nevergrad is a Python 3.6+ library. It can be installed with:
pip3 install git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/nevergrad@master#egg=nevergrad
Alternatively, you can clone the repository and run python3 setup.py develop from inside the repository folder.
The goals of this package are to provide:
- gradient/derivative-free optimization algorithms, including algorithms able to handle noise.
- tools to instrument any code, making it painless to optimize your parameters/hyperparameters, whether they are continuous, discrete or a mixture of continuous and discrete variables.
- functions on which to test the optimization algorithms.
- benchmark routines in order to compare algorithms easily.
The structure of the package follows its goal, you will therefore find subpackages:
optimization: implementing optimization algorithmsinstrumentation: tooling to convert code into a well-defined function to optimize.functions: implementing both simple and complex benchmark functionsbenchmark: for running experiments comparing the algorithms on benchmark functionscommon: a set of tools used throughout the package
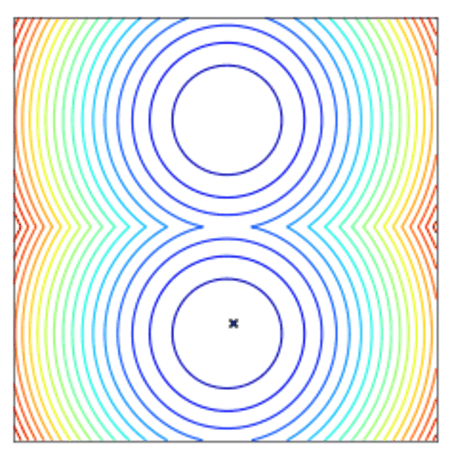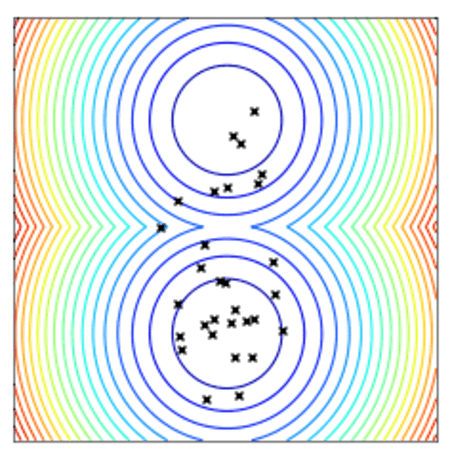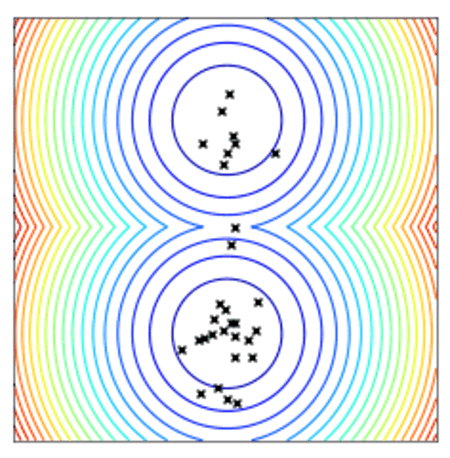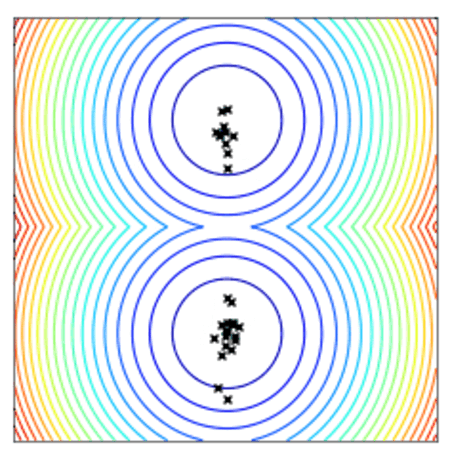
Convergence of a population of points to the minima with two-points DE.
All optimizers assume a centered and reduced prior at the beginning of the optimization (i.e. 0 mean and unitary standard deviation). They are however able to find solutions far from this initial prior.
Optimizing (minimizing!) a function using an optimizer (here OnePlusOne) can be easily run with:
from nevergrad.optimization import optimizerlib
def square(x):
return (x - .5)**2
optimizer = optimizerlib.OnePlusOne(dimension=1, budget=100, num_workers=5)
# alternatively, you can use optimizerlib.registry which is a dict containing all optimizer classes
recommendation = optimizer.optimize(square, executor=None, batch_mode=True)num_workers=5 with batch_mode=True will ask the optimizer for 5 points to evaluate, run the evaluations, then update the optimizer with the 5 function outputs, and repeat until the budget is all spent. Since no executor is provided, the evaluations will be sequential. num_workers > 1 with no executor is therefore suboptimal but nonetheless useful for evaluation purpose (i.e. we simulate parallelism but have no actual parallelism).
Providing an executor is easy:
from concurrent import futures
with futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=optimizer.num_workers) as executor:
recommendation = optimizer.optimize(square, executor=executor, batch_mode=True)batch_mode=False (steady state mode) will ask for a new evaluation whenever a worker is ready. The current implementation is efficient in this sense; but keep in mind that this steady state mode has drawbacks in terms of reproducibility: the order in which evaluations are launched is not controlled.
An ask and tell interface is also available. The 3 key methods for this interface are respectively:
ask: suggest a point on which to evaluate the function to optimize.tell: for updated the optimizer with the value of the function at a given point.provide_recommendation: returns the point the algorithms considers the best. For most optimization algorithms in the platform, they can be called in arbitrary order - asynchronous optimization is OK.
Here is a simpler example in the sequential case (this is what happens in the optimize method for num_workers=1):
for _ in range(optimizer.budget):
x = optimizer.ask()
value = square(x)
optimizer.tell(x, value)
recommendation = optimizer.provide_recommendation()Please make sure that your function returns a float, and that you indeed want to perform minimization and not maximization ;)
The benchmark tools aim at providing a way to evaluate optimizers on a large range of settings. They provide a way to run the optimizers on all settings and record the results, as well as ways to plot the results of the experiments.
Experiment plans are described in nevergrad.benchmark.experiments. Each experiment plan is a generator yielding different Experiment instances (defining function and optimizer settings).
To run an experiment plan, use:
python -m nevergrad.benchmark <experiment_name>
You may try with the experiment name repeated_basic for instance.
Check out python -m nevergrad.benchmark -h for all options. In particular, using --num_workers=4 can speed up the computation by using 4 processes, and
for some experiments, you may provide a seed for reproducibility.
This benchmark command creates a file <experiment_name>.csv holding all information. The output file can be changed with the --output parameter. Each line of the csv file corresponds to one experiment from the experiment plan. The columns correspond to the function and optimizer settings for this experiment as well as its result (loss/regret value, elapsed time...).
In order to plot the data in the csv file, just run:
python -m nevergrad.benchmark.plotting <csv_file>
Check out python -m nevergrad.benchmark.plotting -h for more options.
The plotting tool will create 2 types of plot:
- experiment plots: regret with respect to budget for each optimizer after averaging on all experiments with identical settings.
- fight plots: creates a matrix of size
num_algo x num_algowhere element at positionijis the mean winning rate ofalgo_ioveralgo_jin similar settings. The matrix is ordered to show best algorithms first, and only the first 5 rows (first 5 best algorithms) are displayed.
For simplicity's sake, you can directly plot from the nevergrad.benchmark command by adding a --plot argument. If a path is specified
afterwards, it will be used to save all figures, otherwise it will be saved a folder <csvfilename>_plots alongside the experiment csv file.
The nevergrad.benchmark command has an "import" system which can import additional modules where you defined your own experiments, possibly with your own functions and/or optimizers.
Example (please note that nevergrad needs to be cloned in your working directory for this example to work):
python -m nevergrad.benchmark additional_experiment --imports=nevergrad/benchmark/additional/example.py
See the example file to understand more precisely how functions/optimizers/experiments are specified. You can also submit a pull request to add your code directly in nevergrad.
Functions used for the experiments must derive from nevergrad.functions.BaseFunction. This abstract class helps you set up a description of your function settings through the get_summary method, which is called to create the columns of the data file produced by the experiments. See the docstrings for more information, and functionlib.py and example.py for examples.
If you want your experiment plan to be seedable, be extra careful as to how you handle randomness in the experiment generator, since each individual experiment may be run in any order. See experiments.py for examples of seedable experiment plans. If you do not care for it. For simplicity's sake, the experiment plan generator is however not required to have a seed parameter (but will not be reproducible in this case).
The aim of instrumentation is to turn a piece of code with parameters you want to optimize into a function defined on an n-dimensional continuous space. For this, discrete/categorial variables must be transformed to continuous variables, and all variables concatenated. The instrumentation subpackage will help you do this.
Instrumentation can come in two flavors:
- directly in Python if you have a Python3 function that needs to be optimized on some or all of its arguments.
- through tokens in your code, which will be replaced at runtime by values provided by the optimizer. This allows you to instrument any code even if it is not Python3. The instrumentation will run your code in a subprocess and feed the results into the optimizer.
In both cases, 3 types of variables are provided:
SoftmaxCategorical(token:NG_SC): converts a list of n (unordered) categorial variables into an n dimensional space. The returned element will be sampled as the softmax of the values on these dimensions. Be cautious: this process is non-deterministic and somehow `adds noise to the estimation.OrderedDiscrete(token:NG_OD): converts a list of (ordered) discrete variables into a 1-dimensional variable. The returned value will depend on the value on this dimension: low values corresponding to first elements of the list, and high values to the last.Gaussian(token:NG_G): normalizes a n-dimensional variable with independent Gaussian priors (1-dimension per value).
Tokens are explained below
Here is a basic example of instrumentation:
from nevergrad import instrumentation as instru
def myfunction(arg1, arg2, arg3, value=3):
print(arg1, arg2, arg3)
return value**2
# argument transformation
arg1 = instru.variables.OrderedDiscrete(["a", "b"]) # 1st arg. = positional discrete argument
arg2 = instru.variables.SoftmaxCategorical(["a", "c", "e"]) # 2nd arg. = positional discrete argument
value = instru.variables.Gaussian(mean=1, std=2) # the 4th arg. is a keyword argument with Gaussian prior
# create the instrumented function
ifunc = instru.InstrumentedFunction(myfunction, arg1, arg2, "blublu", value=value)
# the 3rd arg. is a positional arg. which will be kept constant to "blublu"
print(ifunc.dimension) # 5 dimensional space
# The dimension is 5 because:
# - the 1st discrete variable has 1 possible values, represented by a hard thresholding in a 1-dimensional space, i.e. we add 1 coordinate to the continuous problem
# - the 2nd discrete variable has 3 possible values, represented by softmax, i.e. we add 3 coordinates to the continuous problem
# - the 3rd variable has no uncertainty, so it does not introduce any coordinate in the continuous problem
# - the 4th variable is a real number, represented by single coordinate.
ifunc([1, -80, -80, 80, 3]) # will print "b e blublu" and return 49 = (mean + std * arg)**2 = (1 + 2 * 3)**2
# b is selected because 1 > 0 (the threshold is 0 here since there are 2 values.
# e is selected because proba(e) = exp(80) / (exp(80) + exp(-80) + exp(-80))When you have performed optimization on this function and want to trace back to what should your values be, use:
# recover the arguments this way:
result = [-100, 100, -80, -80, 80, 3]
args, kwargs = ifunc.convert_to_arguments(result)
print(args) # should print ["b", "e", "blublu"]
print(kwargs) # should print {"value": 7}
# but be careful, since some variables are stochastic (SoftmaxCategorical ones are), so several runs may lead to several results
# The following will print more information on the conversion to your arguments:
print(ifunc.get_summary(result))Sometimes it is completely impractical or impossible to have a simple Python3 function to optimize. This may happen when the code you want to optimize is a script. Even more so if the code you want to optimize is not Python3.
We provide tooling for this situation. Go through this steps to instrument your code:
- identify the variables (parameters, constants...) you want to optimize, and decide which kind of variable it is: either discrete (a discrete set of values) or continuous. We will need to add a token inside your code to notify nevergrad that those are the variables. A discrete variable will be marked
NG_SC{value_1|value_2|...|value_n}orNG_OD{value_1|value_2|...|value_n}depending on the discretization pattern (respectively SoftmaxCategorical and OrderedDiscrete), while a Gaussian variable will be marked asNG_G{mean, std} - add tokens to your code. In order to avoid breaking it, the line containing them should be commented. To notify that the line should be uncommented for instrumentation, you'll need to add "@nevergrad@" at the start of the comment. Here is an example in C which will notify that we want to optimize on the
step_sizevariable which can take values 0.1, 0.01 or 0.001:
int step_size = 0.1
// @nevergrad@ step_size = NG_OD(0.1|0.01|0.001)- prepare the command to execute that will run your code. Make sure that the last printed line is just a float, which is the value to base the optimization upon. We will be doing minimization here, so this value must decrease for better results.
- create an optimization script in Python3 using
nevergrad, as shown in the "Optimization" section above. This instrumentation script will be the one running your code in subprocesses. The function to optimize will be an instance ofnevergrad.instrumentation.FolderFunction, which you will have set up to run your code:
from nevergrad.instrumentation import FolderFunction
folder = "nevergrad/instrumentation/examples/basic"
command = ["python", "basic/script.py"] # command to run from right outside the provided folder
func = FolderFunction(folder, command, clean_copy=True)
print(func.dimension) # will print the number of variables of the function
func([1, 2, 3, 4])When you have performed the optimization and want to trace back to what should your values be, use:
print(func.get_summary([1, 2, 3, 4]))This will return something like:
In file /var/folders/12/hc34cs5n4dqbf_0ggwj_kqbw4_1hcj/T/tmp_clean_copy_8kk5e3uh/basic/script.py
- on line #4
discrete_value = <[placeholder_1>]
Placeholder 1: Value 100, from data: [2 3 4] yielding probas: "1": 9.0%, "10": 24.0%, "100": 67.0%
- on line #6
continuous_value = <[placeholder_0>]
Placeholder 0: Value 110.0, from data: [1]
Some important things to note:
- using
FolderFunctionargumentclean_copy=Truewill copy your folder so that tempering with it during optimization will run different versions of your code. - under the hood, with or without
clean_copy=True, when calling the function,FolderFunctionwill create symlink copy of the initial folder, remove the files that have tokens, and create new ones with appropriate values. Symlinks are used in order to avoid deplicating large projects, but they have some drawbacks, see next point ;) - one can add a compilation step to
FolderFunction(the compilation just has to be included in the script). However, be extra careful that if the initial folder contains some build files, they could be modified by the compilation step, because of the symlinks. Make sure that during compilation, you remove the build symlinks first! This feature has not been fool proofed yet!!!
To install nevergrad in development mode (if you wish to contribute to it), clone the repository and run python setup.py develop from inside the repository folder.
Run tests with:
nosetests nevergrad --with-coverage --cover-package=nevergrad
You can also run type checking with:
mypy --ignore-missing-imports --strict nevergrad
Please use pre-commit hooks when commiting. This will run pylint and autopep8 on the files you modified. You can install them with:
pre-commit install
@misc{nevergrad,
author = {J. Rapin and O. Teytaud},
title = {{Nevergrad - A gradient-free optimization platform}},
year = {2018},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://GitHub.com/FacebookResearch/Nevergrad}},
}nevergrad is released under the MIT license. See LICENSE for additional details.