Relax like a sloth, let DeText do the understanding for you
DeText is a Deep Text understanding framework for NLP related ranking, classification, and language generation tasks. It leverages semantic matching using deep neural networks to understand member intents in search and recommender systems. As a general NLP framework, currently DeText can be applied to many tasks, including search & recommendation ranking, multi-class classification and query understanding tasks. More details can be found in this blog post.
Design principles for DeText framework:
-
Natural language understanding powered by state-of-the-art deep neural networks
- Automatic feature extraction with deep models
- End-to-end training
- Interaction modeling between ranking sources and targets
-
A general framework with great flexibility to meet requirement of different production applications.
- Flexible deep model types
- Multiple loss function choices
- User defined source/target fields
- Configurable network structure (layer sizes and #layers)
- Tunable hyperparameters ...
-
Reaching a good balance between effectiveness and efficiency to meet the industry requirements.
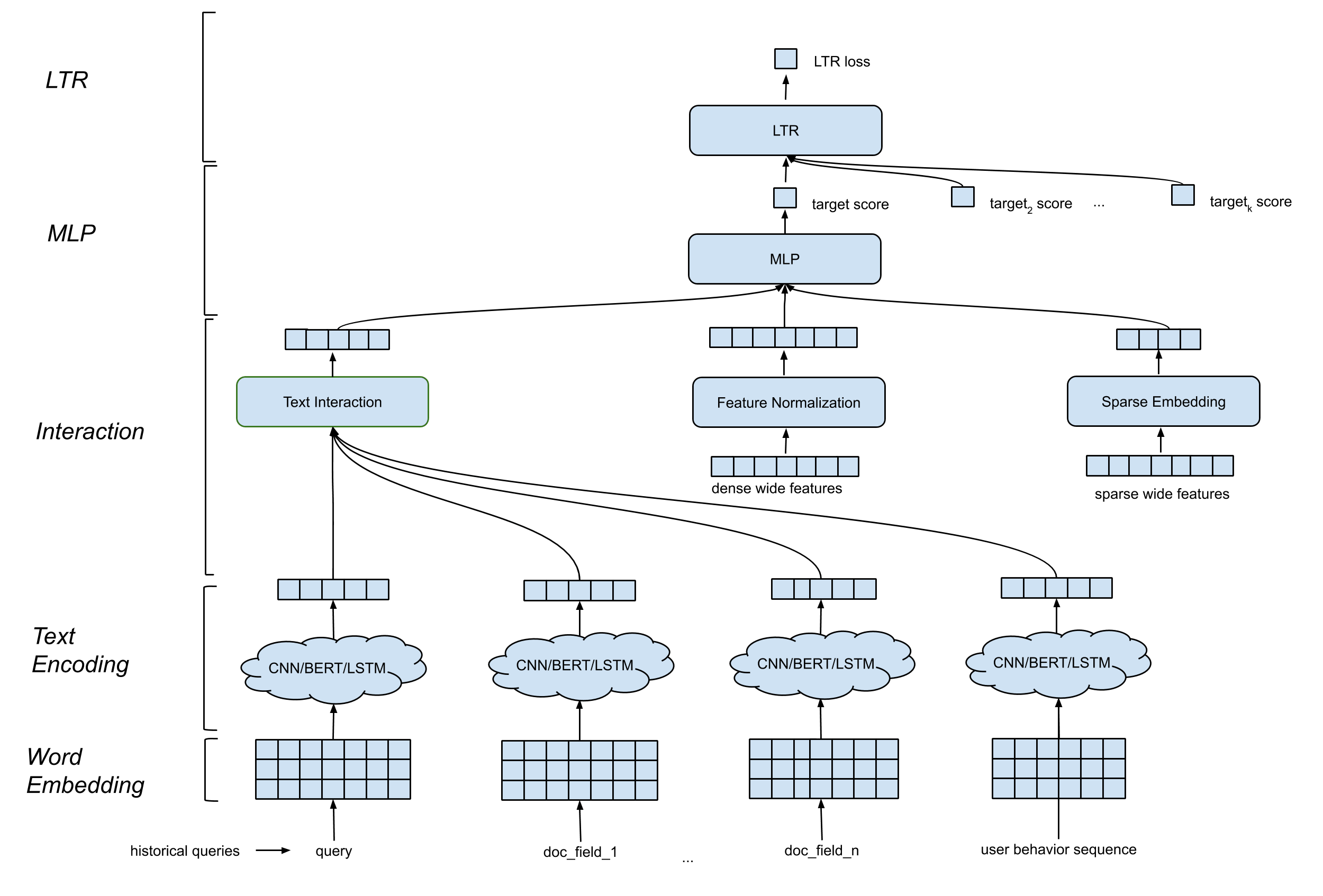
The DeText framework contains multiple components:
Word embedding layer. It converts the sequence of words into a d by n matrix.
CNN/BERT/LSTM for text encoding layer. It takes into the word embedding matrix as input, and maps the text data into a fixed length embedding. It is worth noting that we adopt the representation based methods over the interaction based methods. The main reason is the computational complexity: The time complexity of interaction based methods is at least O(mnd), which is one order higher than the representation based methods max(O(md), O(nd).
Interaction layer. It generates deep features based on the text embeddings. Many options are provided, such as concatenation, cosine similarity, etc.
Wide & Deep Feature Processing. We combine the traditional features with the interaction features (deep features) in a wide & deep fashion.
MLP layer. The MLP layer is to combine wide features and deep features.
It is an end-to-end model where all the parameters are jointly updated to optimize the click probability.
DeText is a general ranking framework that offers great flexibility for clients to build customized networks for their own use cases:
LTR/classification layer: in-house LTR loss implementation, or tf-ranking LTR loss, multi-class classification support.
MLP layer: customizable number of layers and number of dimensions.
Interaction layer: support Cosine Similarity, Outer Product, Hadamard Product, and Concatenation.
Text embedding layer: support CNN, BERT, LSTM-Language-Model with customized parameters on filters, layers, dimensions, etc.
Continuous feature normalization: element-wise scaling, value normalization.
Categorical feature processing: modeled as entity embedding.
All these can be customized via hyper-parameters in the DeText template. Note that tf-ranking is supported in the DeText framework, i.e., users can choose the LTR loss and metrics defined in DeText.
- Create & source your virtualenv
- Run setup for DeText:
python setup.py developRun all tests:
pytest notebooks/text_classification_demo.ipynb shows how to use DeText to train a production ready multi-class text classification model. A public query intent classification dataset is used. The notebook includes detailed steps on data preparation, model training, model inference examples.
[TODO] Add a ranking demo notebook
Users have full control for custom designing DeText models. In the training manual (TRAINING.md), users can find information about the following:
- Training data format and preparation
- Key parameters to customize and train DeText models
- Detailed information about all DeText training parameters for full customization
Please cite DeText in your publications if it helps your research:
@manual{guo-liu20,
author = {Weiwei Guo and
Xiaowei Liu and
Sida Wang and
Huiji Gao and
Bo Long},
title = {DeText: A Deep NLP Framework for Intelligent Text Understanding},
url = {https://engineering.linkedin.com/blog/2020/open-sourcing-detext},
year = {2020}
}
@inproceedings{guo-gao19,
author = {Weiwei Guo and
Huiji Gao and
Jun Shi and
Bo Long},
title = {Deep Natural Language Processing for Search Systems},
booktitle = {ACM SIGIR 2019},
year = {2019}
}
@inproceedings{guo-gao19,
author = {Weiwei Guo and
Huiji Gao and
Jun Shi and
Bo Long and
Liang Zhang and
Bee-Chung Chen and
Deepak Agarwal},
title = {Deep Natural Language Processing for Search and Recommender Systems},
booktitle = {ACM SIGKDD 2019},
year = {2019}
}
@inproceedings{guo-liu20,
author = {Weiwei Guo and
Xiaowei Liu and
Sida Wang and
Huiji Gao and
Ananth Sankar and
Zimeng Yang and
Qi Guo and
Liang Zhang and
Bo Long and
Bee-Chung Chen and
Deepak Agarwal},
title = {DeText: A Deep Text Ranking Framework with BERT},
booktitle = {ACM CIKM 2020},
year = {2020}
}
@inproceedings{jia-long20,
author = {Jun Jia and
Bo Long and
Huiji Gao and
Weiwei Guo and
Jun Shi and
Xiaowei Liu and
Mingzhou Zhou and
Zhoutong Fu and
Sida Wang and
Sandeep Kumar Jha},
title = {Deep Learning for Search and Recommender Systems in Practice},
booktitle = {ACM SIGKDD 2020},
year = {2020}
}
@inproceedings{wang-guo20,
author = {Sida Wang and
Weiwei Guo and
Huiji Gao and
Bo Long},
title = {Efficient Neural Query Auto Completion},
booktitle = {ACM CIKM 2020},
year = {2020}
}
@inproceedings{liu-guo20,
author = {Xiaowei Liu and
Weiwei Guo and
Huiji Gao and
Bo Long},
title = {Deep Search Query Intent Understanding},
booktitle = {arXiv:2008.06759},
year = {2020}
}
Please read CONTRIBUTING.md for details on our code of conduct, and the process for submitting pull requests to us.
This project is licensed under the BSD 2-CLAUSE LICENSE - see the LICENSE.md file for details