| description |
|---|
Fast, easy and reliable testing for your APIs and microservices during development |
Pact is a code-first tool for testing HTTP and message integrations using contract tests. Contract tests assert that inter-application messages conform to a shared understanding that is documented in a contract. Without contract testing, the only way to ensure that applications will work correctly together is by using expensive and brittle integration tests.
Do you set your house on fire to test your smoke alarm? No, you test the contract it holds with your ears by using the testing button. Pact provides that testing button for your code, allowing you to safely confirm that your applications will work together without having to deploy the world first.
{% hint style="info" %} To view an animated step-by-step explanation of how Pact works, check out this page at pactflow.io {% endhint %}
{% hint style="success" %} Ready to jump into the code already? Get started with our 5 minute guide. {% endhint %}
Contract testing is a technique for testing an integration point by checking each application in isolation to ensure the messages it sends or receives conform to a shared understanding that is documented in a "contract".
For applications that communicate via HTTP, these "messages" would be the HTTP request and response, and for an application that used queues, this would be the message that goes on the queue.
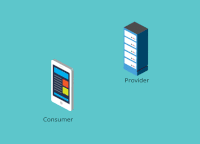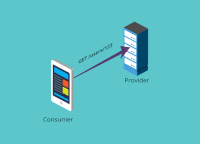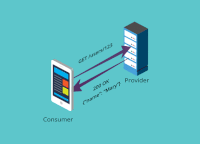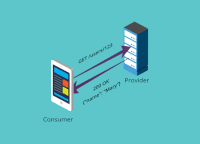
In practice, a common way of implementing contract tests (and the way Pact does it) is to check that all the calls to your test doubles return the same results as a call to the real application would.
Contract testing is immediately applicable anywhere where you have two services that need to communicate - such as an API client and a web front-end. Although a single client and a single service is a common use case, contract testing really shines in an environment with many services (as is common for a microservice architecture). Having well-formed contract tests makes it easy for developers to avoid version hell. Contract testing is the killer app for microservice development and deployment.
In general, a contract is between a consumer (for example, a client that wants to receive some data) and a provider (for example, an API on a server that provides the data the client needs). In microservice architectures, the traditional terms client and server are not always appropriate -- for example, when communication is achieved through message queues. For this reason, we stick to consumer and provider in this documentation.
Pact is a code-first consumer-driven contract testing tool, and is generally used by developers and testers who code. The contract is generated during the execution of the automated consumer tests. A major advantage of this pattern is that only parts of the communication that are actually used by the consumer(s) get tested. This in turn means that any provider behaviour not used by current consumers is free to change without breaking tests.
Unlike a schema or specification (eg. OAS), which is a static artefact that describes all possible states of a resource, a Pact contract is enforced by executing a collection of test cases, each of which describes a single concrete request/response pair - Pact is, in effect, "contract by example".
To learn by doing, get started with our 5 minute guide.