by Moritz Ludolph, Maximilian Bähnisch and Maher Shukur
This project serves as a prototype implementation of a Fog Computing application with edge and cloud components that communicate with each other with a lightweight and reliable messaging system. For this, simulated GPS and device metrics are broadcasted to all connected egde nodes, which could be useful e.g. in a connected-cars scenario. The project is implemented using Python and makes heavy use of the ZeroMQ library to provide atleast-once message delivery garantuee.
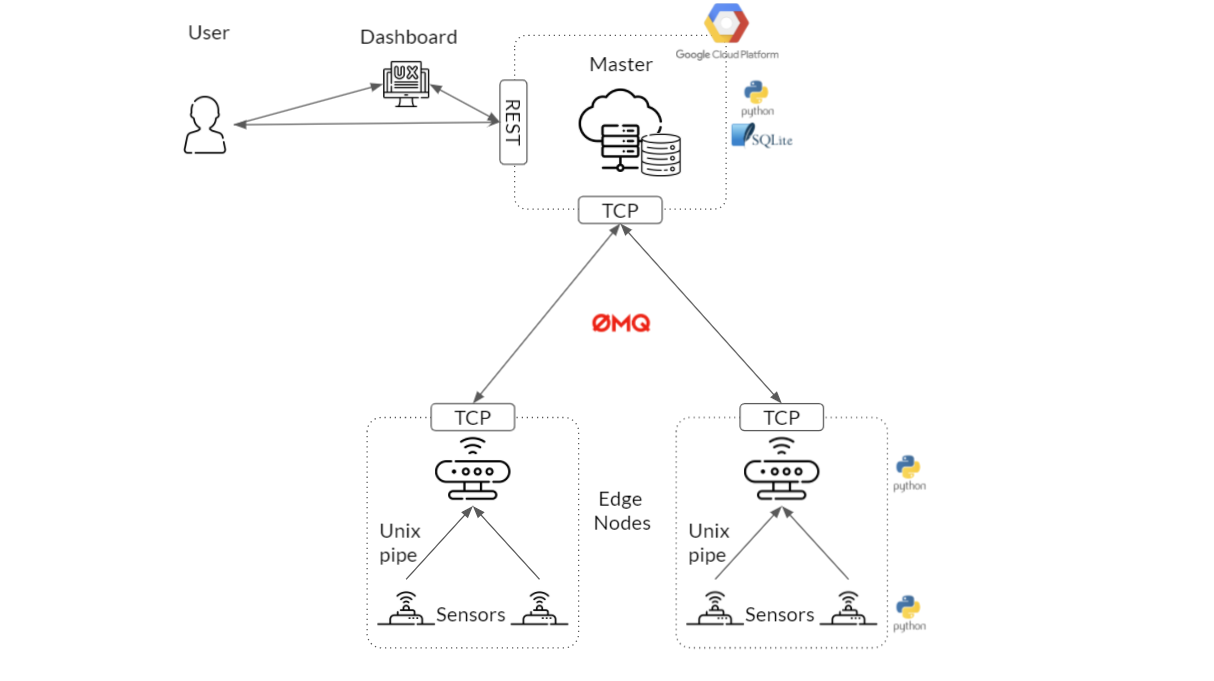 |
|---|
| Architecture Overview |
- Linux based system (Tested on Ubuntu 20.04)
- Python 3 (Tested on version 3.8.2)
- Install wheel, i.e.
pip install wheel - Python Packages from
requirements.txt(i.e. runpip install -r requirements.txt) - If installation of requirements still fails, run
sudo apt-get install build-essential python3-dev --yesand retry to install the python requirements
A master and a node can be easily deployed using the quick start scripts (or using docker):
Scripts:
$ scripts/start_master.sh &
$ scripts/start_node.shDocker:
$ docker-compose -f docker-compose.master.yml up -d
$ docker-compose -f docker-compose.node.yml up -dPlease note that the environment variables might have to be changed to fit a specific setup (i.e. MASTER_HOSTNAME and NODE_ADVERTISED_LISTENER).
Master Arguments/Environment variables:
$ python fogmsg/executables/master.py --help
usage: master.py [-h] [-i IP] [-p PORT] [-uip UI_PORT]
[--sender-queue-length SENDER_QUEUE_LENGTH] [--sender-timeout SENDER_TIMEOUT]
[--persistence-dir PERSISTENCE_DIR]
[--log-level {debug,info,warn,critical}] [--log-file LOG_FILE]
fogmsg Master
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i IP, --ip IP address that the node will bind to
(default: 0.0.0.0, env: MASTER_IP)
-p PORT, --port PORT port that the node will bind to
(default: 4000, env: MASTER_PORT)
-uip UI_PORT, --ui-port UI_PORT
port that the node will bind to
(default: 4002, env: MASTER_UI_PORT)
--sender-queue-length SENDER_QUEUE_LENGTH
length of the sender queues
(default: 1000, env: MASTER_SENDER_QUEUE_LENGTH)
--sender-timeout SENDER_TIMEOUT
timeout of the sender in ms
(default: 1000, env: MASTER_SENDER_TIMEOUT)
--persistence-dir PERSISTENCE_DIR
directory for queue files
(default: ./, env: MASTER_PERSISTENCE_DIR)
--log-level {debug,info,warn,critical}
the log-level (default: info)
--log-file LOG_FILE the path to the log file, default is to write to consoleNode Arguments/Environment Variables:
usage: node.py [-h] [--master-hostname MASTER_HOSTNAME] [-i IP] [-p PORT]
[--advertised-listener ADVERTISED_HOSTNAME]
[--sensor-pipes PIPE_FILES] [--sensor-types SENSOR_TYPES]
[--sender-queue-length SENDER_QUEUE_LENGTH]
[--sender-timeout SENDER_TIMEOUT] [--persistence-dir PERSISTENCE_DIR]
[--log-level {debug,info,warn,critical}] [--log-file LOG_FILE]
fogmsg Node
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--master-hostname MASTER_HOSTNAME
hostname of the master
(default: tcp://localhost:4000, env: MASTER_HOSTNAME)
-i IP, --ip IP address that the node will bind to
(default: 0.0.0.0, env: NODE_IP)
-p PORT, --port PORT port that the node will bind to
(default: 4001, env: NODE_PORT)
--advertised-listener ADVERTISED_HOSTNAME
the advertisement listener of this node
(default: tcp://localhost:4001, env: NODE_ADVERTISED_LISTENER)
--sensor-pipes PIPE_FILES
the pipe file to use for ipc, to use multiple pipes, seperate them by ';'
(default: /tmp/metrics;/tmp/gps)
--sensor-types SENSOR_TYPES
the type of the sensors specified by the pipes, seperate them by ';'
(default: metrics;gps)
--sender-queue-length SENDER_QUEUE_LENGTH
length of the sender queues
(default: 1000, env: NODE_SENDER_QUEUE_LENGTH)
--sender-timeout SENDER_TIMEOUT
timeout of the sender in ms
(default: 1000, env: NODE_SENDER_TIMEOUT)
--persistence-dir PERSISTENCE_DIR
directory for queue files
(default: ./, env: NODE_PERSISTENCE_DIR)
--log-level {debug,info,warn,critical}
the log-level (default: info)
--log-file LOG_FILE the path to the log file, default is to write to consoleOn startup, the edge node creates a receiver thread and a ZeroMQ REP/REQ socket, which handles incoming (i.e. broadcasted) messages for processing. The node then registers itself at the master with its adverstised hostname and pushes messages generated by its connected sensors via another socket in the main sender thread.
All messages pushed to the master have to be acknowledged, otherwise they are not considered as delivered and thus not removed from the message queue to allow for re-transmission.
Currently two types of (mock) sensors are implemented:
- a metrics sensor that collects OS metrics in regular intervals (i.e. CPU or memory usage)
- a gps sensor, that emits historical gps data which was collected from a real person and emitted in regular intervals
The sensors are pushing their data into a unix FIFO pipe. This allows for further extension of the implemented sensors in later works.
When using the quickstart scripts or docker containers, both sensors are deployed on startup.
The master node receives all incoming messages and creates sender threads for each new connection to an edge node. Upon receiving a sensor event, the message can then be broadcast to all previously registered nodes or handled on the master. For each of the senders, a seperate message queue is used, thus garantueeing reliable messaging for multiple clients. As before, the master also only considers messages as delivered when acknowledged by a client.
The master broadcasts all gps messages to other nodes, to demonstrate reliable messaging between multiple nodes.
For the metrics messages, the master checks it against a given threshold (for demo purposes set at 25%, see fogmsg/master/config) and returns control messages to THROTTLE or NOTHROTTLE back to the device.
This demos the capabilities this message framework can have, while being limitted to only mocked/simulated sensors (and no actuators).
A simple script is included at fogmsg/scripts/stress_cpu.sh to simulate CPU load.
The master additionally offers and REST interface and GUI to monitor metrics published by the nodes. For this, all received messages are persisted to a sqlite database, which could easily be replaced by a more specialized database solution (e.g. a TimescaleDB).
The implemented message protocol gives an atleast once delivery garantuee to messages. This is achived by using ZeroMQ REQ/REP sockets and manual acknowledgment of received messages. Additionally, messages are queued on the sender side until acknowledged. The message queues are persisted on the filesystem in order to prevent loss of data in the case of system crashes.
An error free message delivery can be seen in the sequence diagram below:
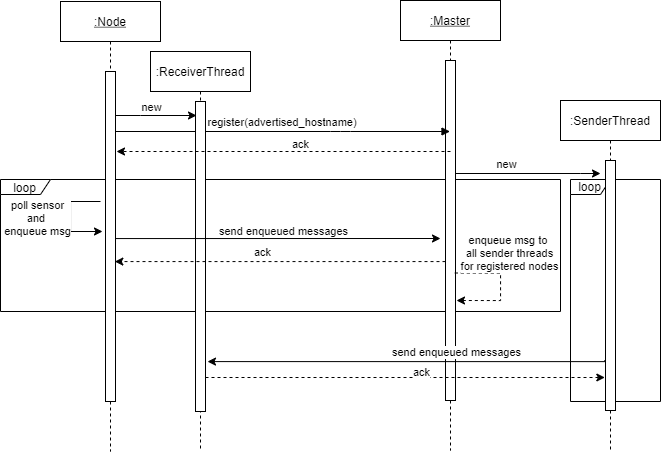 |
|---|
| Messaging: All messages have to be acknowledged by the receiver in order to be considered as processed. |
If any timeout happens during the message delivery, the message is not considered as acknowledged and not dequeued. Thus, once a receiver comes back online, all non-acknowledged messages can be resend.
Since the size of edge-cloud messages is a critical, a lightweight schema-based serialization scheme is used instead of relying on standard JSON serialization.
For this, only values of fields are transmitted by using the provided schema information of the underlying sensors (see fogmsg/utils/messaging.py)
The master also contains a simple REST interface based on the Pyhton library flask, supporting GET requests to list registered nodse and query the last data of a sensor:
GET /api/sensors- list all registered nodes
[
{
"hashId": "81aaf9efe37b664c175a89a7800a5113",
"hostname": "tcp://localhost:4001"
}
]GET /api/messages/<sensor_id>/<type>- get all messages in the last 60 seconds (supported types: metrics, gps)
[
{
"time": 1624802344,
"lat": 52.41214,
"lng": 51.412415
},
...
]- fogmsg/executables: runnable python scripts for Master, Node and Sensor
- fogmsg/frontend: Master REST API and Dashboard
- fogmsg/master: Master, SenderThread and Persistence
- fogmsg/node: Node, ReceiverThread, Sensor and Data Genration
- fogmsg/utils: Persistent Message Queue, Message Serialization and Logging
We fulfill all requirements as stated in the assignment:
- 1 local and 1 cloud component: Node, Master
- 2 virtual sensors: GPS and Metrics sensor
- transmitted regularly between components: Node sends sensors data, Master sends ack's, broadcasts and control messages
- failure tolerant: persistent message queues and atleasts once delivery garantuee
A short video demonstrating the reliable messaging can be found at on YouTube (https://youtu.be/nzpdaKR_xDo).
The software is licensed under MIT and is publicly available as open source on GitHub (https://github.com/mludolph/fogmsg).