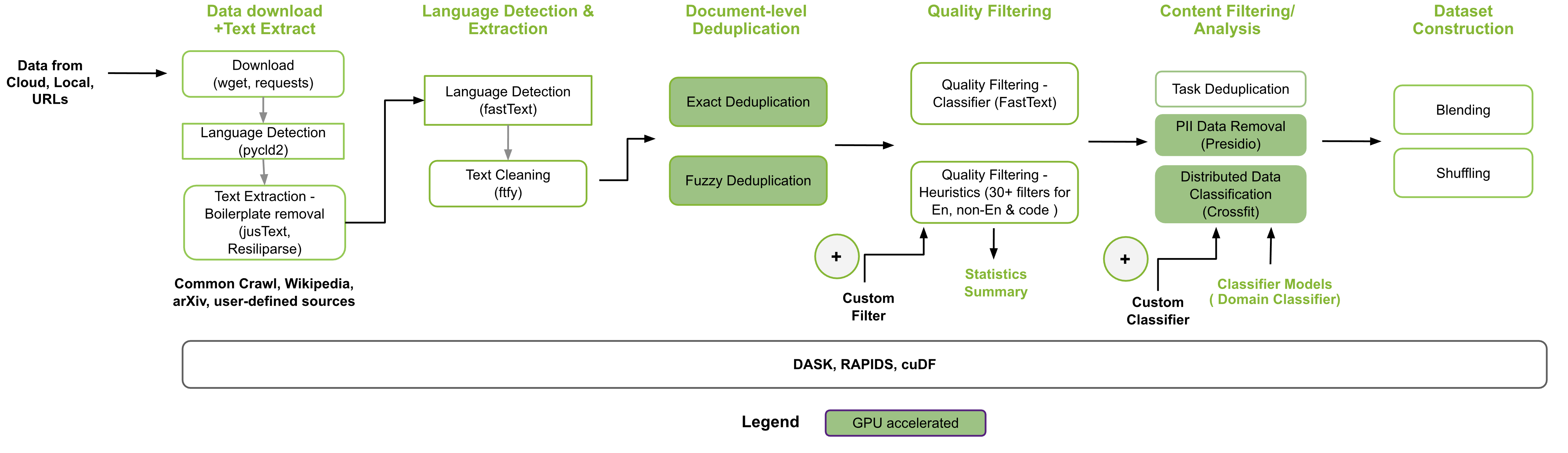
🚀 The GPU-Accelerated Open Source Framework for Efficient Large Language Model Data Curation 🚀
NeMo Curator is a Python library specifically designed for fast and scalable dataset preparation and curation for large language model (LLM) use-cases such as foundation model pretraining, domain-adaptive pretraining (DAPT), supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and paramter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT). It greatly accelerates data curation by leveraging GPUs with Dask and RAPIDS, resulting in significant time savings. The library provides a customizable and modular interface, simplifying pipeline expansion and accelerating model convergence through the preparation of high-quality tokens.
At the core of the NeMo Curator is the DocumentDataset which serves as the the main dataset class. It acts as a straightforward wrapper around a Dask DataFrame. The Python library offers easy-to-use methods for expanding the functionality of your curation pipeline while eliminating scalability concerns.
NeMo Curator provides a collection of scalable data-mining modules. Some of the key features include:
-
Data download and text extraction
- Default implementations for downloading and extracting Common Crawl, Wikipedia, and ArXiv data
- Easily customize the download and extraction and extend to other datasets
-
Language identification and separation with fastText and pycld2
-
Text reformatting and cleaning to fix unicode decoding errors via ftfy
-
- Multilingual heuristic-based filtering
- Classifier-based filtering via fastText
-
- exact and fuzzy (near-identical) deduplication are accelerated using cuDF and Dask
- For fuzzy deduplication, our implementation follows the method described in Microsoft Turing NLG 530B
- For semantic deduplication, our implementation follows the method described in SemDeDup by Meta AI (FAIR) facebookresearch/SemDeDup
-
Multilingual downstream-task decontamination following the approach of OpenAI GPT3 and Microsoft Turing NLG 530B
-
Distributed data classification
- Multi-node, multi-GPU classifier inference
- Provides sophisticated domain and quality classification
- Flexible interface for extending to your own classifier network
-
Personal identifiable information (PII) redaction for removing addresses, credit card numbers, social security numbers, and more
These modules offer flexibility and permit reordering, with only a few exceptions. In addition, the NeMo Framework Launcher provides pre-built pipelines that can serve as a foundation for your customization use cases.
- Documentation
- Examples
- Tutorials
- Blog posts
- Curating Trillion-Token Datasets: Introducing NVIDIA NeMo Data Curator
- Scale and Curate High-Quality Datasets for LLM Training with NVIDIA NeMo Curator
- Curating Custom Datasets for LLM Training with NVIDIA NeMo Curator
- Curating Custom Datasets for LLM Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning with NVIDIA NeMo Curator
- Streamlining Data Processing for Domain Adaptive Pretraining with NVIDIA NeMo Curator
This section explains how to install NeMo Curator and use the Python library, Python modules, and CLI scripts. It also includes a list of tutorials to help you get started right away. Finally, this section explains how to use the NeMo Framework Launcher as an alternative method for interfacing with NeMo Curator.
Before installing NeMo Curator, ensure that the following requirements are met:
- Python 3.10
- Ubuntu 22.04/20.04
- NVIDIA GPU (optional)
- Volta™ or higher (compute capability 7.0+)
- CUDA 12 (or above)
You can install NeMo-Curator
- from PyPi
- from source
- get it through the NeMo Framework container.
To install the CPU-only modules:
pip install cython
pip install nemo-curatorTo install the CPU and CUDA-accelerated modules:
pip install cython
pip install --extra-index-url https://pypi.nvidia.com nemo-curator[cuda12x]-
Clone the NeMo Curator repository in GitHub.
git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA/NeMo-Curator.git cd NeMo-Curator -
Install the modules that you need.
To install the CPU-only modules:
pip install cython pip install .To install the CPU and CUDA-accelerated modules:
pip install cython pip install --extra-index-url https://pypi.nvidia.com ".[cuda12x]"
You can also install NeMo Curator using the Rapids nightly, to do so you can set the environment variable RAPIDS_NIGHTLY=1.
# installing from pypi
RAPIDS_NIGHTLY=1 pip install --extra-index-url=https://pypi.anaconda.org/rapidsai-wheels-nightly/simple "nemo-curator[cuda12x]"
# installing from source
RAPIDS_NIGHTLY=1 pip install --extra-index-url=https://pypi.anaconda.org/rapidsai-wheels-nightly/simple ".[cuda12x]"When the environment variable set to 0 or not set (default behavior) it'll use the stable version of Rapids.
The latest release of NeMo Curator comes preinstalled in the NeMo Framework Container. If you want the latest commit inside the container, you can reinstall NeMo Curator using:
pip uninstall nemo-curator
rm -r /opt/NeMo-Curator
git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA/NeMo-Curator.git /opt/NeMo-Curator
pip install --extra-index-url https://pypi.nvidia.com /opt/NeMo-Curator[cuda12x]And follow the instructions for installing from source from above.
The following snippet demonstrates how to create a small data curation pipeline that downloads and curates a small subset of the Common Crawl dataset.
# Download your dataset
dataset = download_common_crawl("/datasets/common_crawl/", "2021-04", "2021-10", url_limit=10)
# Build your pipeline
curation_pipeline = Sequential([
# Fix unicode
Modify(UnicodeReformatter()),
# Discard short records
ScoreFilter(WordCountFilter(min_words=80)),
# Discard low-quality records
ScoreFilter(FastTextQualityFilter(model_path="model.bin")),
# Discard records from the evaluation metrics to prevent test set leakage.
TaskDecontamination([Winogrande(), Squad(), TriviaQA()])
])
# Execute the pipeline on your dataset
curated_dataset = curation_pipeline(dataset)To get started with NeMo Curator, you can follow the tutorials available here. These tutorials include:
tinystorieswhich focuses on data curation for training LLMs from scratch.peft-curationwhich focuses on data curation for LLM parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) use-cases.distributed_data_classificationwhich focuses on using the quality and domain classifiers to help with data annotation.single_node_tutorialwhich demonstrates an end-to-end data curation pipeline for curating Wikipedia data in Thai.
The NeMo Curator section of the NeMo Framework User Guide provides in-depth information about how the Python modules work. The examples directory in the GitHub repository provides scripts that showcase these modules.
NeMo Curator also offers CLI scripts for you to use. The scripts in nemo_curator/scripts map closely to the supplied Python modules. Refer to the NeMo Framework User Guide for more information about the Python modules and scripts.
As an alternative method for interfacing with NeMo Curator, you can use the NeMo Framework Launcher. The launcher enables you to easily configure the parameters and cluster. It can also automatically generate the SLURM batch scripts that wrap around the CLI scripts required to run your pipeline.
In addition, other methods are available to run NeMo Curator on SLURM. For example, refer to the example scripts in examples/slurm for information on how to run NeMo Curator on SLURM without the NeMo Framework Launcher.
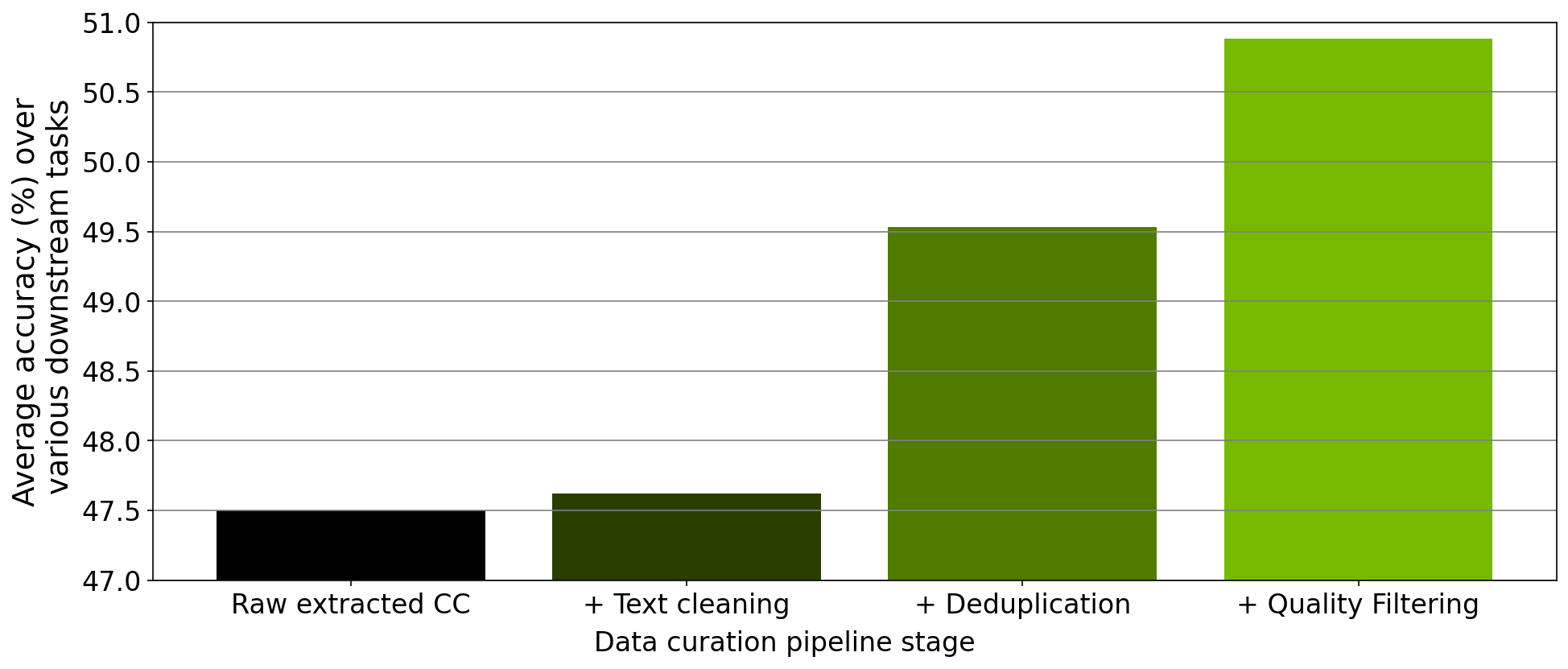
The modules within NeMo Curator were primarily designed to curate high-quality documents from Common Crawl snapshots in a scalable manner. To evaluate the quality of the curated Common Crawl documents, we conducted a series of ablation experiments. In these experiments, we trained a 357M-parameter GPT-style model using datasets generated at various stages of our data curation pipeline, which was implemented in NeMo Curator.
The following figure shows that the use of different data curation modules implemented in NeMo Curator led to improved model zero-shot downstream task performance.
In terms of scalability and compute performance, using the combination of RAPIDS and Dask fuzzy deduplication enabled us to deduplicate the 1.1 Trillion token Red Pajama dataset in 1.8 hours with 64 NVIDIA A100 Tensor Core GPUs.
Additionally, using the CPU-based modules, the following table shows the time required and resulting data size reduction for each processing step Common Crawl snapshot from November/December of 2020 using 30 CPU nodes (with hardware similar to the c5.24xlarge Amazon AWS C5 instance).
| Dataset | Download and text extraction | Text cleaning | Quality filtering | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Output Size | Time | Output Size | Time | Output Size | |
| Common Crawl 2020-50 | 36 hrs | 2.8 TB | 1 hr | 2.8 TB | 0.2 hr | 0.52 TB |
We welcome community contributions! Please refer to CONTRIBUTING.md for the process.