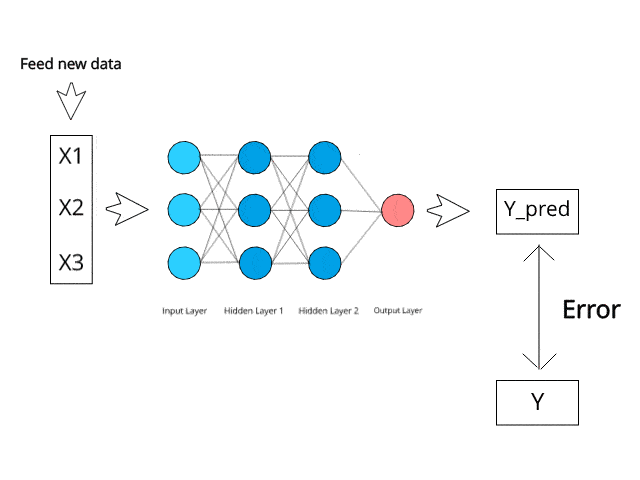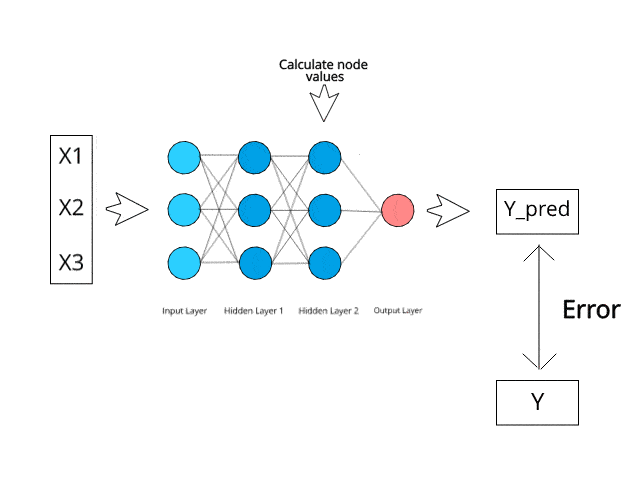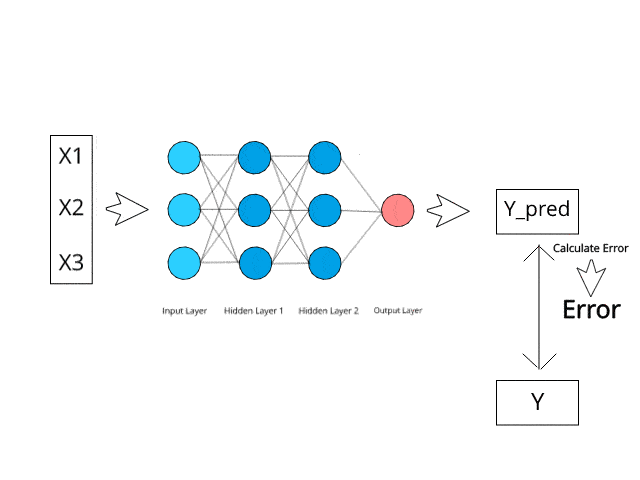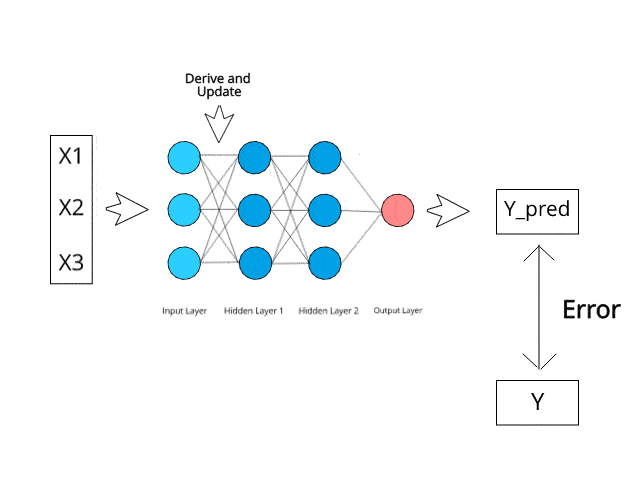
Fraud is a major problem for credit card companies, due to the large volume of transactions that are completed each day and the similarity between fraudulent and normal transactions.
Moreover, fraud detection problems are a type of imbalanced binary classification; where data analysis usually focuses on identifying the rare data (the positive class).
For this particular problem, the machine learning model's performance was measured mainly on the results obtained on the prediction of the positive class; which represent fraudulent transactions. In addition to, a dataset from Kaggle was used for this research; the data consists of credit card transactions that occured over two days in September 2013 by European cardholders. All the details of the cardholders have been anonymized via a Principal Component Analysis (PCA) transform.
Furthermore, each record is classified as class '0' (normal transactions) or class '1' (fraudulent transactions). Specifically, there are 492 fraudulent credit card transactions, out of 284,807 transactions; making a total of about 0.172% of all transactions. This causes an enormous imbalance of the data distributions; therefore, the transactions are heavily skewed towards normal.
- Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow: Concepts, Tools, and Techniques to Build Intelligent Systems
- Applications of Machine Learning
- An Introduction to ML Theory and Its Applications
AI and Machine Learning (ML) have taken over the traditional computing methods, changing how many industries perform and conduct their day-to-day operations. From research and manufacturing to modernizing finance and healthcare streams, leading AI has changed everything in a relatively short amount of time.
AI and related technologies have had a positive impact on the way the IT sector works. To put it simply, artificial intelligence is a branch of computer science that looks to turning computers into intelligent machines that would, otherwise, not be possible without direct human intervention. By making use of computer-based training and advanced algorithms, AI and machine learning can be used to create systems capable of mimicking human behaviors, provide solutions to difficult and complicated problems, and further develop simulations, aiming to become human-level AI
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifierclass ggml.classification.MLPClassificationTrainer(arch, env_builder=<ggml.common.LearningEnvironmentBuilder object>, loss='mse', learning_rate=0.1, max_iter=1000, batch_size=100, loc_iter=10, seed=None)¶ Bases: ggml.classification.ClassificationTrainer
init(arch, env_builder=<ggml.common.LearningEnvironmentBuilder object>, loss='mse', learning_rate=0.1, max_iter=1000, batch_size=100, loc_iter=10, seed=None) Constructs a new instance of MLP classification trainer.
env_builder : Environment builder. arch : Architecture. loss : Loss function (‘mse’, ‘log’, ‘l2’, ‘l1’ or ‘hinge’, default value is ‘mse’). update_strategy : Update strategy. max_iter : Max number of iterations. batch_size : Batch size. loc_iter : Number of local iterations. seed : Seed.
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifierclass ggml.classification.RandomForestClassificationTrainer(features, env_builder=<ggml.common.LearningEnvironmentBuilder object>, trees=1, sub_sample_size=1.0, max_depth=5, min_impurity_delta=0.0, seed=None) Bases: ggml.classification.ClassificationTrainer
init(features, env_builder=<ggml.common.LearningEnvironmentBuilder object>, trees=1, sub_sample_size=1.0, max_depth=5, min_impurity_delta=0.0, seed=None)¶ Constructs a new instance of RandomForest classification trainer.
features : Number of features. env_builder : Environment builder. trees : Number of trees. sub_sample_size : Sub sample size. max_depth : Max depth. min_impurity_delta : Min impurity delta. seed : Seed.
from sklearn.ensemble import IsolationForestclass sklearn.ensemble.IsolationForest(*, n_estimators=100, max_samples='auto', contamination='auto', max_features=1.0, bootstrap=False, n_jobs=None, random_state=None, verbose=0, warm_start=False)
Install my-project with npm
npm install my-project
cd my-projectTo deploy this project run
npm run deployDownload the dataset used for credit card predictions:
There are several methods for evaluating a machine learning model's performance. In addition to, the most commonly used metric is accuracy. It tells us how many instance are correctly classified among the total records.
However, in scenarios of highly skewed data distributions (such as this one), metrics such as Precision, Recall, F-Score, and AUC are more reliable. This enormous data imbalance can cause highly biased model predictions and poor accuracy results.
Moreover, the Random Forest Classifier algorithm and Multi-layer Perceptron Classifier neural network are best suited for this particular ML application.