Gianni Fenu, Hicham Lafhouli, Giacomo Medda, Giacomo Meloni, Mirko Marras
University of Cagliari
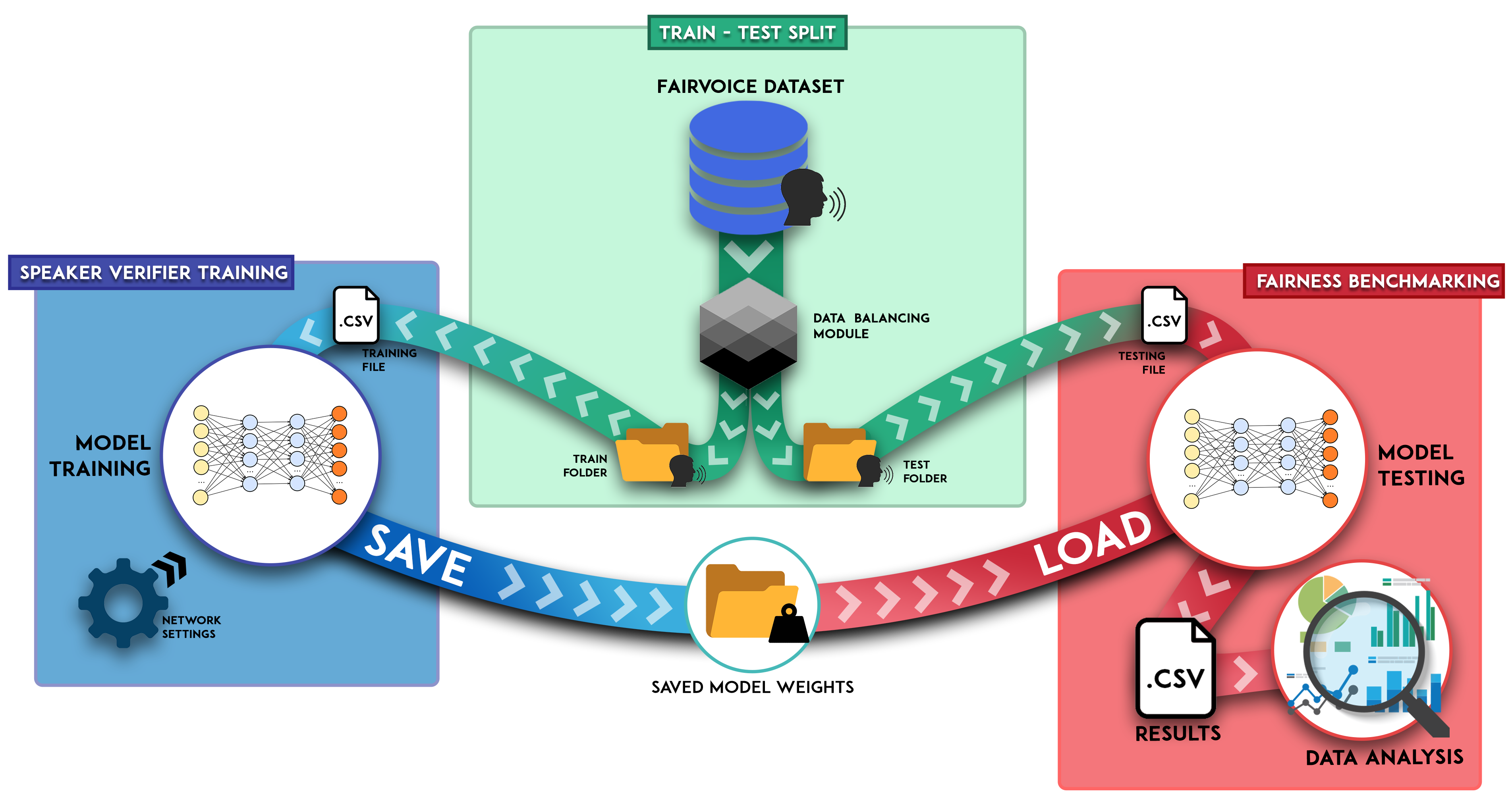
This repository contains a Python framework for bias mitigation analysis in Speaker Verification Models, in order to be able to verify and study what possible solutions may be to reduce the disparities in performance between sensitive categories such as gender and age.
This repository contains the source code of the following articles:
- "Exploring Algorithmic Fairness in Deep Speaker Verification", In Proc. of the International Conference on Computational Science and its Applications (ICSSA2020), Springer.
- "Improving Fairness in Speaker Recognition", In Proc. of the Symposium on Pattern Recognition and Applications (SPRA 2020), Rome.
- Installation
- Fair-Voice Dataset
- Fair-Voice Data Folder Description
- Pre-processing Module
- Models
- Train
- Test
- Experiment Utils
- Reported Results
- Contribution
- Citations
- License
Install Python (>=3.7):
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install python3.7
Install all the requirements needed:
$ pip install -r https://github.com/mirkomarras/fair-voice/blob/master/requirements.txt
Clone this repository:
$ git clone https://github.com/mirkomarras/fair-voice.git
Our work is based on training and testing models using the Fair-Voice Dataset. This dataset was composed by downloading utterances from the Common Voice Mozilla public datasets which can be found here.
The composite dataset was cleaned of any damaged audio tracks and organized by languages with enough samples to allow for proper processing. Subsequently, the audio files originally in MP3 format were converted to WAV format in order to make them suitable for the extraction of the features to be fed to the models.
To download the Fair-Voice dataset click the reported link and follow the steps below:
https://docs.google.com/forms/d/1Et3VxKpG2xKwOF46uT5sZvnTmOMiXYhVkZUJRwL7aFA/prefill
- Fill out the form you find via the link above;
- Download, in the project folder, the zip of the dataset whose link will be provided via email;
- Create the destination folder for the dataset and unzip the folder inside project:
If the unzip command isn't already installed on your system, then run:
$ mkdir FairVoice/ && unzip file.zip -d FairVoice$ sudo apt-get install unzip
- Remove the .zip file:
$ sudo rm file.zip
The Fair-Voice dataset consists of audio samples of 6 languages: Chinese, English, French, German, Kabyle, Spanish. In particular, the Chinese one has been created gathering together the Common Voice datasets Chinese (China) and Chinese (Taiwan), and the Spanish one gathering together the Common Voice datasets Spanish, Basque and Catalan.
The Fair-Voice dataset is organized in folders as follows:
Fair-Voice
| metadata.csv
└───English
| └───id00000
| └───id00001
| └───...
| └───idXXXXX
| | audio00000.wav
| | audio00001.wav
| | ...
└───German
└───...
In the structure above, the audio00001.wav belongs to the user with idXXXXX as id and it is an audio sample in English.
metadata.csv is the file containing the metadata as the name suggests. Each row represents a user described by the following attribues:
- id_user: an ID that identifies uniquely a user of a particular language in the format idXXXXX, e.g. id00001
- hash_user: the hash of the attributes of the user, it can be equal among users of different languages
- language_l1: it is the language of "higher" level or the own language of the user, e.g. Spanish for Basque, Catalan and Spanish or English for only English
- language_l2: it is the language of origin, e.g. "ba" for Basque or "zh-TW" for Chinese (Taiwan)
- gender: the gender of the user, it can be empty
- age: the age group of the user, e.g. teens or fourties, it can be empty
- accent: the accent of the user, e.g. indian for English, it can be empty
- n_sensitive: the number of sensitive attributes provided by the user considering age, gender and accent as sensitive attributes
- n_sample: the number of audio samples of the user
The file ./fairvoice_dataset_manager/dataset_preprocess.py is the Python module that can be imported in your code to prepare the files for the learning process.
It relies on the metadata.csv described above to generate new metadata files from which tbe module can create the train and test files. These new metadata files
can be generated passing some parameters to decide the distribution of female and male users, the distribution of young and old users (a user is considered young if their age
is smaller than the parameter young_cap, old if their age is greater than or equal to the same parameter), the minimum number of audio samples per user et cetera.
The functions of this module that should be used are:
def prepare_fair_voice(metadata="metadata.csv",
encoding="utf-8",
dir_metadata="./FairVoice/metadata",
young_cap=default,
min_sample=5,
group_by_lang=default,
lang_equality=False,
female_male_ratio=default,
young_old_ratio=default,
mode=Modes.MERGE,
tot_test_users=100):This is the function of generation of metadatas. It takes some parameters and creates some metadatas in basis of passed parameters, one metadata for each parameter, so multiple values for each parameter results in a total of metadatas equals to the cartesian product of each value of each parameter. It can creates metadatas where users are distributed in terms of gender for 30% (0.3) of females and 70% (0.7) of males or in terms of age, or both, with or without the equalisation of users in terms of language. ##NOT FULLY IMPLEMENTED##
Parameters:
metadata: the file with the metadata of all the users
encoding: encoding of the csv, they are the same of the built-in "open" function
dir_metadata: directory where the file of metadata is saved
young_cap: array of caps. Each cap determines the age group from which a user is considered "old". If young_cap = ["thirties", "fourties"] two types of metadatas will be created, one where users with an age greater than or equals to thirties are considered old (the others young), and the other one where users with an age greater than or equals to fourties are considered old.
min_sample: it filters all the users taking only the ones with almost the specified minimum of audio samples
group_by_lang: array of the languages that need to be considered. If not specified all languages of the dataset are taken into consideration. If set to None the metadata is processed in basis of the other parameters
lang_equality: if True it creates metadatas with a number of users equal among all the languages of group_by_lang (if group_by_lang is None this value is discarded).
female_male_ratio: an array of couples of ratios with a sum of 1.0. It specifies the proportion of gender in the created metadatas. Default value is [(0.3, 0.7), (0.4, 0.6), (0.5, 0.5), (0.6, 0.4)]. One metadata is created for each value (or more depending on the number of values of the other parameters). First value is for females, the second for males.
young_old_ratio: an array of couples of ratios with a sum of 1.0. It specifies the proportion of age in the created metadatas. Default value is [(0.4, 0.6), (0.5, 0.5), (0.6, 0.4)]. One metadata is created for each value (or more depending on the number of values of the other parameters). First values is for the young, the second for the old.
mode: the following are its possible values:
- distinct: create a csv for each of the value in group_by_lang, female_male_ratio (young_old_ratio and young_cap)
metadata_1.csv = female_male_ratio[0]
...
metadata_n.csv = group_by_lang[0]
metadata_n+1.csv = young_old_ratio[0] for each cap in young_cap
example with young_old_ratio = [(0.3, 0.7)] and young_cap = ["fourties", "fifties"]
metadata_1.csv = labels with (0.3, 0.7) young old ratio where "young" is each row with age < "fourties"
metadata_2.csv = labels with (0.3, 0.7) young old ratio where "young" is each row with age < "fifties" - merge: create a csv for each of the value of the group (female_male_ratio, (young_old_ratio and young_cap)) with the entries of all languages in group_by_lang
metadata_1.csv = all langs in group_by_lang, (female_male_ratio[0], (young_old_ratio[0] and young_cap[0]))
...
metadata_n.csv = all langs in group_by_lang, (female_male_ratio[0], (young_old_ratio[0] and young_cap[0]))
metadata_n+1.csv = all langs in group_by_lang, (female_male_ratio[0], (young_old_ratio[0] and young_cap[1]))
metadata_n+m.csv = all langs in group_by_lang, (female_male_ratio[3], (young_old_ratio[1] and young_cap[1])) - merge_foreach_lang: same behaviour of merge, but taking into account one language at a time. So if "merge" creates N csvs, "merge_foreach_lang" creates N*len(group_by_lang) csvs
- distinct_merge: shortcut to do both merge and distinct at once
- distinct_merge_foreach_lang: shortcut to do both merge_foreach_lang and distinct at once
tot_test_users: This parameter needs an integer value, that is the number of users used for testing. This integer is used to load a file with a name in the form "test_users_LANGUAGE_100" where 100 is the value of tot_test_users. This file contains the users used for testing and it will be created by the function "split_dataset", one for each language. It can be useful when it is necessary to create different metadata with several types of distribution of the users, but maintaining the same users for testing and the users are distributed by this function without losing those users that are present in testing files. Right now is available only in distinct mode and it needs "lang_equality" to be True and "group_by_lang" not to be None.
This function returns the id of the first metadata generated by this function. It can be passed to "split_dataset", which takes all the metadatas present in the file "info_metadata_X_Y" (X is equal to the id returned by this function) and split them in train and test.
def split_dataset(metadata="metadata.csv",
info_start_id=None,
encoding="utf-8",
dir_metadata="./FairVoice/metadata",
dir_dataset="./FairVoice",
test_percentage=0.2,
sample_equality=False,
sample_cap=default,
strong_equality=False,
sample_groups_equality=False,
tot_test_users=None,
test_equality=default,
test_per_lang=False,
load_test_users=False):Function that takes the metadata files generated by "prepare_fair_voice" function and generated the csv files that will be used for testing and training.
Parameters:
metadata: the file with the metadata of all the users
info_start_id: the id of the first metadata from which the split need to start. If "info_start_id" = X then split_dataset will process all the files described in the file "info_metadata_X_Y.csv", so all the files unitl Y will be splitted
encoding: encoding of the csv, they are the same of the built-in "open" function
dir_metadata: directory where the file of metadata is saved
dir_dataset: directory where the dataset is saved
test_percentage: percentage of the dataset to be used for testing
sample_equality: if True it can be used a cap to reduce the number of audio samples considered for each user. The cap is specified by the parameter "sample_cap".
sample_cap: as a dictionary it can be used to specify the cap of audios of each user for each language dataset where the key is the language and the values is the cap, so the audio samples of each user will not be more than the specified value. As an integer it will be used as the cap for every language. This parameter is used only when "sample_equality" is True.
strong_equality: for each group N users are taken for tests. N is chosen in this way:
N * groups = len(dataset) * test_percentage
It can happen that some groups are represented by a number of users less than N. In this situation:
- strong_equality = True ensures the equality of users in the groups for testingchanging the value of N = len(group with least number of users), but the number of users for testing does not satisfy the test_percentage.
- strong_equality = False does not satisfy the equality of users among the groups, and satisfies the test_percentage taking more users from the most represented group
sample_groups_equality: if True the number of audio samples will be equalised among the groups (female old, female young, male old, male young)
tot_test_users: if not None it is equal to the number of users used for testing
test_equality: an array of 3 possible values ["random", "age", "gender"]. For each value a testing file will be generated with the type of balancing chosen. With "random" the couples of audio paths for test are chosen randomly, with "age" the couples are balanced by age and with "gender" the couples are balanced by gender.
test_per_lang: if True the audio paths couples used for testing will be separated in multiple files depending on the language of the users, so each testing file will have couples among users of the same language
load_test_users: if True the users used for testing are loaded from the files or the users chosen for testing will be saved at the end of the function if "tot_test_users" is None
This function does not return anything.
Based on the work done by our previous studies, we have made available a set of pre-trained models that can be downloaded here. In this link you can find all the models trained from our two previous studies:
- trained_model_iccsa ("Exploring Algorithmic Fairness in Deep Speaker Verification") [Thin-ResNet34];
- trained_model_spra ("Improving Fairness in Speaker Recognition") [Thin-ResNet34, X-Vector].
Each model needs to be copied into the appropriate folder ./exp/trained_model/.
This toolbox allows you to train a speaker model from scratch. For instance, a Thin-ResNet model can be trained by running the following script and indicating the specific type of speaker model to train:
$ python3 ./src/train.py --net resnet34voxIt is necessary to specify the CSV file that indicates at the script which audio file use for training. These .CSV files are stored in ./exp/train/ folder. For instance:
$ python3 ./src/train.py --train_csv_path ./exp/test/English-train1.csv"As we have seen, various parameters can be initialized for this script:
$ python train.py --train_csv_path "Path of the csv file that you want to use for train"
--audio_dir "Path of the directory that contains all the audio file"
--net "Network architecture. Possible choices: [resnet34vox , xvector , resnet50vox , vggvo]"
--n_epochs "Number of epochs"
--batch "Batch size"
--learning_rate "Learning rate "
--decay_factor "Decay factor"
--decay_step "Decay step"
--loss "Loss"
--aggregation "Aggregation strategy"
--vlad_cluster "Number of Vlad Cluster"
--ghost_clusters "Number of Ghost Cluster"
It is possibile to customize the default choice for this parameters by modify the train script changing the default parameter, in order to optimize the use of the script:
parser.add_argument('--net', dest='net', default='resnet34vox', type=str, action='store', help='Network model architecture')The training script will save the model each epoch in ./exp/trained_model/ in a folder with the following formatting name:
NETWORK-NAME_DDMMYYYY_hh:mm_INFO-DATASET
Inside each folder is saved a "model.h5" file per epoch.
This toolbox manage several speaker verification models:
| Model | Input | Shape |
|---|---|---|
| ResNet34vox (Thin-ResNet) | Spectrogram | (256,None,1) |
| X-Vector | Filter-banks | (None,24) |
| ResNet50vox | Spectrogram | (256,None,1) |
| VggVox | Spectrogram | (256,None,1) |
This toolbox provides a script to test a pre-trained model in order to elaborate subsequently different metrics on the basis of the results. For instance, a Thin-ResNet model can be tested by running the following script and indicating the specific type of speaker model to train and the path of the pre-trained model:
$ python3 ./src/test.py --net resnet34vox --model_path "./exp/trained_model/resnet34vox_18062020_2334_English-Spanish-train3/weights-15-0.993.h5"It is necessary to specify the CSV file that indicates at the script which audio file use for testing. These .CSV files are stored in ./exp/test/ folder. For instance:
$ python3 ./src/test.py --test_file ./exp/train/English-test1.csv"As we have seen, various parameters can be initialized for this script:
$ python test.py --net "Network architecture. Possible choices: [resnet34vox , xvector , resnet50vox , vggvo]"
--test_file "Path of the csv file that we want to use for our tests"
--audio_dir "Path of the directory that contains all the audio file"
--model_path "Path of the h5 file saved frome the training session and used to load the model"
--aggregation "Aggregation strategy"
It is possibile to customize the default choice for this parameters by modify the test script changing the default parameter, in order to optimize the use of the script:
parser.add_argument('--net', dest='net', default='resnet34vox', type=str, action='store', help='Network model architecture')Every test will save a .CSV file in the folder ./exp/results/ with the following format:
NETWORK-ARCHITECTURE_INFO-DATASET-TRAIN_ACCURACY_DDMMYYYY_hh:mm_INFO-DATASET-TEST
Every result file contains the following information:
> audio1 path of the first audio utterance
> audio2 path of the second audio utterance
> age1 age info of the first speaker ('young' <= 40yo, 'old' > 40yo)
> age2 age info of the second speaker ('young' <= 40yo, 'old' > 40yo)
> gender1 gender info of the first speaker ('male', 'female')
> gender2 gender info of the second speaker ('male', 'female')
> label expeted result
> similarity predicted result
Our framework allows, on the basis of the results processed, to calculate a series of metrics useful for comparing the performance of the trained models, especially from the point of view of the disparity between the sensitive categories considered (gender, age).
All the scripts related to these calculations are inside the ./exp_utils/ folder.
To compare the performance of the trained models using metric like EER (Equal Error Rate), FAR (False Acceptance Rate), FRR(False Rejection Rate), both in general and individually for each group of users (male, female, young, old), it is possible to use the script exp_utils.py:
$ python exp_utils.pyThe script takes two different parameters:
$ python exp_utils.py --result_path "Results folder path"
--dest_folder "Destination path to save the computed metrics"
By default the result path is set in ./exp/results/ folder.
The script processes all .CSV files inside the results folder and return as output three .CSV files (EER.csv, FAR.csv, FRR.csv) with all the calculated metrics for each result file.
By default the metric file is stored inside ./exp/metrics/. Each time this script is run, the contents of this folder are deleted and all results currently contained in the result folder are retried.
In every metric file are specified common information concerning the architecture, the train and test datasets used for experiments and finally the accuracy of the considered model.
> Architecture path of the first audio utterance
> Train File path of the second audio utterance
> Test File age info of the first speaker ('young' <= 40yo, 'old' > 40yo)
> Accuracy age info of the second speaker ('young' <= 40yo, 'old' > 40yo)
Based on the metric, information about the general performance and the performance of the individual sensitive categories will then be reported for each result file.
Thanks to the script statistic_distribution.py it is possible to check if the reported results present a similar distribution between two categories results in order to understand if the results are co-related or not.
A supporting .JSON file named 'path_best_results.json' is used to process a specific set of results: inside it the paths of the best results to be compared are inserted, divided by defined tests.
{
"English-test1": [
"/home/meddameloni/dl-fair-voice/exp/results/xvector_English-train1_991_11062020_English-test1.csv",
"/home/meddameloni/dl-fair-voice/exp/results/xvector_English-train2_962_11062020_English-test1.csv"
],
"English-test2": [
"/home/meddameloni/dl-fair-voice/exp/results/xvector_English-train1_969_11062020_English-test2.csv",
"/home/meddameloni/dl-fair-voice/exp/results/xvector_English-train2_987_11062020_English-test2.csv"
]
}Once this file has been defined, it will be possible to execute the script by specifying one of the following parameters:
$ python statistic_distribution.py --eer statistical correlations are processed regarding EER results
--far statistical correlations are processed regarding FAR results
--frr statistical correlations are processed regarding FRR resultsDepending on your preference, statistical correlations will be calculated based on a specific metric. These processing are done only on the files specified in the JSON.
If the processing is done for EER a .CSV file is generated in the output folder ./exp/statistics/ where for each result file it is specified whether the results of the related sensitive categories are statistically similar with a 'Y' or an 'N'.
If the processing is done for FAR or FRR then a .CSV file is generated in the output folder ./exp/statistics/ where for each result file it is specified what we said above and the report of total cases by sensitive category grouped by user is added.
Before introducing the script that can evaluates the statistical relation between the audio sample, it is necessary to describe
the sample_info files, that is a type of file generated by the script ./exp_utils/audio_info.py which takes train or test files and generates csv files of average characteristics of audio samples of each group.
These sample_info files are taken as input by the script for the audio features similarities.
The script for the generation of sample_info files provides two functions that can be used to generate this type of files:
def sample_group_info(source,
type_file=None,
metadata="/home/meddameloni/FairVoice/metadata/metadata.csv",
dataset_dir="/home/meddameloni/FairVoice",
distinct_group=False,
young_cap="fourties"):This function takes users from different sources and returns a csv file with the average of several audio info of the audios of each user
Parameters:
source: file containing data (list of users, train file, test file, dataframe)
type_file: type_file controls which users are considered for audios, if it is not None users are taken from "train" or "test" files
metadata: file containing metadata of the users if source is not a dataframe
dataset_dir: base directory of audio files
distinct_group: if true returns info of audios of each user considering the distinct group "female", "male", "old", "young", so each user is present 2 times in the output file. if false returns info of audios of each unique group, so "female old", "female young", "male old", "male young"
young_cap: this should be the same value used to generate train and test files. It is not re-written in other files, so it needs to be given manually as input
This function does not return anything.
def sample_group_info_groupby(sample_info_file):This function should should be used on a "sample_info_file", that is the file generated from the function "sample_group_info". It returns a csv file containing the average of the audio info for each group, so a csv file with only 4 rows.
Parameters:
sample_info_file: the sample info file given in input containing the average of the audio info of all the audios of each user
This function does not return anything
The function sample_group_info is the one that creates the sample_info files that should be given in input to the
script ./exp_utils/statistic_measures.py, which evaluates the statistical relation between the audio files of each group with "paired T-test" where each group can be one of female_old, female_young, male_old, male_young.
statistic_measuers.py creates a txt file specifying if the audio files of the two groups have the same distribution or not. The variable out_path can be modified to set the path where the output txt files will be saved.
The script can be executed with the following command:
$ python3 statistic_measures.py SAMPLE_INFO_FILE_PATHAll results reported in the "Improving Fairness in Speaker Recognition" study are uploaded online and are freely accessible on Google Drive.
You can consult the results and download the .CSV files used both for train and test tasks and read the .CSV results files. The folders are structured as follow:
In this folder you can find all the .CSV files concerning the metrics for every test done in our experiments. The .CSV structure is composed as follows:
- EER.csv: in this file are collected all the results in terms of Equal Error Rate of every test done. The metric it's been calculated both for overall groups and for singular sensitive category group independently.
| Architecture | Train File | Test File | Accuracy | EER | EER M. | EER F. | EER Y. | EER O. |
|---|
- FAR.csv: in this file are collected all the results in terms of False Acceptance Rate of every test done. The metric it's been calculated both for overall groups and for singular sensitive category group independently.
| Architecture | Train File | Test File | Accuracy | FAR | FAR M. | FAR F. | FAR Y. | FAR O. |
|---|
- FRR.csv: in this file are collected all the results in terms of False Rejection Rate of every test done. The metric it's been calculated both for overall groups and for singular sensitive category group independently.
| Architecture | Train File | Test File | Accuracy | FRR | FRR M. | FRR F. | FRR Y. | FRR O. |
|---|
In this folder are collected all the results stored after the tests. The .CSV file containing these results is structure as follows:
| audio 1 | audio 2 | age 1 | age 2 | gender 1 | gender 2 | label | similarity |
|---|
audio 1 > path of the first utterance
audio 2 > path of the second utterance
age 1 > age of the first speaker
age 2 > age of the second speaker
gender 1 > gender of the first speaker
gender 2 > gender of the second speaker
label > expected result
similarity > predicted result
This folder contains the results of the similarity measurements between the various results based on the reference metric (EER, FAR, FRR).
- statistic_distribution_rel.csv: this file indicates, for each results file, whether there are statistical correlations between the results of male and female and young and old categories considering EER metric.
| Test File | Network | Train File | Accuracy | Distribution M/F | Distribution Y/O |
|---|
- statistic_distribution_FAR.csv: this file indicates, for each results file, whether there are statistical correlations between the results of male and female and young and old categories considering FAR metric. This report contains the singol FAR ratio for each category group.
| Test File | Network | Train File | Accuracy | Count M FAR | Count F FAR | Count Y FAR | Count O FAR | Stats Correl M/F | Stats Correl Y/O |
|---|
- statistic_distribution_FRR.csv: this file indicates, for each results file, whether there are statistical correlations between the results of male and female and young and old categories considering FRR metric. This report contains the singol FAR ratio for each category group.
| Test File | Network | Train File | Accuracy | Count M FRR | Count F FRR | Count Y FRR | Count O FRR | Stats Correl M/F | Stats Correl Y/O |
|---|
Supporting .csv files are saved in this folder to tell the model which audio files to use for testing. The structure of these .csv files is structured as follows:
| audio 1 | audio 2 | age 1 | age 2 | gender 1 | gender 2 | label |
|---|
Supporting .csv files are saved in this folder to tell the model which audio files to use for training. The structure of these .csv files is structured as follows:
| audio 1 | label |
|---|
This code is provided for educational purposes and aims to facilitate reproduction of our results, and further research in this direction. We have done our best to document, refactor, and test the code before publication.
If you find any bugs or would like to contribute new models, training protocols, etc, please let us know.
Please feel free to file issues and pull requests on the repo and we will address them as we can.
Fenu, G., Lafhouli, H. and Marras, M. (2020).
Exploring Algorithmic Fairness in Deep Speaker Verification.
In: International Conference on Computational Science and its Applications (ICSSA2020)
Fenu, G., Marras, M., Medda, G. and Meloni, G. (2020).
Improving Fairness in Speaker Recognition.
In: Symposium on Pattern Recognition and Applications (SPRA 2020)
This code is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but without any warranty; without even the implied warranty of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. See the GNU General Public License for details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this source code. If not, go the following link: http://www.gnu.org/licenses/.