Vehicle Detection Project
The goals / steps of this project are the following:
- Perform a Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG) feature extraction on a labeled training set of images and train a classifier Linear SVM classifier
- Apply a color transform and append binned color features, as well as histograms of color, to the HOG feature vector.
- Implement a sliding-window technique and use the trained classifier to search for vehicles in images.
- Run the pipeline on a video stream (start with the test_video.mp4 and later implement on full project_video.mp4) and create a heat map of recurring detections frame by frame to reject outliers and follow detected vehicles.
- Estimate a bounding box for vehicles detected.
Rubric Points
###Here I will consider the rubric points individually and describe how I addressed each point in my implementation.
###Writeup / README
####1. Provide a Writeup / README that includes all the rubric points and how you addressed each one. You can submit your writeup as markdown or pdf. Here is a template writeup for this project you can use as a guide and a starting point.
You're reading it!
The code is fully contained in the IPython notebook.
###Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG)
####1. Explain how (and identify where in your code) you extracted HOG features from the training images.
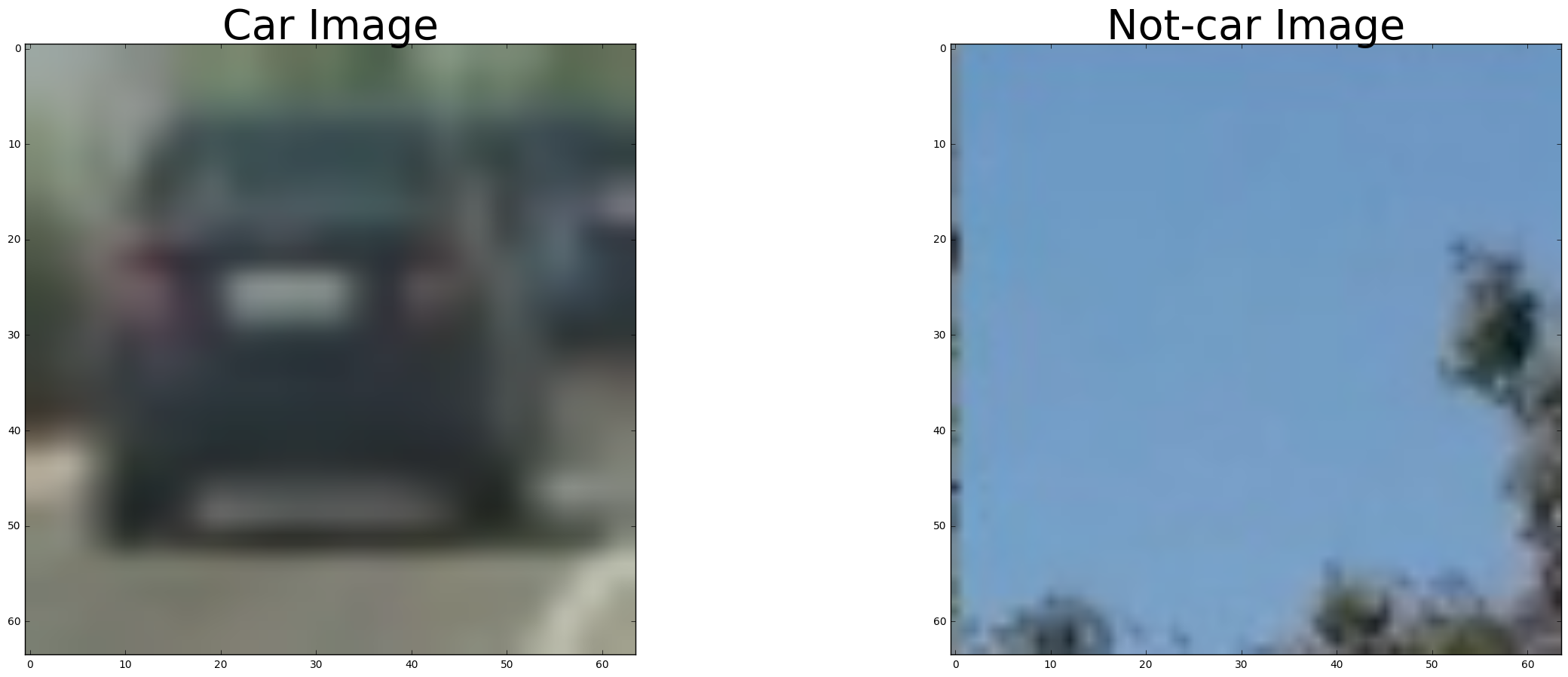
The first cell of the notebook contains some utility code for loading training data and displaying image plots in the notebook. This code simply reads in all the vehicle and non-vehicle images from the training set. Here is an example of one of each of the vehicle and non-vehicle classes:
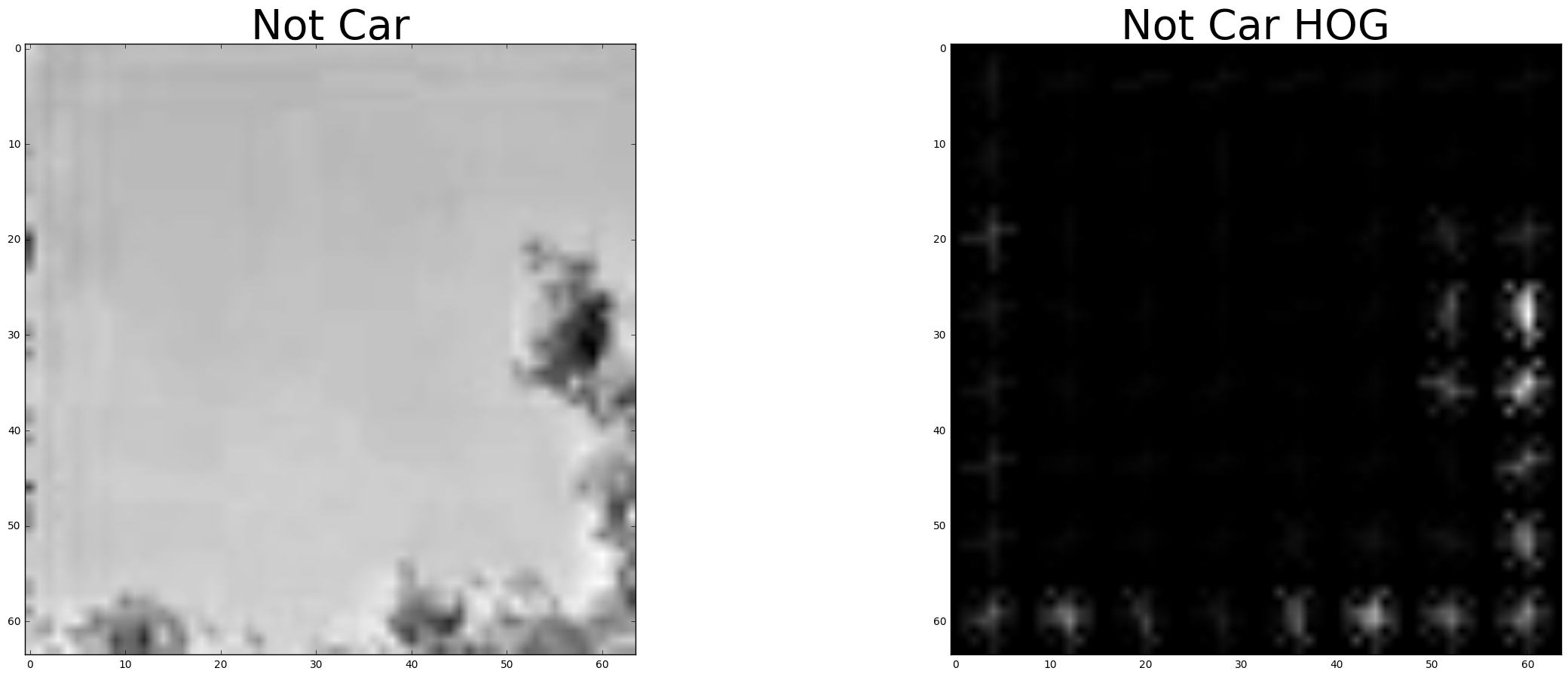
The next cell in the notebook explores different color spaces and different skimage.hog() parameters (orientations, pixels_per_cell, and cells_per_block). Random images from each of the two classes are displayed along side the hog visualization image to see what the output looks like.
Here is an example of each a car and non-car using the YCrCb color space and HOG parameters of orientations=9, pixels_per_cell=(8, 8) and cells_per_block=(2, 2):
####2. Explain how you settled on your final choice of HOG parameters.
Various combinations of parameter settings were used to train the SVM classifier with the extracted features from the training data. The accuracty of the classifier was evaluated for the test set. The parameters that gave the best test set accuracy were used for the remainder of the project.
####3. Describe how (and identify where in your code) you trained a classifier using your selected HOG features (and color features if you used them).
The third code cell of the notebook contains code to train the linear SVM classifier. The HOG, binned color features as well as the color histogram features were extracted and appended into one feature vector for each image in the training set. The extracted features were scaled before training the classifier.
99.21% was the best accuracy achieved by the classifier on the test data set.
###Sliding Window Search
####1. Describe how (and identify where in your code) you implemented a sliding window search. How did you decide what scales to search and how much to overlap windows?
The "HOG subsampling window search" technique from the lesson notes was used pretty much as is. Only a few modifications were used to make it easier to debug and then actually fix bugs in the original code. The fourth cell of the notebook contains the sliding window search implementation.
The technique involves generating the HOG for the entire input image then iterating through the set of search windows defined by input parameters. Features for each search window of the input and HOG images were fed into the SVM classifier to determine which regions of the input were classified as a vehicle. The rect for each window classified as a vehicle was accumulated in a list and returned as the result of the search process. The search region of the input images was limited to y-values between 350 and 675 pixels since pixes outside this range would never contain vehicles.
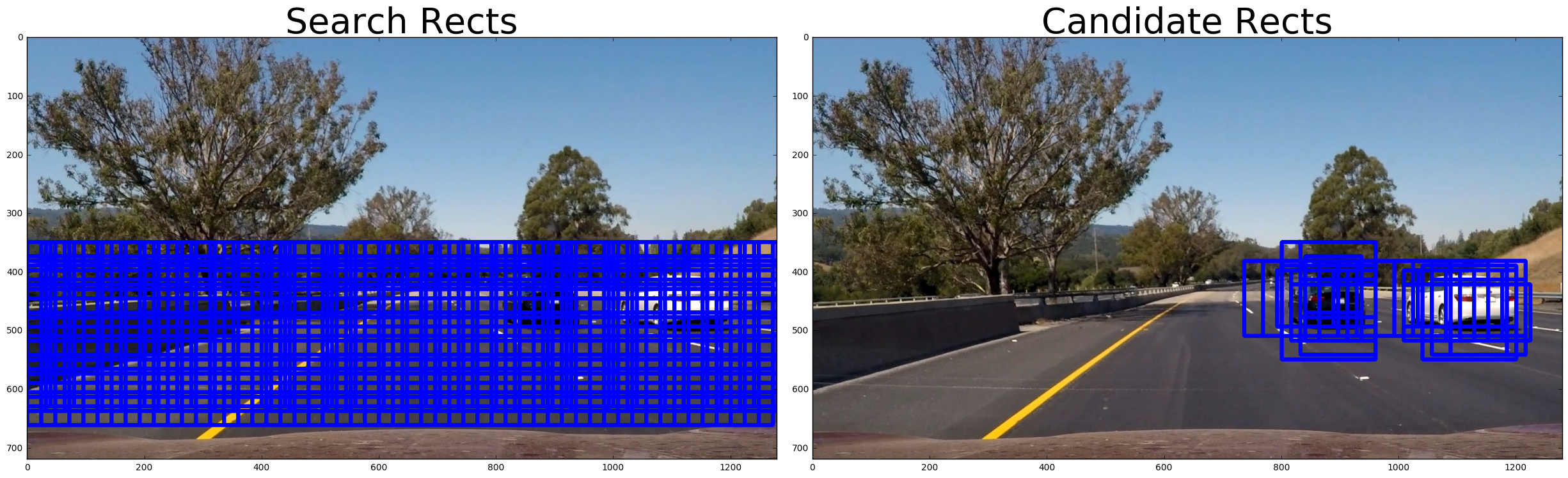
A debug mode would return all search window rects in order to help visualize what part of the image was being searched. Here is an example of the debug output of all search windows on the left and on the right are the search windows that were classified as cars:
This search process is repeated for various scales in order to detect vehicles at varying distances from the camera. The final detection algorithm used scales 1.5, 2 and 2.5. This seemed to be a good balance between performance and accuracy. This code is in the next (fifth) code cell of the notebook.
####2. Describe how (and identify where in your code) you implemented some kind of filter for false positives and some method for combining overlapping bounding boxes.
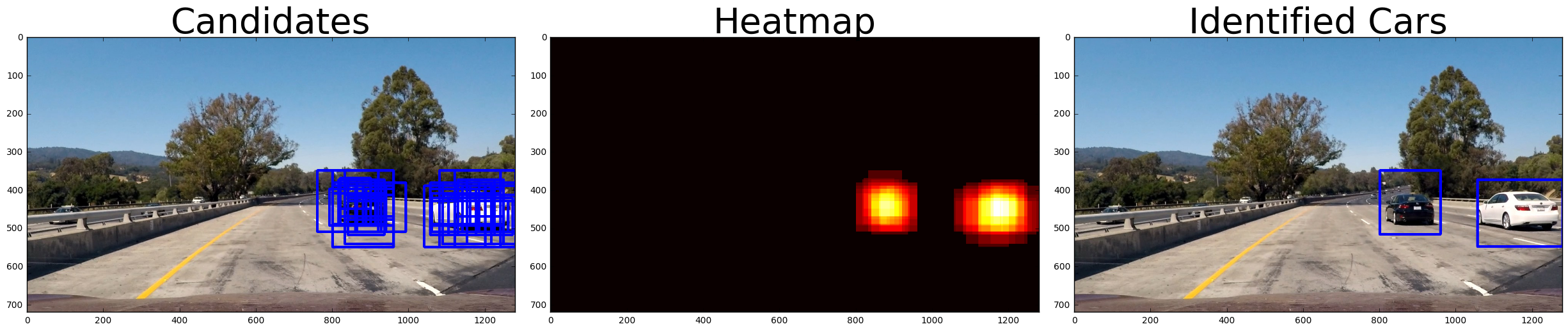
All rects for cars detected at each of the various scales were collected into one array. At this point it was necessary to filter outliers using a heatmap approach. Each detected car rect was added to a heatmap which was then thresholded such that any region with less than 2 detections was removed. The final bounding rects was drawn around each blob remaining in the heatmap after thresholding.
####3. Show some examples of test images to demonstrate how your pipeline is working. What did you do to optimize the performance of your classifier?
The final algorithm searchs 3 scales of the YCrCb 3-channel HOG features plus spatially binned color and histograms of color in the feature vector, which provided a decent result. Here are some example images showing the input image, the heatmap and finally the identified car rects:
####1. Provide a link to your final video output. Your pipeline should perform reasonably well on the entire project video (somewhat wobbly or unstable bounding boxes are ok as long as you are identifying the vehicles most of the time with minimal false positives.)
Here's a link to the video result
###Discussion
####1. Briefly discuss any problems / issues you faced in your implementation of this project. Where will your pipeline likely fail? What could you do to make it more robust?
This approach seems to work ok. The end result could definitely use some smoothing so that it doesn't jump around from frame to frame so much. The main drawbacks of this algorithm are performance, accuracy and complexity. One alternative idea that would have been more interesting and consistent with the middle portion of the term 1 course content would have been to use a conv net to remove the sensitivity of the variations of scale of cars in the input images. This is one of the strenghts of conv net image classification and was surprised with the sliding window approach (though it was interesting nonetheless).