This tutorial describes how to run an arbitrary executable or shell script triggered by the connection of an external device (usb/thunderbolt) to a Mac.
This relies on Apple's IOKit library for device detection and a daemon for running the desired executable.
See BSD man page on xpc_events:
man xpc_eventsFor the daemon to not be triggered repeatedly after connecting the device, a special stream handler (created by Ford Parsons) is used to "consume" the com.apple.iokit.matching event, as explained here.
For example, this can be used to spoof the MAC address of an ethernet adapter when it is connected to the Mac.
The setup is explained using the MAC spoofing scenario example files in example-spoof-MAC but can be generalized to arbitrary executables and devices.
Adapt the shell script spoofmac.sh to your needs and
make it executable:
sudo chmod 755 spoofmac.sh
Then move it into /usr/local/bin, or some other directory:
cp spoofmac.sh /usr/local/bin/
The stream handler is universal (no need to adapt) and can be built on a Mac (with xcode installed):
gcc -framework Foundation -o xpc_set_event_stream_handler xpc_set_event_stream_handler.m
Let's place it into /usr/local/bin, like the main executable for the daemon.
cp xpc_set_event_stream_handler /usr/local/bin/
The stream handler is also compiled via a Github Action on every commit.
This uses a Github macos-latest machine.
The plist file com.spoofmac.plist contains the properties of the daemon that will run the executable on device connect trigger.
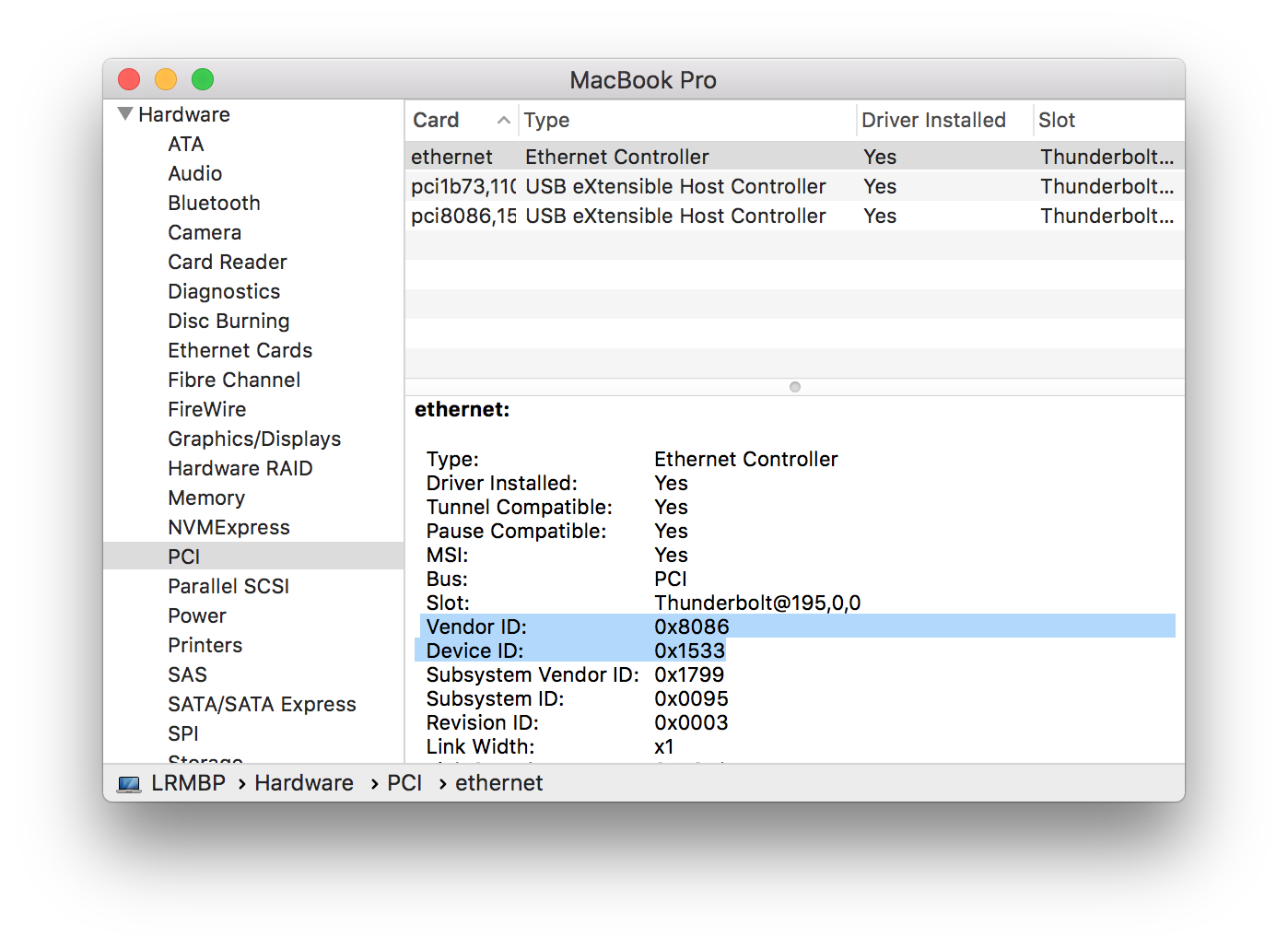
It contains information for identifying the device you want to base your trigger on, like idVendor, idProduct, IOProviderClass.
Get them via the output of
ioreg -p IOProviderClass -lwhere <IOProviderClass> should be either IOPCI (Thunderbolt) or IOUSB (USB).
The identifiers can also be obtained from the System Information App on your Mac.
Convert the hex identifiers to integers before inserting into the plist file (for example using int(0x8086) in python).
IOProviderClass should be either IOPCIDevice (Thunderbolt) or IOUSBDevice (USB).
The other relevant entry in the plist file is the location of xpc_set_event_stream_handler and the executable.
Other entries include the location of standard output (log) files and the executing user.
Since MAC spoofing requires root privileges, we put com.spoofmac.plist into /Library/LaunchDaemons:
cp com.spoofmac.plist /Library/LaunchDaemons/
not into a LaunchAgents folder. Launch agents ignore the UserName argument.
Insure that the owner of the file is root:
sudo chown root:wheel /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.spoofmac.plist
Activate the daemon:
launchctl load /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.spoofmac.plist
and you are good to go.
Unloading is done using launchctl unload.
If you like this tutorial and code and you would like to support me,