Over 100 million people visit Quora every month, so it's no surprise that many people ask similarly worded questions. Multiple questions with the same intent can cause seekers to spend more time finding the best answer to their question, and make writers feel they need to answer multiple versions of the same question. Quora values canonical questions because they provide a better experience to active seekers and writers, and offer more value to both of these groups in the long term. so main aim of project is that predicting whether pair of questions are similar or not. This could be useful to instantly provide answers to questions that have already been answered. Credits: Kaggle
Identify which questions asked on Quora are duplicates of questions that have already been asked.
- The cost of a mis-classification can be very high.
- You would want a probability of a pair of questions to be duplicates so that you can choose any threshold of choice.
- No strict latency concerns.
- Interpretability is partially important.
- log-loss
- Binary Confusion Matrix
Train.csv contains 5 columns : qid1, qid2, question1, question2, is_duplicate. Total we have 404290 entries. Splitted data into train and test with 70% and 30%.
i derived some features from questions like no of common words, word share and some distances between questions with the help of word vectors. will discuss those below. You can check my total work here
-
- freq_qid1 = Frequency of qid1's
- freq_qid2 = Frequency of qid2's
- q1len = Length of q1
- q2len = Length of q2
- q1_n_words = Number of words in Question 1
- q2_n_words = Number of words in Question 2
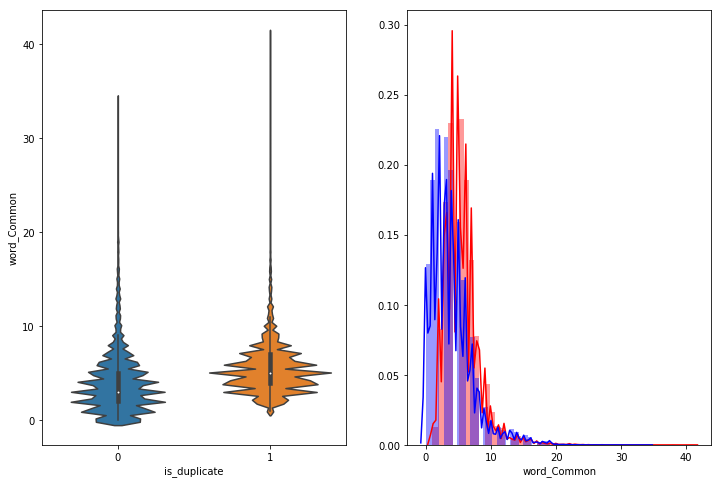
- word_Common = (Number of common unique words in Question 1 and Question 2)
- word_Total =(Total num of words in Question 1 + Total num of words in Question 2)
- word_share = (word_common)/(word_Total)
- freq_q1+freq_q2 = sum total of frequency of qid1 and qid2
- freq_q1-freq_q2 = absolute difference of frequency of qid1 and qid2
-
Advanced Features - Did some preprocessing of texts and extracted some other features. i am giving some definitions which are used below.
Token- You get a token by splitting sentence by space ,Stop_Word- stop words as per NLTK,Word-A token that is not a stop_word.- cwc_min = common_word_count / (min(len(q1_words), len(q2_words))
- cwc_max = common_word_count / (max(len(q1_words), len(q2_words))
- csc_min = common_stop_count / (min(len(q1_stops), len(q2_stops))
- csc_max = common_stop_count / (max(len(q1_stops), len(q2_stops))
- ctc_min = common_token_count / (min(len(q1_tokens), len(q2_tokens))
- ctc_max = common_token_count / (max(len(q1_tokens), len(q2_tokens))
- last_word_eq = Check if Last word of both questions is equal or not (int(q1_tokens[-1] == q2_tokens[-1]))
- first_word_eq = Check if First word of both questions is equal or not (int(q1_tokens[0] == q2_tokens[0]) )
- abs_len_diff = abs(len(q1_tokens) - len(q2_tokens))
- mean_len = (len(q1_tokens) + len(q2_tokens))/2
- fuzz_ratio = How much percentage these two strings are similar, measured with edit distance.
- fuzz_partial_ratio = if two strings are of noticeably different lengths, we are getting the score of the best matching lowest length substring.
- token_sort_ratio = sorting the tokens in string and then scoring fuzz_ratio.
- longest_substr_ratio = len(longest common substring) / (min(len(q1_tokens), len(q2_tokens))
-
Got Word Movers Distance with pretrained glove word vectors.
-
From Pretrained glove word vectors got average word vector for question1 and question2. With this avg word vector got below distances.
- Cosine distance
- Cityblock distance
- Canberra distance
- Euclidean distance
- Minkowski distance
-
word_share - We can check from below that it is overlaping a bit, but it is giving some classifiable score for disimilar questions.
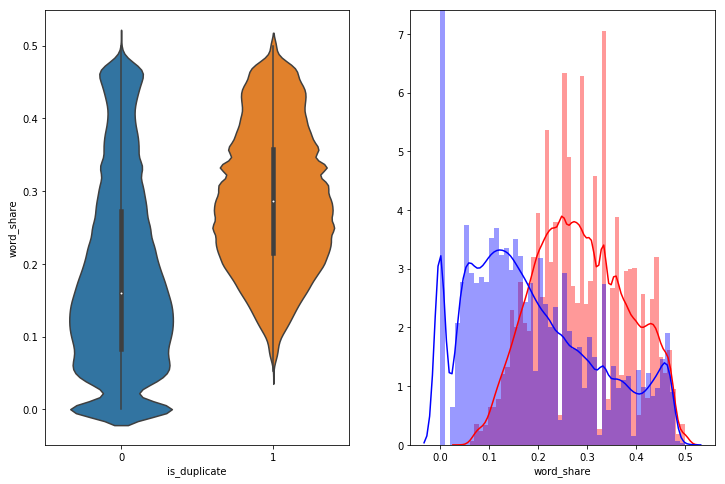
-
-
Bivariate analysis of features 'ctc_min', 'cwc_min', 'csc_min', 'token_sort_ratio'. We can observe that we can divide duplicate and non duplicate with some of these features with some patterns.
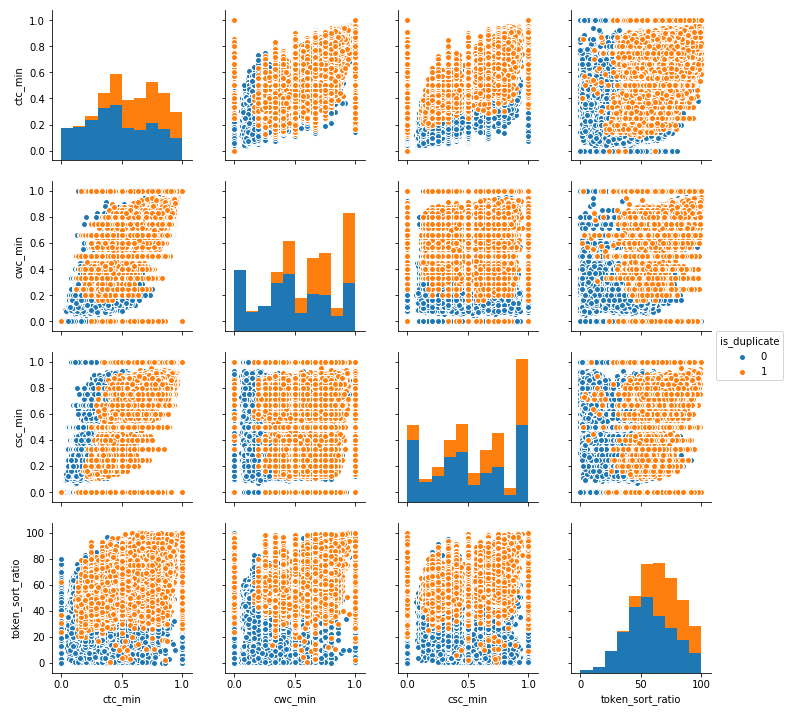
-
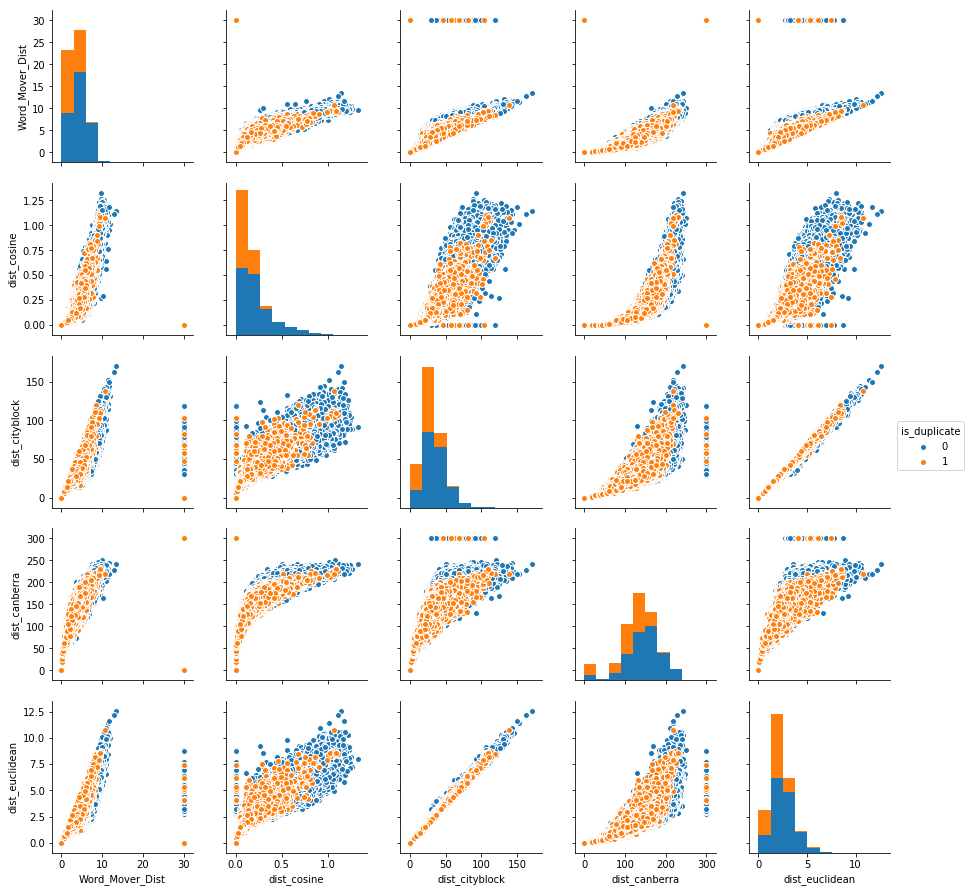
Bivariate analysis of features 'Word_Mover_Dist', 'dist_cosine', 'dist_cityblock', 'dist_canberra','dist_euclidean'.This also giving some patterns to classify.
- Trained a random model to check Worst case log loss and got log loss as 0.887699
- Trained some models and also tuned hyperparameters using Random and Grid search. I didnt used total train data to train my algorithms. Because of ram availability constraint in my PC, i sampled some data and Trained my models. below are models and their logloss scores. you can check total modelling and feature extraction here
For below table BF - Basic features, AF - Advanced features, DF - Distance Features including WMD.
| Model | Features Used | Log Loss |
|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | BF + AF | 0.4003415 |
| Linear SVM | BF + AF | 0.4036245 |
| Random Forest | BF + AF | 0.4143914 |
| XGBoost | BF + AF | 0.362546 |
| Logistic Regression | BF + AF + Tf-Idf | 0.358445 |
| Linear SVM | BF + AF + Tf-Idf | 0.362049 |
| Logistic Regression | BF + AF + DF + AVG-W2V | 0.3882535 |
| Linear SVM | BF + AF + DF + AVG-W2V | 0.394458 |
| XGBoost | BF + AF + DF + AVG-W2V | 0.313341 |
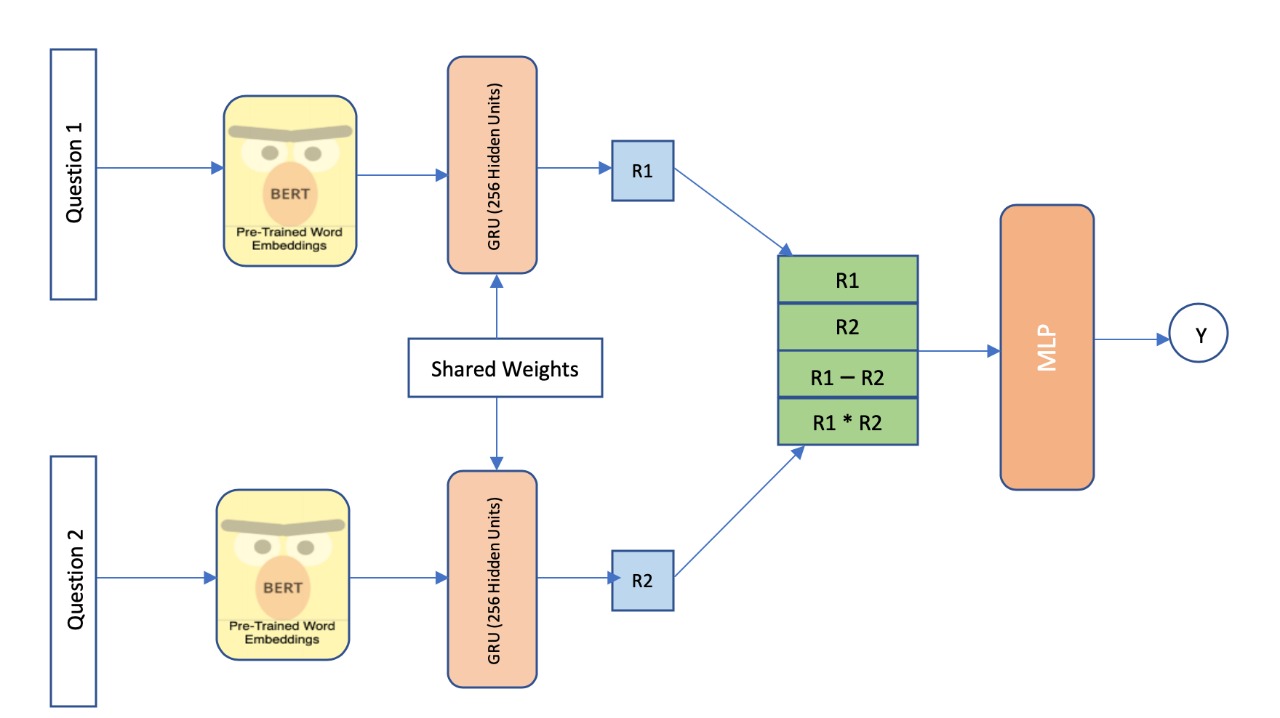
- Why the Siamese network? A siamese network is when two different inputs go through the exact same neural network and finally the end-feature vectors that come out of them are merged or compared. In face recognition, a siamese network is often used to tell if two face pictures are of the same person or different persons. Here, once we'll have embeddings of the text, we could use a similar approach.
- Each sentence is first tokenized and mapped to its numeric index so each question is represented as word vectors that is padded to be 'c' word long. Then it is fed into model for learning which learns high level representations in the subsequent layers and makes use of those higher level features to perform the final classification (duplicate or not).
- Embedding Layer: We tried two different type of embedding:
- Glove Embedding as our initial word embeddings. GloVe is a context-free model which generates a single word embedding for each individual word. We experimented with 50, 100, 300 dimension vectors and found 300 dimensions to produce the best results. We used Spacy which has in-built GloVe embeddings dataset called ”en core web sm” with 300 dimension vectors, this is the most used word to vector embeddings with a lot of common words used in human text, this makes it ideal for our dataset of questions asked by humans.
- We also used BERT [12]: Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding [13] which is also a contextual model which generates a representation of each word that is based on the other words in the sentence thus capturing the relationship in a bi-directional way. These embeddings are useful for semantic search and information retrieval, thus making it ideal for our task of determining duplicate questions. These vectors are high quality feature inputs to downstream models. BERT has several advantages over GloVe in the sense that BERT can capture polysemy, this context-informed word embeddings capture more accurate feature representations, which resulted in better model performance.
| Model | Features Used | Log Loss | Precision | Recall | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Siamese Network | Glove Embeddings | 0.29568 | 88.32 | 89.3 | 86.4 |
| Siamese Network | Bert Embeddings | 0.27761 | 88.6 | 86.4 | 91.7 |
Please check full analysis, conclusion and future work here
- https://www.kaggle.com/c/quora-question-pairs
- https://www.kaggle.com/c/quora-question-pairs/discussion
- Applied AI Course
- https://github.com/seatgeek/fuzzywuzzy#usage , https://chairnerd.seatgeek.com/fuzzywuzzy-fuzzy-string-matching-in-python/
- http://proceedings.mlr.press/v37/kusnerb15.pdf
- Jacob Devlin and Ming-Wei Chang and Kenton Lee and Kristina Toutanova (2018). BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language UnderstandingCoRR, abs/1810.04805. [14] Radim Rehurek, Petr Sojka (2010). Software Framework for Topic Modelling with Large Corpora. In Proceedings of the LREC 2010 Workshop on New Challenges for NLP Frameworks (pp. 45–50). ELRA.
- Thomas Wolf, Lysandre Debut, Victor Sanh, Julien Chaumond, Clement Delangue, Anthony Moi, Pierric Cistac, Tim Rault, R’emi Louf, Morgan Funtowicz, Jamie Brew (2019). HuggingFace’s Transformers: State-of-the-art Natural Language ProcessingArXiv, abs/1910.03771.
- Jeffrey Pennington, Richard Socher, Christopher D. Manning (2014). Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In In EMNLP.




