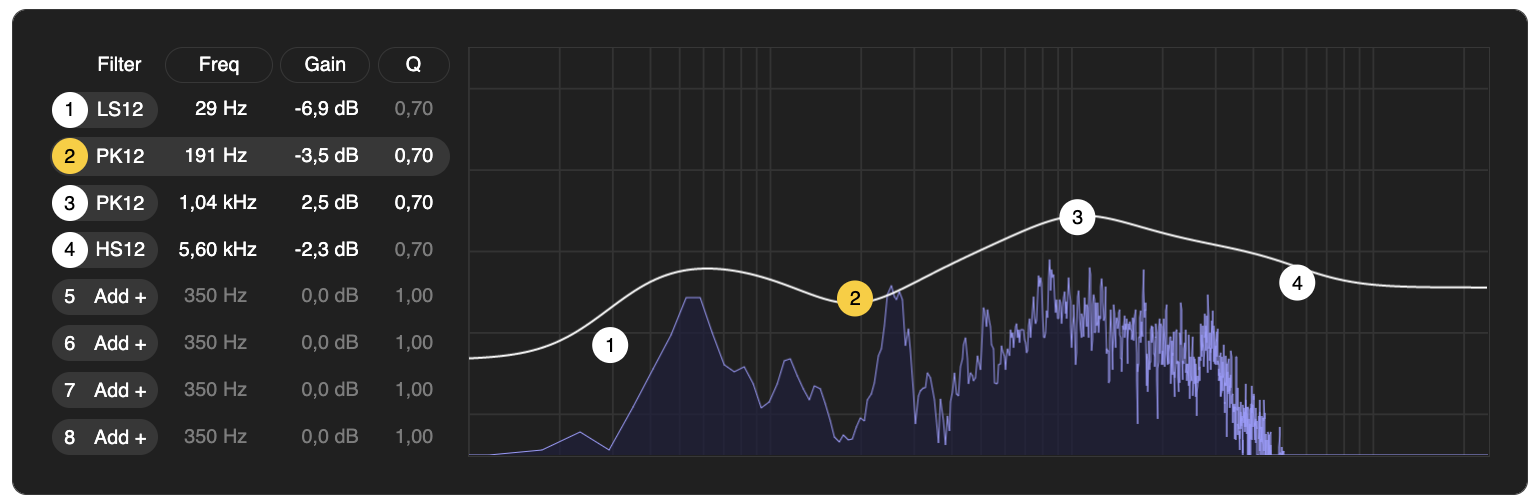
A parametric equaliser for Web Audio.
Try the live demo.
Sculpt the spectrum of your Web Audio graph using a filter bank of up to eight filters, with an intuitive UI inspired by Ableton Live's EQ Eight.
- Built on top of standard BiquadFilterNodes.
- Includes lowpass, highpass, lowshelf, highshelf, peaking, and notch filters, all with -12dB or -24dB roll-off.
- Controlled with a Web Component UI, or headlessly with a TypeScript/JavaScript API.
As an NPM package:
yarn add weq8
# or
npm install weq8The audio processing of the equaliser all happens in an instance of the WEQ8Runtime class. You'll need to import it, initialise it using your AudioContext, and connect it to the signal path of the audio source you wish to equalise:
import { WEQ8Runtime } from "weq8"; // or from "https://cdn.skypack.dev/weq8"
let weq8 = new WEQ8Runtime(yourAudioCtx);
yourAudioSourceNode.connect(weq8.input);
weq8.connect(yourAudioDestinationNode);The user interface for the equaliser is provided by a Web Component called <weq8-ui />. First import the UI module so that this web component gets registered:
import "weq8/ui"; // or "https://cdn.skypack.dev/weq8/ui"Then in your HTML, where you want the equaliser UI to appear, add the element:
<weq8-ui />And finally, connect the WEQ8Runtime you initialised into this UI by setting it as a property:
document.querySelector("weq8-ui").runtime = weq8;You should see the fully functional UI appear on your page.
You can also control the EQ runtime directly with JavaScript. This is useful if you have some alternative UI controls you wish to use, or if you want to operate the EQ fully headlessly.
Note: If you're only using programmatic control, you need not import the weq8/ui module at all, and can operate purely on the runtime.
All control methods take the filter number 0-7 as the first argument.
weq8.setFilterType(filterNumber, "lowpass12"); // or "lowpass24", "highpass12", "highpass24", "bandpass", "lowshelf12", "lowshelf24", "highshelf12", "highshelf24", "peaking12", "peaking24", "notch12", "notch24"
weq8.toggleBypass(filterNumber, true); // true to bypass this filter, false to (re-)connect it.
weq8.setFilterFrequency(filterNumber, 1000); // filter frequency in Hz
weq8.setFilterQ(filterNumber, 1.0); // filter Q
weq8.setFilterGain(filterNumber, 0.0); // filter gain in dBThe types, frequencies, Qs, and gains are as documented for the standard BiquadFilterNode. The filter types suffixed with 12 are singular BiquadFilterNodes and the types suffixed with 24 are two BiquadFilterNodes in series.
This library does not persist the filter configuration between page loads. Instead, it provides a data structure you can serialize and load back, so that you may persist it on the application level.
To get notified whenever the filter state changes, subscribe to the filtersChanged event on the runtime:
weq8.on("filtersChanged", (state) => {
// state is a data structure you can store in a variable, or serialize to JSON.
});When initialising the runtime on a subsequent load, you may provide a previous state to directly load the equaliser into:
let weq8 = new WEQ8Runtime(yourAudioCtx, state);Run yarn dev and open your browser in http://localhost:3000 to get a development page with live reloading.