The storage system of sealos, aiming to be a high-performance, highly reliable and auto-scalable distributed file system which fits the cloud native environment.
The architecture of sealfs is decentralized, and there is no single metadata node. sealfs hopes to improve the read and write performance as much as possible and solve the problems of storing large amounts of small files.
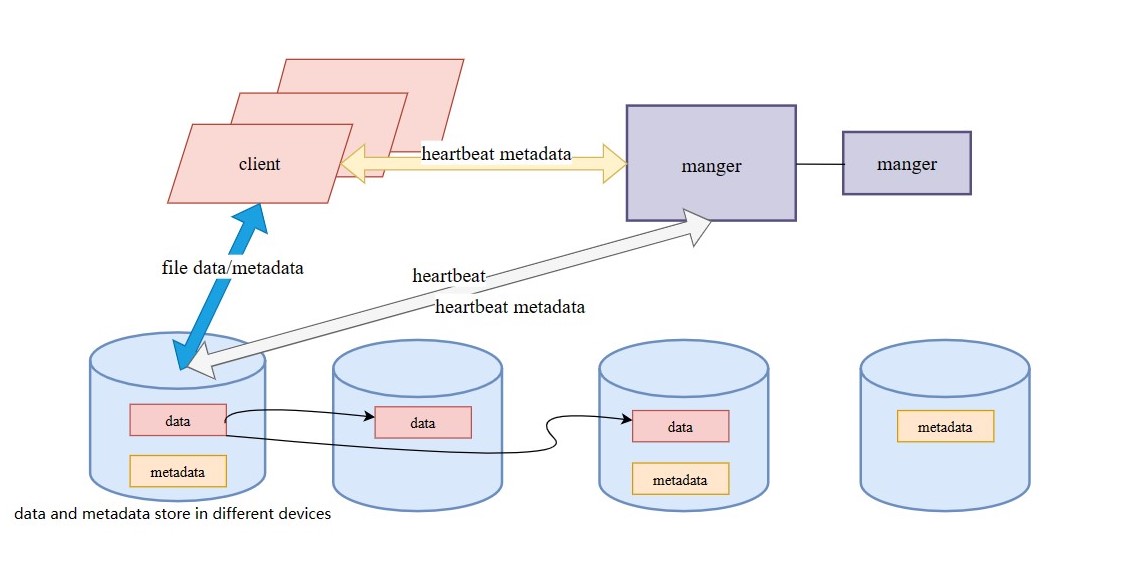
Sealfs consists of the following three components:
Server component is responsible for storing files and metadata. sealfs separates data and metadata into different disks, since metadata is undoubtedly the hot file on distributed file-system. This way, users can choose better hardware to store metadata.
Client component implements the file-system in user mode. It intercepts file requests, stores, and addresses them through hash algorithms.
Manager component is responsible for coordinating the cluster.
The System Architecture can be shown as follow:
With specific hardware, sealos hopes to support user-mode completely, from file request hijacking on the client side, to the network, and to the storage, for maximum performance improvement.
More designs can be referred to:
Currently, we are committed to improving the performance thoroughly. For other design aspects, such as high reliability and high availability, the priority would be lower.
- first version Function:
-
Client:
- fuse file system interface
- System call hijacking(file system of user mode)
- location algorithm
- batch process
-
Sever:
- bypass file system
- file Storage
- disk manager
- catalogue manager
- Metadata persistent memory storage
- file index
- file lock
- Persistent data structure
-
Manger:
- heart manager
-
Network:
- RDMA
- socket network
-
Test
- IO500
- function test
-
cargo buildmkdir ~/fs
./target/debug/server &
./target/debug/client ~/fsshow directory
ll ~/fscreate & write file
echo "test" >> ~/fs/test.logread file
cat ~/fs/test.logdelete file
rm ~/fs/test.logmake directory
mkdir ~/fs/dremove directory
rm ~/fs/d