Replacing earlier version NocMigR
This package provides workflows for processing sound files, especially
comprising bird vocalisations sampled with autonomous recording devices
(e.g., NocMig, NFC and AudioMoth recordings), with a main emphasis
on (semi-)automatising the the detection and labelling of events with
proper times-stamps. Resulting data can then be reviewed and validated
using Audacity (recommended version
3.0.2).
Among others, this package relies on the following libraries:
R packages: bioacoustics, seewave, tuneR, WarbleR
python: audioop, BirdNET-Analyzer, pydub
To install the package, use devtools:
devtools::install_github("mottensmann/NocMigR2")NocMigR2 depends on warbleR which is currently (as of 2024-07-26)
missing on CRAN. If the installation above fails try:
devtools::install_github("maRce10/warbleR")Load the package once installed:
library(NocMigR2)Rename audio files using a string of the form YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS that
denotes the date and time of the recording start.
This convenient format is for example used by the
AudioMoth), whereas other
popular recording devices (e.g. PCM recorders by Olympus, Tascam and
alike) typically use rather uninformative naming schemes (date +
chronological number at best). rename_recording retrieves the ctime
(creation time) from audio files to compose a date_time
('YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS'}) string. Note, audio recorders vary in the way
individual audio files are saved when in continuous recording mode.
Supported options are:
-
ctime = 'first': (e.g. Olympus LS-3) Each audio file shares the ctime of the first file. Therefore ctime of subsequent recordings are easily computed. -
ctime = 'each': (e.g. Sony PCM D100) Each audio file is handled individually and therefore saved with unique ctime.
## Example:
## new.name corresponds to creation time of package!
## -------
rename_recording(
## path to file(s)
path = system.file("extdata", package = "NocMigR2"),
## specify how to handle ctimes
ctime = "first",
## file extension
format = "wav",
## only show new name
.simulate = TRUE)
#> old.name new.name
#> 1 20211220_064253.wav 20240806_142737.wavRetrieve time of dusk and dawn for a given location using the suncalc package:
## Example
## -------
dusk2dawn(
date = Sys.Date(), ## Date
lat = 52.032090, ## Latitude in decimal degrees
lon = 8.516775, # Longitude in decimal degrees
tz = "CET") # Time zone
#> dusk dawn string
#> 1 2024-08-06 21:49:09 2024-08-07 05:18:52 6.8-7.8.2024, 21:49-05:18Create header used to add a comment to observation lists ornitho:
Composing a string describing a past NocMig night following recommendations by Schütze et al 2022 (HGON) using:
- Bright Sky (de Maeyer 2020) to retrieve weather data for a given location.
- suncalc to retrieve time of dusk and dawn
## usage -------
NocMig_meta(date = Sys.Date() - 1, lat = 52.032, lon = 8.517)
#> Teilliste 1: 5.8-6.8.2024, 21:51-05:17, trocken, 15°C, SE, 11 km/h
#> Teilliste 2: 5.8-6.8.2024, 21:51-05:17, trocken, 14°C, SSW, 4 km/hCreate custom species list for target species:
Filters the extensive BirdNET_GLOBAL_6K_V2.4_Labels file for selected target species. Target species can be selected based on scientific species names or common species names in all languages currently supported by BirdNET-Analyzer.
## examples
## --------
BirdNET_species.list(
## target species
names = c("Glaucidium passerinum", "Bubo bubo"),
sciNames = TRUE,
BirdNET_path = "../BirdNET-Analyzer/",
species_list = "Insert Path here ... ",
## only show df, not exporting to text file
.write_text = FALSE)
#> sciName comName
#> 1 Bubo bubo Eurasian Eagle-Owl
#> 2 Glaucidium passerinum Eurasian Pygmy-Owl
BirdNET_species.list(
names = c("Sperlingskauz", "Uhu"),
lang = "de",
sciNames = FALSE,
BirdNET_path = "../BirdNET-Analyzer/",
species_list = "Insert Path here ... ",
## only show df, not exporting to text file
.write_text = FALSE)
#> sciName comName
#> 1 Bubo bubo Eurasian Eagle-Owl
#> 2 Glaucidium passerinum Eurasian Pygmy-OwlUsing BirdNET-Analyzer to process audio data
- Installing Ubuntu environment. Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) works well for this purpose. see WSL for explanations
- Setup BirdNET-Analyzer following the Setup Ubuntu section
Then bash code-chunks (shown below) can be executed using WSL. Pre-
and post processing stays within R.
- Setup BirdNET-Analyzer following the Setup Ubuntu section
Then, using
RStudio
analyzer.py can be used by simply inserting bash code-chunks within
RMarkdown documents!
Using analyzer.py for detecting signals:
- Use the sample audio file for demonstration purposes:
## create temp folder
dir.create("test_folder")
#> Warning in dir.create("test_folder"): 'test_folder' already exists
## Copy sample
sample <- system.file("extdata", "20211220_064253.wav", package = "NocMigR2")
file.copy(from = sample, to = file.path("test_folder", "20211220_064253.wav"))- Run
analyzer.py(See documentation here)
## bash
## -----------------------------------
## Set working dir to BirdNET-Analyzer
cd PATH TO BirdNET-Analyzer## bash
## ---------------
## run analyze.py
python3 analyze.py --i /test_folder --o /test_folder
--min_conf 0.7 --rtype 'audacity' --threads 1 --locale 'de'## Example RStudio on Raspberry Pi 4
## -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
cd ../BirdNET-Analyzer
python3 analyze.py --i ../NocMigR2/test_folder --o ../NocMigR2/test_folder --min_conf 0.7 --rtype 'audacity'The function BirdNET (see ?BirdNET for details) does the following:
- Reshape audacity labels created by
analyze.py(with--rtype 'audacity') to include the event time estimated from file names: [CreatesBirdNET.labels.txtfor eachBirdNET.results.txtfile] - Write records to BirdNET.xlsx as a template to simplify inspection and verification of the records.
df <- BirdNET(path = "test_folder/",
## adding optional meta data
meta = BirdNET_meta(
Location = "Place A",
Lat = 52,
Lon = 8,
Device = "Recorder B",
Micro = "Mic C",
## analyze.py settings
Min_conf = 0.7,
Overlap = 0,
Sensitivity = 1.0,
Slist = "BirdNET_V2.4"))
#> Calculate total duration of 1 recordings:
#> Created test_folder//BirdNET.xlsx## load and show overview overview
str(openxlsx::read.xlsx("test_folder/BirdNET.xlsx", "Records"))
#> 'data.frame': 1 obs. of 12 variables:
#> $ Taxon : chr "Eurasian Pygmy-Owl"
#> $ Detector : chr "BirdNET"
#> $ ID : num NA
#> $ T1 : num 44550
#> $ T2 : num 44550
#> $ Score : num 0.776
#> $ Verification: num NA
#> $ Correction : num NA
#> $ Quality : num NA
#> $ Comment : num NA
#> $ T0 : num 44550
#> $ File : chr "test_folder/20211220_064253.BirdNET.results.txt"
str(openxlsx::read.xlsx("test_folder/BirdNET.xlsx", "Meta"))
#> 'data.frame': 1 obs. of 12 variables:
#> $ Location : chr "Place A"
#> $ Lat : num 52
#> $ Lon : num 8
#> $ From : num 44550
#> $ To : num 44550
#> $ Duration : chr "14.92 seconds"
#> $ Device : chr "Recorder B"
#> $ Micro : chr "Mic C"
#> $ Min_conf : num 0.7
#> $ Overlap : num 0
#> $ Sensitivity: num 1
#> $ Slist : chr "BirdNET_V2.4"Extract detections and export them as wave files. For easier access to
verify records files are named as ‘Species_Date_Time.WAV’ and
corresponding hyperlinks are inserted in the .xlsx file created with
BirdNET() (see below).
## extract events and add hyperlink
BirdNET_extract(path = "test_folder", hyperlink = TRUE)
#> Extract events ...## show created dirs
list.dirs("test_folder/extracted/", recursive = F)
#> [1] "test_folder/extracted/Eurasian Pygmy-Owl"
## show content for Eurasian Pygmy-OWl
list.files("test_folder/extracted/Eurasian Pygmy-Owl/")
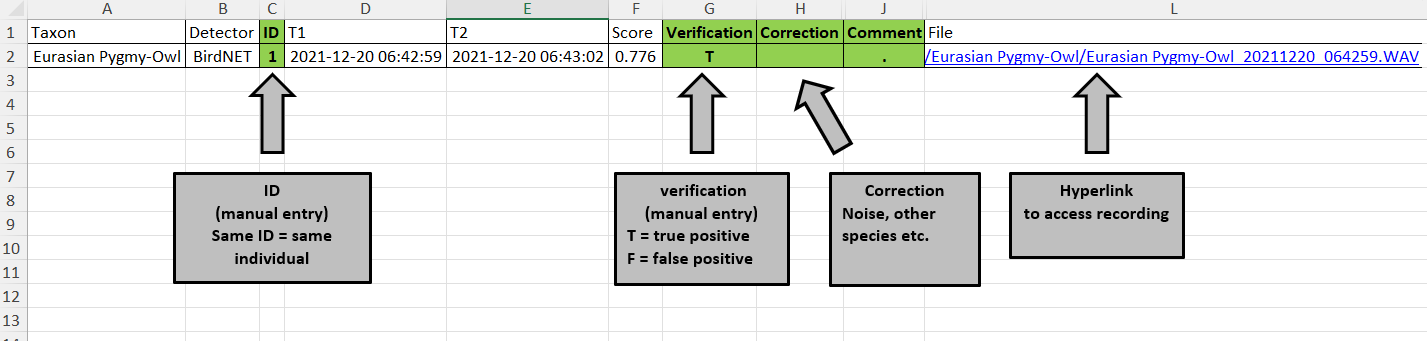
#> [1] "Eurasian Pygmy-Owl_20211220_064259.WAV"- Content of
xlsx file
Summary table of BirdNET detection ready for manual review &
verification (attributes: Verification, Correction, Comment).
Automatically provided are BirdNET annotations (Taxon) along with the
corresponding confidence score (Score) and event time (T1 = start,
T2 = end). Manually recovered events may be added to the same file by
setting Detector = 'Manual' or alike}
Under development
Archive verified records (see screenshot above) using
BirdNET_archive:
out <- BirdNET_archive(BirdNET_results = "test_folder/BirdNET.xlsx", path2archive = "test_folder",
db = "test_folder/db.xlsx", NocMig = FALSE, keep.false = TRUE)
str(out)
#> 'data.frame': 1 obs. of 19 variables:
#> $ Date : chr "2021-12-20"
#> $ Taxon : chr "Eurasian Pygmy-Owl"
#> $ sum : int 1
#> $ sum1 : int 0
#> $ str1 : logi NA
#> $ sum2 : int 1
#> $ str2 : chr "06:1"
#> $ Location : chr "Place A"
#> $ Lat : num 52
#> $ Lon : num 8
#> $ From : POSIXct, format: "2021-12-20 06:42:53"
#> $ To : POSIXct, format: "2021-12-20 06:43:07"
#> $ Duration : chr "14.92 seconds"
#> $ Device : chr "Recorder B"
#> $ Micro : chr "Mic C"
#> $ Min_conf : num 0.7
#> $ Overlap : num 0
#> $ Sensitivity: num 1
#> $ Slist : chr "BirdNET_V2.4"
## show folder structure
list.files("test_folder/")
#> [1] "20211220_064253.BirdNET.labels.txt" "20211220_064253.BirdNET.results.txt"
#> [3] "20211220_064253.wav" "BirdNET.xlsx"
#> [5] "db.xlsx" "extracted"
#> [7] "False positives" "True positives"Mainly a backup from previous package NocMigR)
Signal detection based on SNR (signal to noise ratio) wrapping
threshold_detection() of the
bioacoustics package.
Additional parameters allow further fine-tuning by specifying frequency
characteristics and call length of targets of interest. Note: For bird
calls using
BirdNET-Analyzer is the
recommended alternative. Detections are exported as Audacity labels
using seewave:
TD <- find_events(wav.file = "test_folder/20211220_064253.wav",
audacity = TRUE, # Write audacity labels
threshold = 8, # SNR in db
min_dur = 20, # min length in ms
max_dur = 300, # max length in ms
LPF = 5000, # low-pass filter at 500 Hz
HPF = 1000) # high-pass filter at 4 kHz
## Review events
head(TD$data$event_data[,c("filename", "starting_time", "duration", "freq_max_amp")])
#> filename starting_time duration freq_max_amp
#> 1 20211220_064253.wav 00:00:06.169 169.07029 1483.850
#> 2 20211220_064253.wav 00:00:06.638 192.29025 1647.574
#> 3 20211220_064253.wav 00:00:07.481 116.09977 1790.988
#> 4 20211220_064253.wav 00:00:07.872 150.20408 1900.730
#> 5 20211220_064253.wav 00:00:08.365 94.33107 2032.121
#> 6 20211220_064253.wav 00:00:08.945 29.02494 2180.925If audacity = TRUE a file with labels for reviewing events in
Audacity is created (wrapping seewave::write.audacity()).
- Extract detected events from raw audio file
Refines the output of find_events by first adding a buffer (default 1
second on both sides of the event) and subsequently merging overlapping
selections (detections likely belonging to the same calling event) to
make the output more pretty. Additionally, allows to filter based on
expected frequencies (i.e., checks maximum amplitude frequency is within
the frequency band defined by LPF and HPF). Returns a shortened
audio file containing only the selected events (e.g,
“20211220_064253_extracted.txt” along with the corresponding Audacity
labels “20211220_064253_extracted.txt”)
## extract events based on object TD
df <- extract_events(threshold_detection = TD, path = "test_folder", format = "wav",
LPF = 4000, HPF = 1000, buffer = 1)Basic function to split large audio files in chunks. Internally calls the python library pydub with reticulate.:
Short audio segments are saved in a subfolder named ‘split’.
## split in segments
split_wave(file = "20211220_064253.wav", # audio file
path = "test_folder/", # folder
segment = 3) # cut in 3 sec segments
#> Split ...
## show files
list.files("test_folder/split/")
#> [1] "20211220_064253.wav" "20211220_064256.wav" "20211220_064259.wav"
#> [4] "20211220_064302.wav" "20211220_064305.wav"