Josh Broomberg, Yoav Rabinovich
This project probes the role which renormalization plays in the operation of (certain) deep neural networks. It builds on work by Mehta & Schwab (2014), proving the equivalence of training deep belief networks to variational block spin renormalization on the 2D Ising model, and Alexandrou et al. (2019), training an autoencoder on Ising model equilibrium states and showing how the encoded states contain information about the phase transition. It was done in as a final project for our junior undergraduate courses in simulation and in statistical mechanics, and due to this being a collaboration, two reports were written.
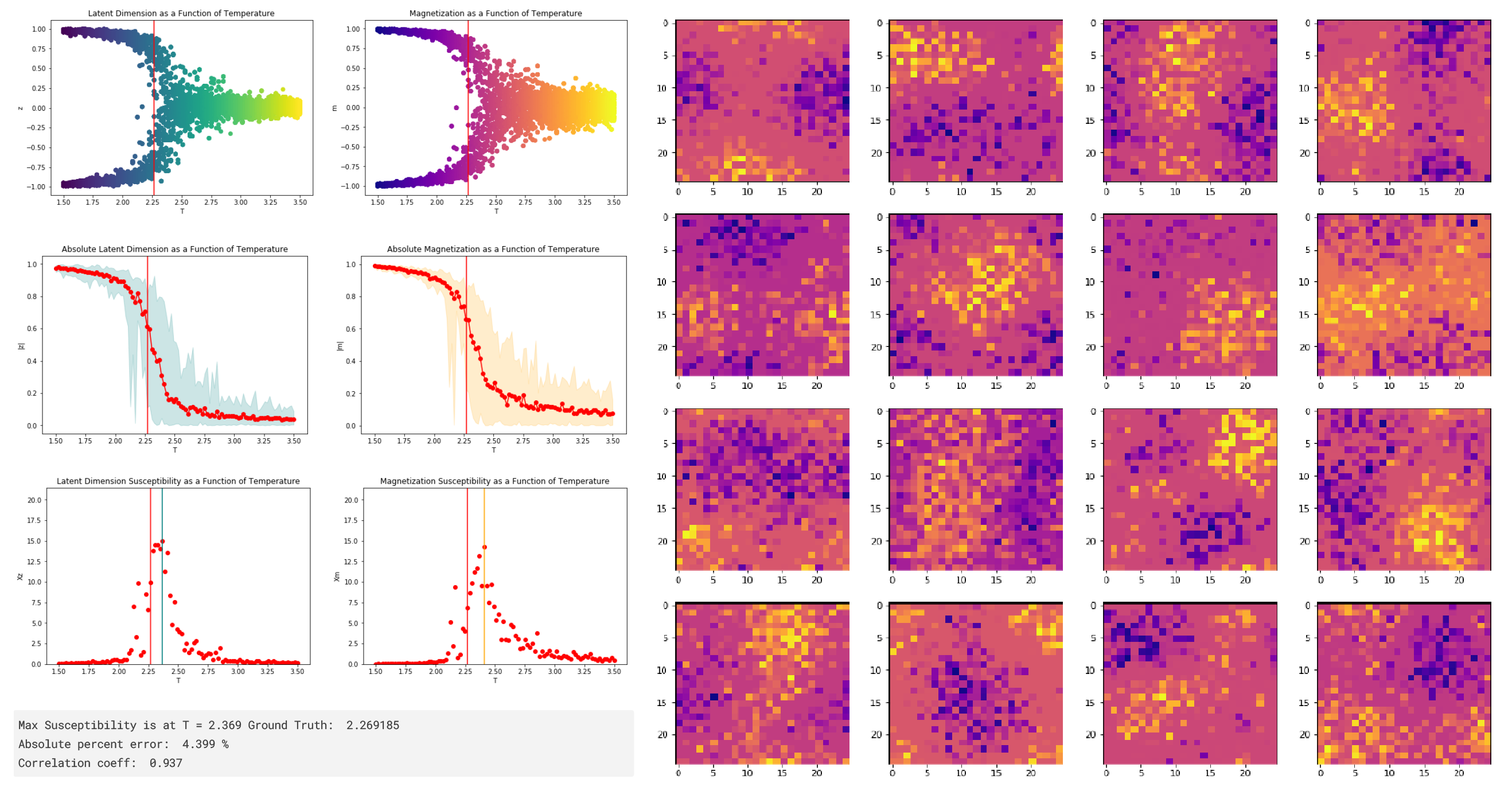
Firstly, we replicate the work done by Alexandrou et al. and then probe the results using some of the methods in Mehta & Schwab (2014) to test the hypothesis that the autoencoder converges on block renormalization as an inference technique.
We expand upon Alexandrou et al. by widening the latent dimension, and upon Mehta & Schwab by implementing back propagation to visualize neuron activations in an autoencoder.
While the work revealed many interesting properties of the autoencoder model, the results did not support the hypothesis. The reports summarize the process we used to investigate the hypothesis and reach our conclusion.
Alexandrou, C., Athenodorou, A., Chrysostomou, C., & Paul, S. (2019). Unsupervised identification of the phase transition on the 2D-Ising model. Retrieved from http://arxiv.org/abs/1903.03506
Kyalondawa Kyimba, E.-A. (2006). Comparison of Monte Carlo Metropolis, Swendsen-Wang, and Wolff Algorithms in the Critical Region for the 2-Dimensional Ising Model. (Under the direction of Dean J. Lee.). Retrieved from https://repository.lib.ncsu.edu/bitstream/handle/1840.16/110/etd.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Mehta, P., & Schwab, D. J. (2014). An exact mapping between the Variational Renormalization Group and Deep Learning. Retrieved from http://arxiv.org/abs/1410.3831
Stanley, H. E. (1999). Scaling, universality, and renormalization: Three pillars of modern critical phenomena. In Reviews of Modern Physics (Vol. 71). Retrieved from http://cps-www.bu.edu/hes/articles/s99a.pdf