This Docker image serves two purposes:
- Boots a live ISO image in QEMU (based on
tianon/qemu:native) - Provides an HTTP server from which the ISO itself can be downloaded
By default this image is built with Tiny Core Linux ISO as an example. Modify the ISO_URL argument when building the image to provide your own ISO URL. Or, create a child Dockerfile based on this image to add a local ISO:
FROM oci.guero.top/qemu-live-iso:latest
ARG QEMU_CPU=4
ARG QEMU_RAM=4096
ENV QEMU_CPU $QEMU_CPU
ENV QEMU_RAM $QEMU_RAM
ADD --chown=${DEFAULT_UID}:${DEFAULT_GID} foobar.iso /image/live.iso
Set the following environment variables to control runtime parameters. See the Dockerfile for a complete list of environment variables.
QEMU_CPU- the number of CPU cores for QEMU (default2)QEMU_RAM- the megabytes of RAM for QEMU (default1024)QEMU_START- whether to start QEMU when the container is run (defaulttrue)QEMU_RESTART- whether to retart QEMU if it stops (defaulttrue)
Additionally, you may bind mount your ISO as /image/live.iso in the container to boot your own ISO without rebuilding the Docker image:
$ docker run --detach --publish-all --rm --device /dev/kvm --volume /path/to/foobar.iso:/image/live.iso oci.guero.top/qemu-live-iso:latest
QEMU can take advantage of KVM acceleration if available. This can be accomplished by including --device /dev/kvm as illustrated in the example above.
Execute docker run with --publish-all (-P) and connect to the mapped HTTP and VNC ports to access the services provided by the container:
$ docker run --detach --publish-all --rm --device /dev/kvm oci.guero.top/qemu-live-iso:latest
fdaea77d8c383edc0689dd710b0df5c1187ad75b0b429e3ee56061d29fa6488c
$ docker ps -a | grep qemu-live-iso
fdaea77d8c38 oci.guero.top/qemu-live-iso "/usr/bin/supervisor…" 10 seconds ago Up 8 seconds 0.0.0.0:49190->22/tcp, 0.0.0.0:49169->5900/tcp, 0.0.0.0:49174->8000/tcp, 0.0.0.0:49191->8081/tcp competent_black
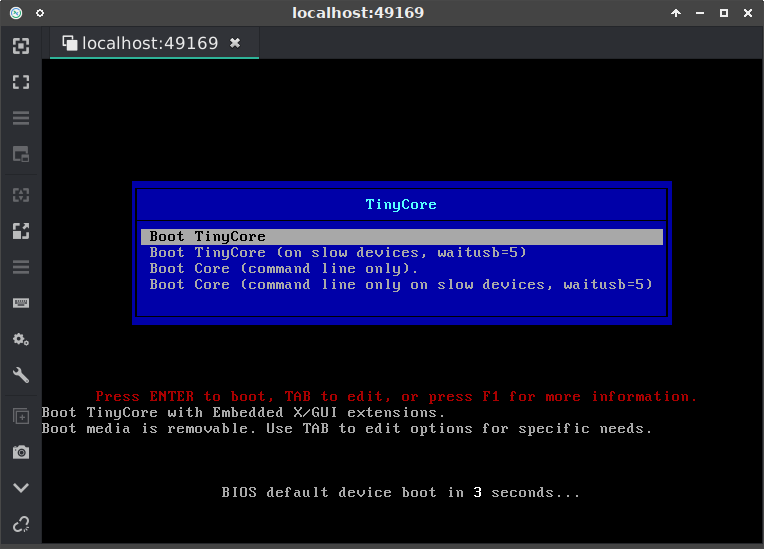
The VNC service is the one mapped to 5900/tcp, and can be connected to with your VNC client of choice (vncviewer, remmina, etc.):
$ remmina vnc://localhost:49169
Alternately, an HTML VNC client (noVNC) can be accessed via your browser at http://localhost:XXXXX/vnc_auto.html, where XXXXX is the port mapped to 8081/tcp:
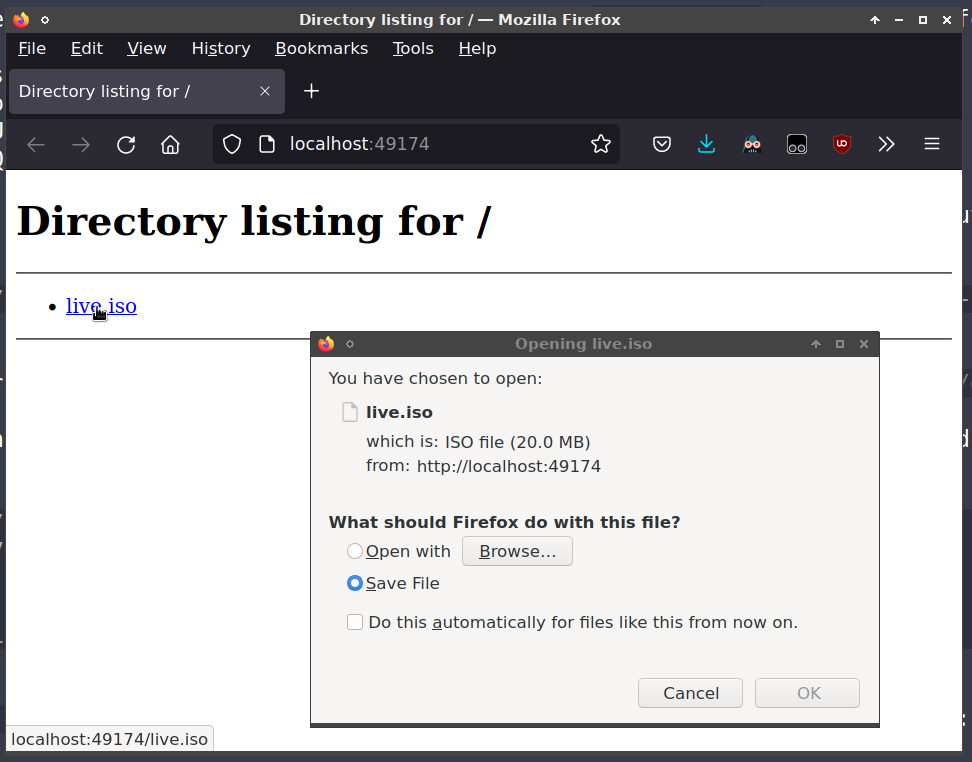
The HTTP service (for downloading the ISO) is the one mapped to 8000/tcp, and can be accessed with a web browser:
Note that none of the services mentioned above are encrypted or otherwise secured. This image is intended for testing or internal use only, and may not be suitable for production use.