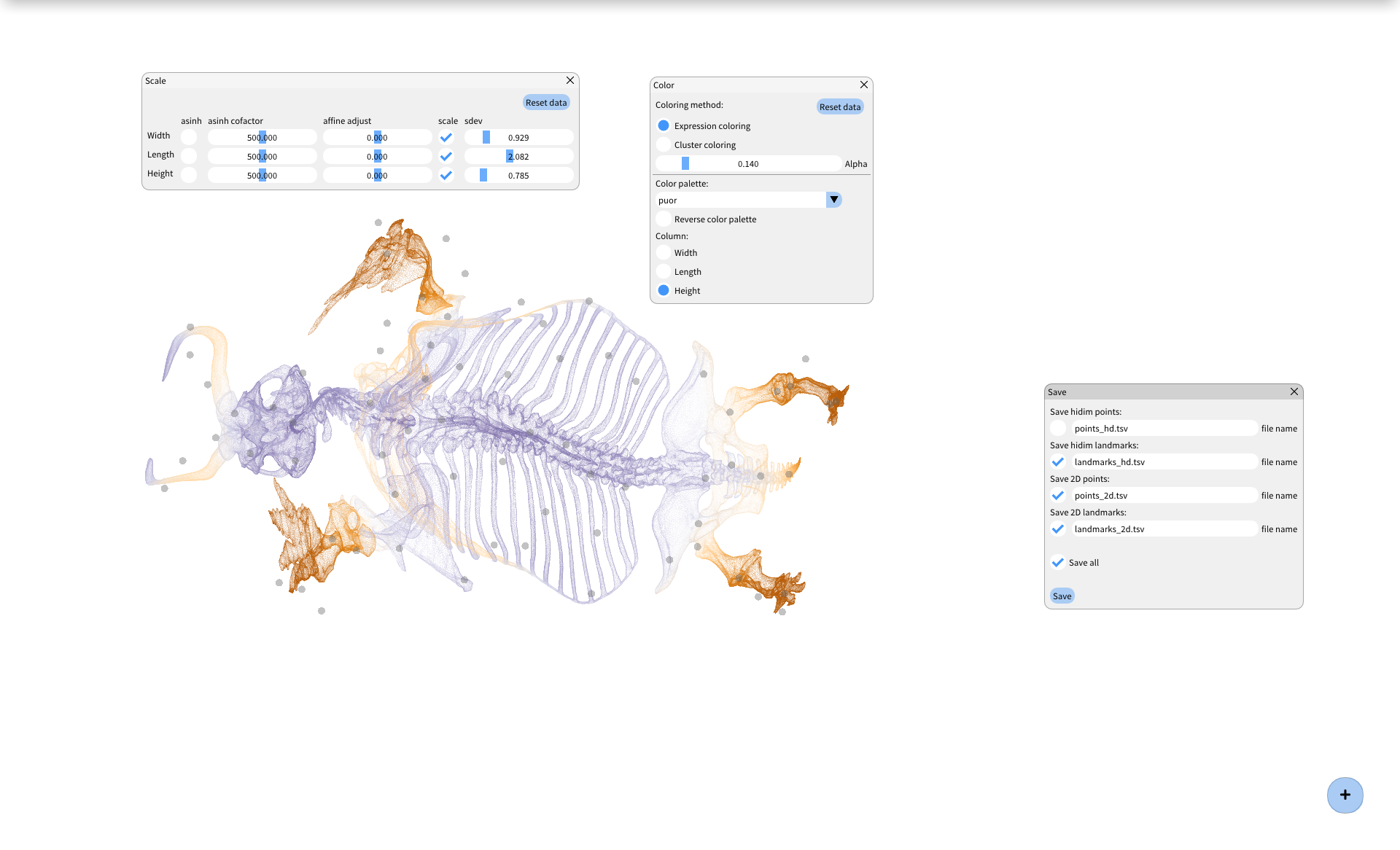
BlosSOM is a graphical environment for running semi-supervised dimensionality reduction with EmbedSOM. You can use it to explore multidimensional datasets, and produce great-looking 2-dimensional visualizations.
WARNING: BlosSOM is still under development, some stuff may not work right, but things will magically improve without notice. Feel free to open an issue if something looks wrong.
- ❓ Overview
- 🔧 Compiling and running
- ➡️ How-To 💡
- 📘 Documentation
BlosSOM was developed at the MFF UK Prague, in cooperation with IOCB Prague.
BlosSOM creates a landmark-based model of the dataset, and dynamically projects all dataset point to your screen (using EmbedSOM). Several other algorithms and tools are provided to manage the landmarks; a quick overview follows:
- High-dimensional landmark positioning:
- Self-organizing maps
- k-Means
- 2D landmark positioning
- k-NN graph generation (only adds edges, not vertices)
- force-based graph layouting
- dynamic t-SNE
- Dimensionality reduction
- EmbedSOM
- CUDA EmbedSOM (with roughly 500x speedup, enabling smooth display of a few millions of points)
- Manual landmark position optimization
- Visualization settings (colors, transparencies, cluster coloring, ...)
- Dataset transformations and dimension scaling
- Import from matrix-like data files
- FCS3.0 (Flow Cytometry Standard files)
- TSV (Tab-separated CSV)
- Export of the data for plotting
You will need cmake build system, GLFW OpenGL library and GLM mathematics library for graphics.
For CUDA EmbedSOM to work, you need the NVIDIA CUDA toolkit.
Append -DBUILD_CUDA=1 to cmake options to enable the CUDA version.
A version for Windows is currently not supported but may be in the future, stay tuned.
The project requires GLFW and GLM as an external dependency. Install libglfw3-dev, libglm-dev and libgl-dev (on
Debian-based systems) or similar
(depending on the Linux distribution). You should be able to install cmake
package the same way.
git submodule update --init --recursive
mkdir build
cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=./inst # or any other directory
# to compile CUDA, set proper gcc/g++ compiler compatible with your version of CUDA/nvcc
# cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=./inst -DBUILD_CUDA=1 -DCMAKE_C_COMPILER=/usr/bin/gcc-10 -DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=/usr/bin/g++-10
make install # use -j option to speed up the build./inst/bin/blossom
# to run CUDA version
# ./inst/bin/blossom_cuda- Basic usage of the software and the description of the user interface is available in HOWTO.md.
- Some technical details about the code may be found in src/README.md.
- Doxygen-generated documentation of the source code can be found at https://molnsona.github.io/blossom/
- Click on the "plus" button on the bottom right side of the window
- Choose Open file (the first button from the top) and open a file from the
demo_data/directory - You can now add and delete landmarks using ctrl+mouse click, and drag them around.
- Use the tools and settings available under the "plus" button to optimize the landmark positions and get a better visualization.
See the HOWTO for more details and hints.
If you pass -DBUILD_CUDA=1 to the cmake commands, you will get extra
executable called blossom_cuda (or blossom_cuda.exe, on Windows).
The 2 versions of BlosSOM executable differ mainly in the performance of EmbedSOM projection, which is more than 100× faster on GPUs than on CPUs. If the dataset gets large, only a fixed-size slice of the dataset gets processed each frame (e.g., at most 1000 points in case of CPU) to keep the framerate in a usable range. The defaults in BlosSOM should work smoothly for many use-cases (defaulting at 1k points per frame on CPU and 50k points per frame on GPU).
If required (e.g., if you have a really fast GPU), you may modify the constants
in the corresponding source files, around the call sites of clean_range(),
which is the function that manages the round-robin refreshing of the data.
Functionality that dynamically chooses the best data-crunching rate is being
implemented and should be available soon.
BlosSOM is licensed under GPLv3 or later. Several small libraries bundled in the repository are licensed with MIT-style licenses.