-data
Type=simple
WorkingDirectory=/home/web/spiderweb
Environment="PATH=/home/web/spiderweb"
ExecStart=/usr/bin/python3 /home/web/spiderweb/wsgi.py
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetThen you can install and start the daemon:
foo@bar:~$ sudo systemctl enable spiderweb.service
foo@bar:~$ sudo systemctl start spiderweb.service
foo@bar:~$ sudo systemctl status spiderweb.service
● spiderweb.service - bjoern instance spiderweb
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/spiderweb.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2020-10-25 09:56:35 UTC; 8h ago
Main PID: 6518 (python3)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 420)
CGroup: /system.slice/spiderweb.service
└─6518 /usr/bin/python3 /home/web/spiderweb/wsgi.py
Oct 25 09:56:35 dxcluster01 systemd[1]: Started bjoern instance spiderweb.Now you can install and configur NGINX
Install with:
foo@bar:~$ sudo apt install nginxConfigure:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/myappserver {
listen 80;
server_name iu1bow.it www.iu1bow.it;
location ^~ /.well-known/ {
alias /home/web/verify/.well-known/;
}
location / {
ssi off;
include proxy_params;
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
}
}
For SSL I'm using Cloudflare. This is a free service that alow you to use https and a proxy cache.
Search engine indexing: when you are on-line, if you would to index your website on search engines, you have to generate a file named sitemap.xml and put it in /static/ folder. There are many tool to generate sitemap.xml, for example [www.xml-sitemaps.com] (https://www.xml-sitemaps.com/)
Index on MySQL: if you would to increase speed on callsign search, you could define some index on the table 'spot'. You can see more details on "create_mysql_index.sql"
Cookie settings: if you don't use https, but you use http, you have to change the following setting in webapp.py:
SESSION_COOKIE_SECURE=True,
to
SESSION_COOKIE_SECURE=False,
you can use the scritp scripts/monitoring.sh in order to monitoring your system. Check instruction inside this scripts.
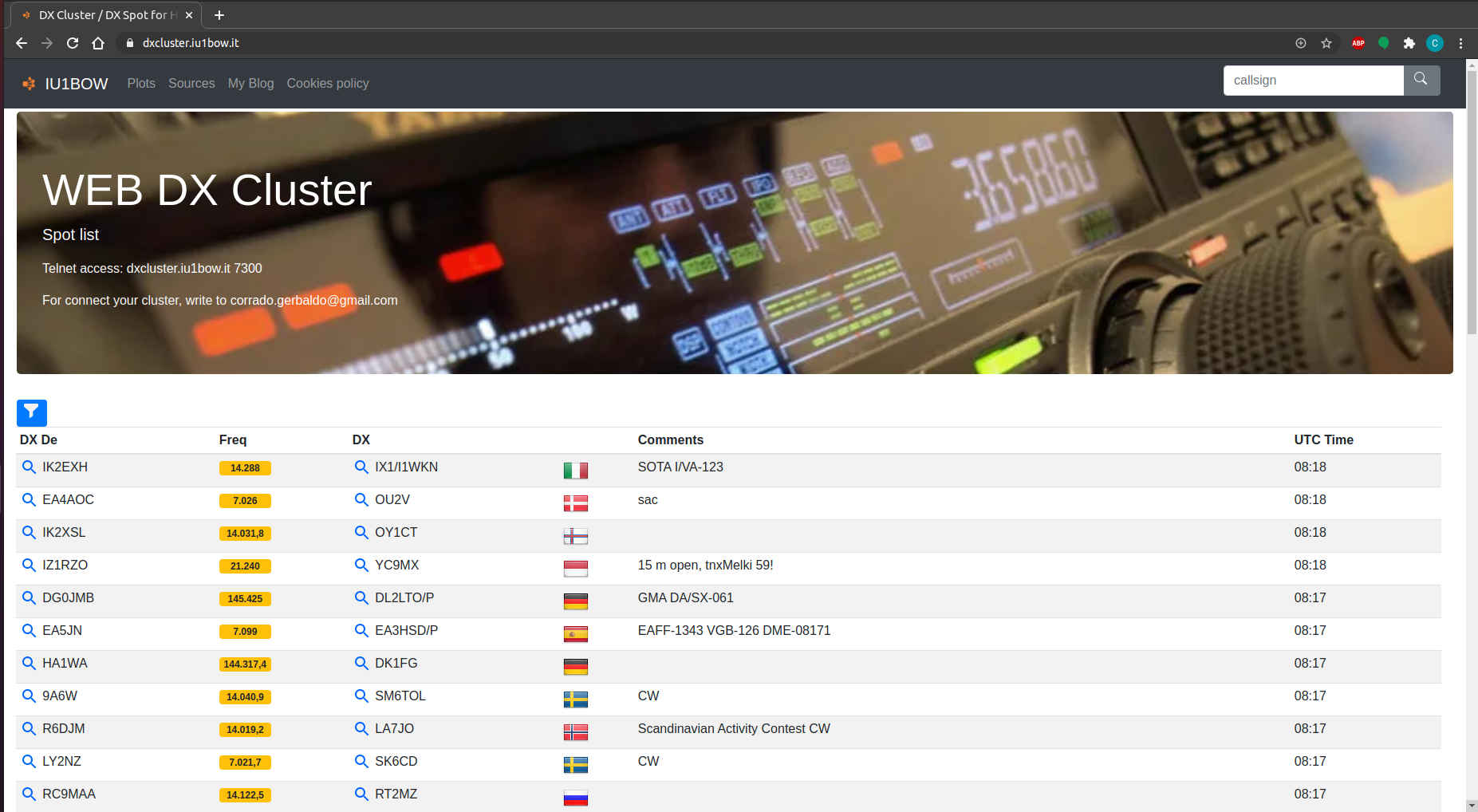
Spot list
You can retrive last spots calling "/spotlist"; For example [www.iu1bow.com/spotlist] (https://www.iu1bow.com/spotlist)
country of a callsign
You cam retrive some informations about a callsign with callsign; For example [www.iu1bow.com/callsign?c=IU1BOW] (https://www.iu1bow.com/callsign?c=IU1BOW)