terraform-riak allows you to provision a Riak KV or a Riak TS cluster on AWS with a single Terraform command. You can also provision a separate instance pre-configured with the Python, Java and Erlang clients.
You will need to create an AWS SSH key pair as well as a set of access keys. Please note that AWS SSH keys are region-specific, and that terraform-riak defaults to the US-East (N. Virginia) region.
Set the following environment variables accordingly:
$ export KEY_PATH=[PATH_TO_AWS_SSH_KEY]
$ export AWS_ACCESS_KEY=[AWS_ACCESS_KEY]
$ export AWS_SECRET_KEY=[AWS_SECRET_KEY]For example:
$ export KEY_PATH=$HOME/.ssh/aws-us-east.pem
$ export AWS_ACCESS_KEY=AKIAI3MEITMDDTB00000
$ export AWS_SECRET_KEY=b/keH4gFgERz12K3Eai7Q+zGZG8PJ1f4Oy100000Terraform swallows error messages - so you get something like "doesn't work, meh" so it is best to ensure that your AWS user and security stuff is correct and lets you connect to boxes before trying to use terraform.
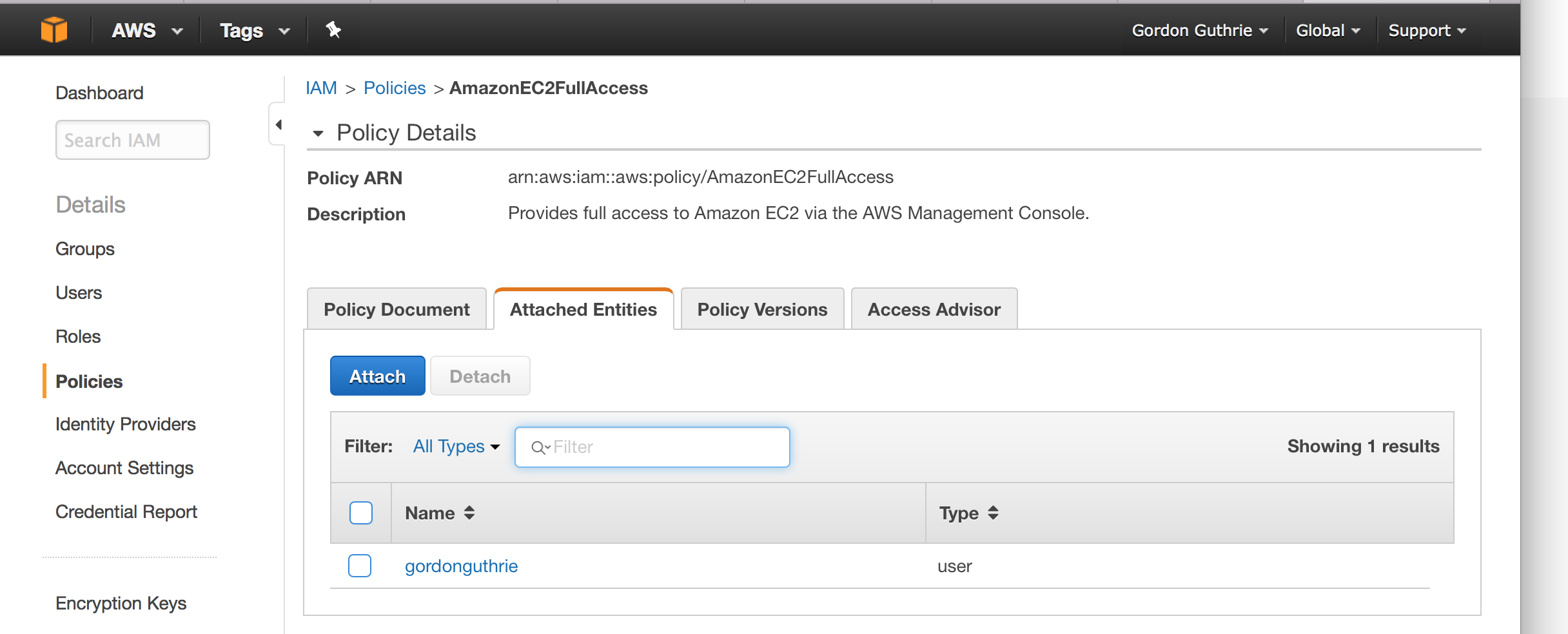
Give that user access to do stuff on the box with a security policy - AmazonEC2FullAccess is the brute force one:
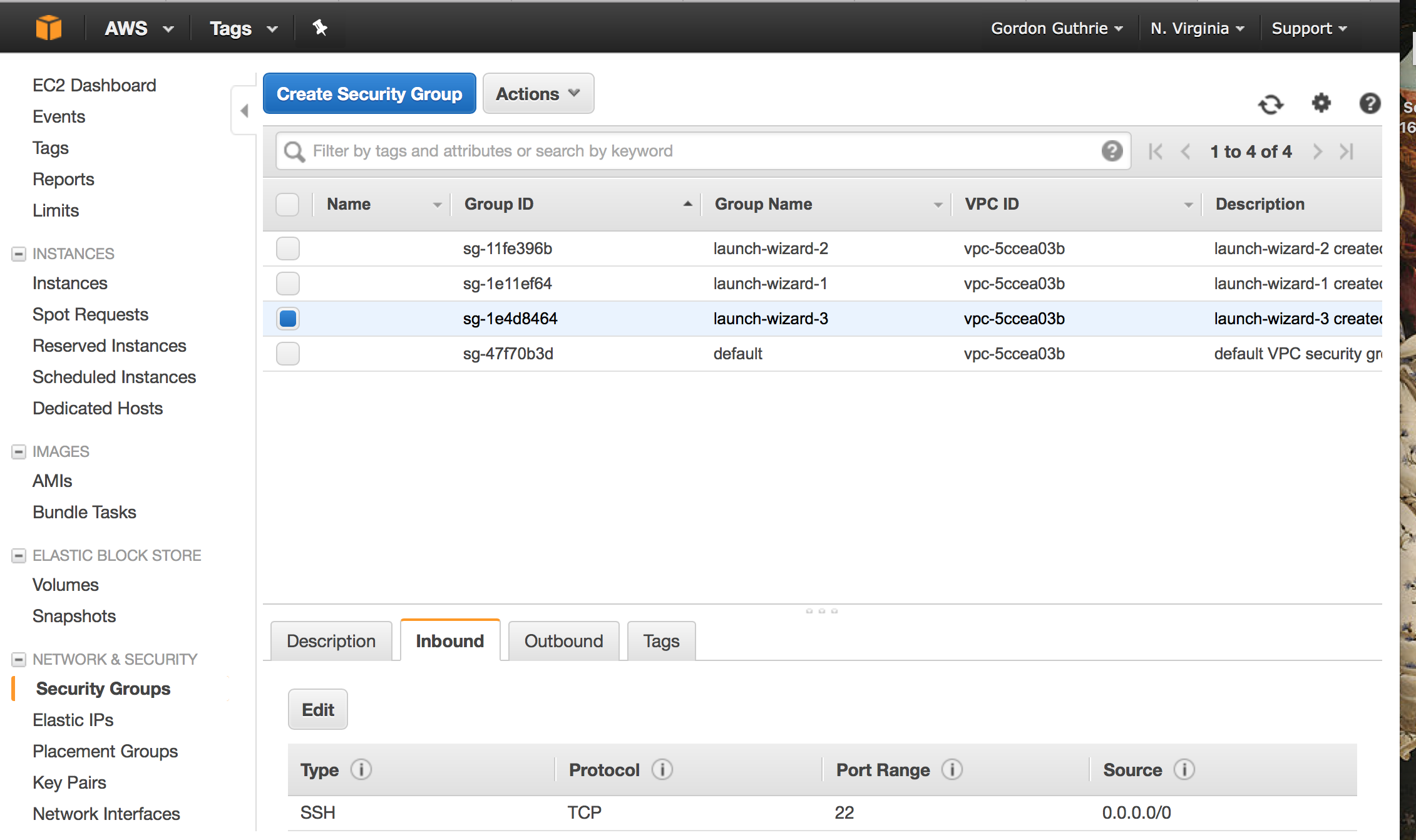
But you also need to 'wire up' the instances to make them visible to the outside world via Security Groups:
The repo includes a Vagrantfile for your convenience. The OS used by Vagrant can be set using the VAGRANT_OS environment variable (set to UBUNTU or CENTOS).
$ git clone https://github.com/basho-labs/terraform-riak.git
$ cd terraform-riak
$ export VAGRANT_OS=UBUNTU
$ vagrant plugin install vagrant-env
$ vagrant up
$ vagrant sshVerify that your AWS credentials and access keys have been properly set in aws/global.tf (scroll to the bottom).
Use the relevant bootstrap script as a reference for the required dependencies or just run it as-is:
$ git clone https://github.com/basho-labs/terraform-riak.git
$ cd terraform-riak
$ bash bootstrap-ubuntu.sh
$ PATH=$PATH:$PWDIf you opt not to run one of the bootstrap scripts directly, you will need to populate the AWS configs in aws/global.tf directly.
Create working subdirectories for your cluster and client(s)
$ mkdir -p working/cluster working/clientsThe terraform apply command takes the following variables for a Riak cluster config:
product_version(default: ts-1.3; options: ts-1.3, ts-1.2, kv-2.1.3, kv-2.0.6)platform(default: ubuntu14; options: rhel6, rhel7, ubuntu12, ubuntu14, debian7)nodes(default: 5; options: must be >= 3)instance_type(default: t2.medium; options: any AWS instance type)
The following command uses the default settings to provision a 5-node Riak TS 1.3 cluster using the Ubuntu 14 package:
$ cd working/cluster
$ terraform apply ../../aws/riakTo provision a Riak KV 2.1.3 cluster using the RHEL 6 package:
$ terraform apply -var 'product_version=kv-2.1.3' -var 'platform=rhel6' ../../aws/riakTo provision a client instance, first change to the clients working subdirectory:
$ cd working/clients
$ terraform apply ../../aws/clientsYou can provision multiple client instances with a single command by adding the count variable:
$ cd working/clients
$ terraform apply -var 'count=2' ../../aws/clientsTake note of the IPs printed to the console at the end of each process.
To destroy provisioned infrastructure, simply replace apply with destroy in the commands above. Run the command from the relevant working subdirectory. For example:
$ cd working/cluster
$ terraform destroy ../../aws/riak
$ cd working/clients
$ terraform destroy ../../aws/clientsThe Riak client config downloads a sample time series data file (containing traffic data), and includes example Python scripts to both load and query the data. To run the examples, first SSH in to your client instance:
$ ssh -i [PATH_TO_AWS_SSH_KEY] ubuntu@[CLIENT_IP]Then, run:
$ export RIAK_IP=[RIAK_PRIVATE_IP]
$ export TABLE=table1
$ python examples/load.py $RIAK_IP $TABLE
$ python examples/query.py $RIAK_IP $TABLEYou can get a RIAK_PRIVATE_IP from the output of the relevant terraform apply command. The table name table1 is arbitrary.
Ansible can be used to remotely execute ad-hoc commands against a client or the Riak cluster. Ansible is pre-installed, but requires activation:
$ source ansible/hacking/env-setup
$ ssh-agent bash
$ ssh-add [PATH_TO_AWS_SSH_KEY]Command example:
$ RIAK_IP=[RIAK_PUBLIC_IP]
$ ansible all -i "$RIAK_IP," -u "ubuntu" -m shell -a "sudo riak ping"
$ ansible all -i "$RIAK_IP," -u "ubuntu" -m shell -a "sudo riak-admin member_status"Ansible ad-hoc commands require the target host's Linux user name (-u parameter above). Use ubuntu for Ubuntu-based instances, ec2-user for RHEL-based instances and admin for Debian-based instances.