This repo provides the lab materials for class CSCI 5854 (Foundations of Autonomous Systems), University of Colorado Boulder, USA. The lab software includes the following suite of tools:
- SCOTS: a tool for abstraction-based controller synthesis
- OmegaThreads: a tool for controller synthesis from omega-regular specifications
To install the required software, we build and use s Docker image. First, make sure you have docker installed (see Docker installation guide for: MacOS, Ubuntu Linux or Windows). Also, make sure to configure Docker to use sufficient resources (e.g., enough CPU cores). Otherwise, OmegaThreads will run slower than expected.
Here, we assume you will be using a Linux or MacOS machine. Commands will be very similar on Windows if you use Windows PowerShell.
The following steps builds the required Docker image:
$ git clone https://github.com/mkhaled87/CSCI5854_lab
$ cd CSCI5854_lab$ docker build -t csci5854/latest .Building the Docker image may take up to 30 minutes and you may recieve some messages in red. Ignore the red-messages unless they are errors that stop the building process.
- For MacOS or Linux Docker hosts, run:
$ docker run -it -v ~/docker_shared:/docker_shared csci5854/latest- For Windows Docker hosts, run:
> docker run -it -v C:\docker_shared:/docker_shared csci5854/latestNote that we run the docker container and share a volume (i.e., a folder) between it and the host. In case of MacOS or Linux Docker hosts, the shared folder is located in the at: ~/docker_shared. In case of Windows Docker hosts, the shared folder is located in the at: C:\docker_shared.
You need to have MATLAB installed in your host machine (not inside the Docker container) to be able to simulate the controllers resulting from SCOTS. You need to also have a C++ compiler compatible with MATLAB. Check this guide to configure MATLAB's mex compiler with your compatible C++ compiler. For Windows, this guide is tested with Microsoft Visual Studio 2019 Comunity Edition. For MacOS/Linux, this guide is tested with Gcc/G++ and Clang/Clang++. Now, follow the steps below to get the interface installed:
- Open MATLAB.
- Navigate from inside Matlab to the folder ./scots-matlab.
- Run the Matlab script file: Install.m.
You need first to have Python 3.5+ installed. You need also the python package installer (pip). Then, install the following required python packages: Arcade and Parglare. Start a terminal window and run:
$ pip install arcade parglareFor Linux, you may need an additional package (dataclasses):
$ pip install arcade dataclassesNow you need to add the simulation interface to Python search Path:
- For MacOS/Linus, add the following line to your shell profile file (we assume you cloned the repo in /home/X/CSCI5854_lab, change it accordingly):
export PYTHONPATH="${PYTHONPATH}:/home/X/omegathreads-python"- For Winodws (PowerShell) (we assume you cloned the repo in C:\CSCI5854_lab, change it accordingly):
> $env:PYTHONPATH = "C:\CSCI5854_lab\omegathreads-python\"The Python interface of OmegaThreads doesn not need to be built. You will directly call Python modules from inisde the folder ./omegathreads-python/.
We run an example to test the installtion of SCOTS and its simulation inrerface. We assume you ran and enered the Docker ciontainer. Navigate to the vehicle example in SCOTS's examples directory:
/# cd /scots/examples/hscc16/vehicle1For SCOTS each example needs to be built separately as SCOTS itself is a header-only library. Build the example:
/# makeRun the example's binary:
/# ./vehicleThe last command will run SCOTS to synthesize a controller for an autonomous vehicle. The complete details about the example (e.g., vehicle dynamics, the arena, and design requirements) are given in the example source file vehicle.cc in the example's folder. Once SCOTS finiishes synthesizing the controller, copy the generated files (.BDD files) and the simulation script to the shared Docker folder:
/# cp *.bdd /docker_shared/
/# cp vehicle.m /docker_shared/Now, keep the terminal open and open MATLAB in your host machine. Navigate to the shared Docker folder (C:\docker_shared in windows, or ~/docker_shared/ in MAcOS/Linux). You should see the copied files from the Docker container. Run the MATLAB script (vehicle.m) from inside the MATLAB command line to start the simulation:
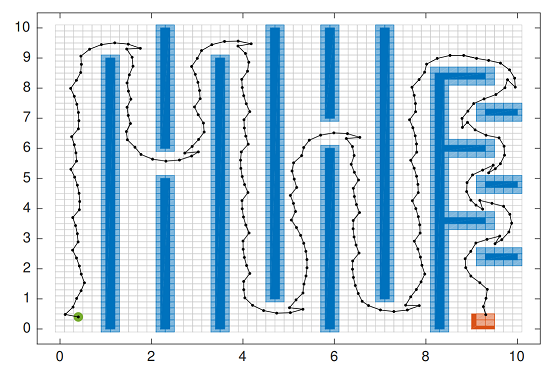
>> vehicle.mIn Windows, generating the simulation results can take up to 10 minues. MATLAB should then show a figure of the vehicle's arena and the path the vehicle should take to avoid some obstacles before reaching a target. The figure should look like:
We run an example to test the installtion of OmegaThreads and its simulation inrerface. We assume you ran and enered the Docker ciontainer. Navigate to the Pickup-Delivery drone example in OmegaThreads's examples directory:
/# cd /pFaces-OmegaThreads/examples/pickupdeliveryRun the example:
/# oclgrind sh solve.shThe last command will run OmegaThreads to synthesize a controller for a Pickup-Delivery drone whose requirements is given in linear temporal langiage (LTL) fomulae. The complete details about the example (e.g., the drone dynamics, the arena, and LTL formula of the design requirements) are given in the example configuration file pickupdelivery.cfg in the example's folder. Once OmegaThreads finiishes synthesizing the controller, copy the generated files and the simulation script to the shared Docker folder:
/# cp pickupdelivery.cfg /docker_shared/
/# cp pickupdelivery.mdf /docker_shared/
/# cp drone.png /docker_shared/
/# cp simulate.py /docker_shared/
/# cp ../../interface/python/*.py /docker_shared/
/# cp $PFACES_SDK_ROOT/../interface/python/*.* /docker_shared/Now, without closing the running docker container, start a new terminal on the host and simulate the controller (we navigate to the shared Docker folder first):
For MacOS/Linux:
$ cd ~/docker_shared
$ python3 simulate.pyFor Windows:
> cd C:\docker_shared
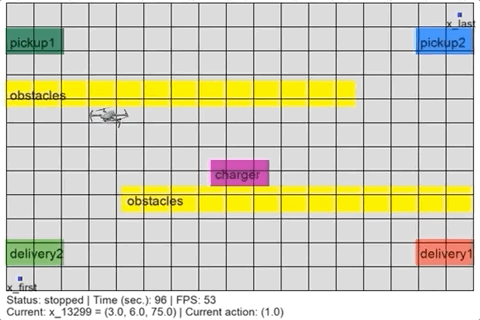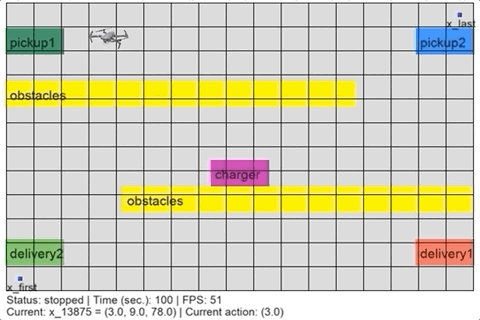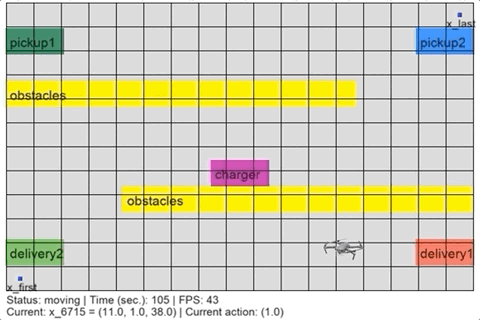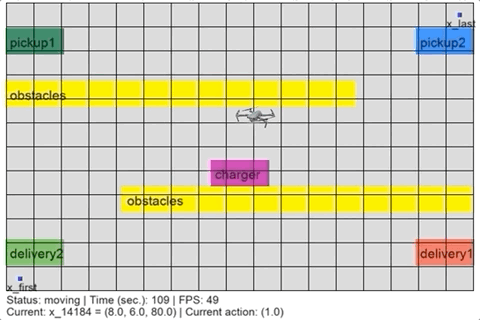
> python simulate.pyThe simulation script should show a figure like: