Dependency-free purrr-like apply/map/iterate functions
Install the development version from Github with:
## install remotes pkg if not already
if (!requireNamespace("remotes", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("remotes")
}
## install from github
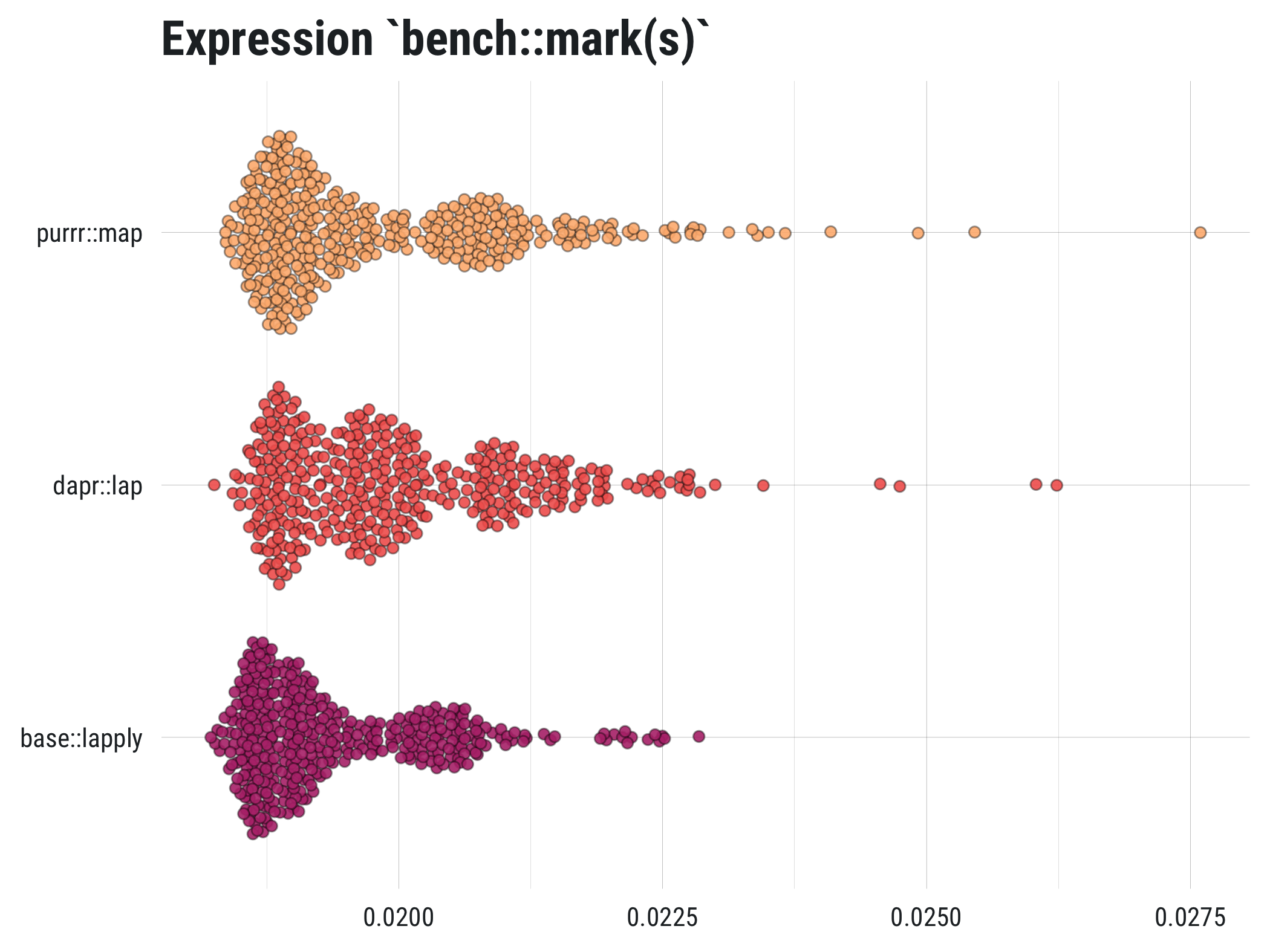
remotes::install_github("mkearney/dapr"){dapr} provides the ease and consistency of
{purrr}, (see also: simple benchmark
results plot below) including use of ~ and .x, without all the
dependencies. In other words, use {dapr} when you want a purrr-like
experience but you need a lightweight solution.
Function names use the convention *ap() where * is the first
letter of output data type.
vapfor vectorslapfor listsdapfor data frames
Common inputs:
.dataInput object–numeric, character, list, data frame, etc.–over which elements will be iterated. If matrix or data frame, each column will be treated as the elements which are to be iterated over..fFunction to apply to each element of input object. This can be written as a single function name e.g.,mean, a formula-like function call where.xis assumed to be the iterated over element of input data e.g.,~ mean(.x), or an in-line function definition e.g.,function(x) mean(x).
Functions that apply expressions to input data objects and return atomic vectors e.g., numeric (double), character, logical.
vap_dbl()Iterate and return numeric vector.vap_int()Iterate and return integer vector.vap_lgl()Iterate and return logical vector.vap_chr()Iterate and return character vector.
## create data
set.seed(2018)
d <- replicate(5, rnorm(10), simplify = FALSE)
e <- replicate(5, sample(letters, 10), simplify = FALSE)
## numeric
vap_dbl(d, ~ mean(.x))
#> [1] 0.26934527 -0.55232322 0.05559290 -0.06253258 -0.11183760
## integer
vap_int(d, length)
#> [1] 10 10 10 10 10
## logical
vap_lgl(d, ~ max(.x) > 3)
#> [1] FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE
## character
vap_chr(e, paste, collapse = "")
#> [1] "hizjpgcexk" "rbeovimtxh" "ujrimwgvzs" "euwrlytgbj" "qkrhylgmnx"Function(s) that apply expressions to input data objects and return lists.
lap()Iterate and return a list vector.
## list of strings
lap(e[1:2], ~ paste0(.x, "."))
#> [[1]]
#> [1] "h." "i." "z." "j." "p." "g." "c." "e." "x." "k."
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] "r." "b." "e." "o." "v." "i." "m." "t." "x." "h."ilap()Iterate over sequence length.i(instead of.x) and return a list vector.
## list of strings
ilap(1:4, ~ paste0(letters[.i], rev(LETTERS)[.i]))
#> [[1]]
#> [1] "aZ"
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] "bY"
#>
#> [[3]]
#> [1] "cX"
#>
#> [[4]]
#> [1] "dW"Functions that apply expressions to input data objects and return data frames.
dap*()Iterate and return a data framedapc()Iterate over columnsdapr()Iterate over rows
dap*_if()Conditionally iteratedapc_if()Conditionally iterate over columnsdapr_if()Conditionally iterate over rows
## some data
d <- data.frame(
a = letters[1:3],
b = rnorm(3),
c = rnorm(3),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE
)
## column explicit (same as dap)
dapc(d[-1], ~ round(.x, 2))
#> b c
#> 1 -0.50 -0.09
#> 2 -1.87 1.08
#> 3 0.74 -1.36
## rows
dapr(d[-1], round, 3)
#> b c
#> 1 -0.499 -0.089
#> 2 -1.869 1.081
#> 3 0.743 -1.365
## conditional COLUMNS
dapc_if(d, is.numeric, ~ round(.x, 4))
#> a b c
#> 1 a -0.4994 -0.0892
#> 2 b -1.8686 1.0812
#> 3 c 0.7434 -1.3646
## conditional ROWS
dapr_if(d[-1], ~ sum(.x) >= -.7, ~ round(.x, 0))
#> b c
#> 1 0.000000 0.000000
#> 2 -1.868615 1.081164
#> 3 1.000000 -1.000000