This confluence checker is designed to check backwards-confluence of hypergraph replacement grammars with a data structure property. This tool is designed to help Attestor check grammars for confluence and complete them in case they are not confluent. This guarantees uniquenes of abstraction in the symbolic execution phase of Attestors verification process. A confluent grammar especially allows efficient language inclusion check, as well as entailment checking for a fragement of seperation logic.
The following software has to be installed prior to the installation of Attestor:
To install the latest version of the Attestor confluence checker, please proceed as follows:
$ git clone https://github.com/moves-rwth/attestor-confluence.git
$ mvn install
Please note that the installation requires an internet connection as maven will install additional dependencies.
After installation, an executable jar file is created in the directory target within the cloned repository. The name of executable jar is of the form
attestor-confluence-<VERSION>-jar-with-dependencies.jar
where <VERSION> is the previously cloned version of the Attestor repository.
To execute Attestor, it suffices to run
$ java -jar attestor-confluence-<VERSION>-jar-with-dependencies.jar
from within the target directory.
This should display a help page explaining all available command line options.
Since the above jar file contains all dependencies, it is safe to rename it and move the file to a more convenient directory.
The confluence checker for Attestor comes with a command line inspired by the main project with a subset of its features. The confluence checker allows
-
parsing data structure grammars in a JSON format,
-
parsing inductive predicate definitions specifying predicates in a symbolic heap fragment of separation logic,
-
checking confluence of the specified grammar,
-
trying to complete the specified grammar to confluence, and
-
exporting LaTeXfiles graphically depicting the grammars and critical pairs.
In the following, we will give a tour on how to use the confluence checker that is sufficient for most cases. For further details, please consult the documentation of all command line options.
To specify the grammar, there are multiple ways to do so as mentioned before. For this tour, we will stick to a data structure grammar in JSON format. A grammar consists of an array of rules. Each rule object defines the set of rules with the same nonterminal on the left-hand side. We further have to specify the rank of that nonterminal (as we allow nonterminal edges to have more than two connected nodes) and an array of graphs that depict the right-hand sides of rules. The right-hand sides define heap configuration objects (read hypergraphs) which we also define using JSON syntax. As this tool's main purpose is to analyze heap-manipulating programs, the definition of grammars is highly adapted to graphs that depict (possible abstracted) heaps. For this reason, we assume that all our terminal graphs are labelled digraphs of rank 2. We define a heap configuration object by
-
node objects, which themselves consist of a type and an id,
-
an array of ids of nodes depicting the external nodes,
-
an array of variables, which we will ignore and leave empty,
-
an array of selectors, i.e., terminal edges of rank 2, consisting of a label, an origin node and a target node, and
-
an array of hyperedges, i.e., nonterminal edges, consisting of a label and an array of ids of nodes. The order of nodes in the array also specifies the order in which external nodes are mapped to these nodes in case of a graph transformation.
Assuming that file ./sDLL.json contains the grammar SimpleDLL in
JSON format, we can issue the command
java -jar attestor-confluence.jar -g ./sDLL.json
to load the grammar and check its confluence. After successful computation, the following report is displayed:
[Version] attestor-confluence - version 0.4.1-SNAPSHOT
[Summary] The grammar is NOT backwards confluent.
+-------------------------+------------------+
| Strongly Joinable Pairs | 2 |
| Weakly Joinable Pairs | 0 |
| Non-Joinable Pairs | 1 |
+-------------------------+------------------+
+-----------------------------+--------------+
[Summary] | Phase | Runtime |
+-----------------------------+--------------+
| Confluence Command Line | 0.001 s |
| Parse grammar | 0.044 s |
| Confluence Check | 0.020 s |
| Confluence Completion | 0.000 s |
| Confluence Report | 0.000 s |
+-----------------------------+--------------+
| Total verification time | 0.020 s |
| Total runtime | 0.065 s |
+-----------------------------+--------------+
This report tells us that the grammar is not backwards confluent in
the first line of the summary and afterwards presents the number of
critical pairs. The strongly joinable pairs are irrelevant for further
computation, as they do not infer with confluence. To complete the
grammar, we have to choose a heuristic algorithm. Here, we select
singleNonterminalRuleAddingHeuristic by appending it as a new option:
java -jar attestor-confluence.jar -g ./sDLL.json
-ca singleNonterminalRuleAddingHeuristic
This command produces the following report:
[Version] attestor-confluence - version 0.4.1-SNAPSHOT
[Summary] The grammar is NOT backwards confluent.
+-------------------------+------------------+
| Strongly Joinable Pairs | 2 |
| Weakly Joinable Pairs | 0 |
| Non-Joinable Pairs | 1 |
+-------------------------+------------------+
[Summary] The grammar is backwards confluent after completion.
+-----------------------------+--------------+
[Summary] | Phase | Runtime |
+-----------------------------+--------------+
| Confluence Command Line | 0.001 s |
| Parse grammar | 0.040 s |
| Confluence Check | 0.020 s |
| Confluence Completion | 0.056 s |
| Confluence Report | 0.000 s |
+-----------------------------+--------------+
| Total verification time | 0.020 s |
| Total runtime | 0.117 s |
+-----------------------------+--------------+
Thus we see that the completion was successful. Lastly, we can also output tikz representations of all critical pairs, the input grammar and the (completed) output grammar by adding a path to the output folder:
java -jar attestor-confluence.jar -g ./sDLL.json
-ca singleNonterminalRuleAddingHeuristic -export-latex ./export
This will fill the output directory ./export with LaTeXfiles that need
to be compiled using the lualatex compiler. The compiled tikz
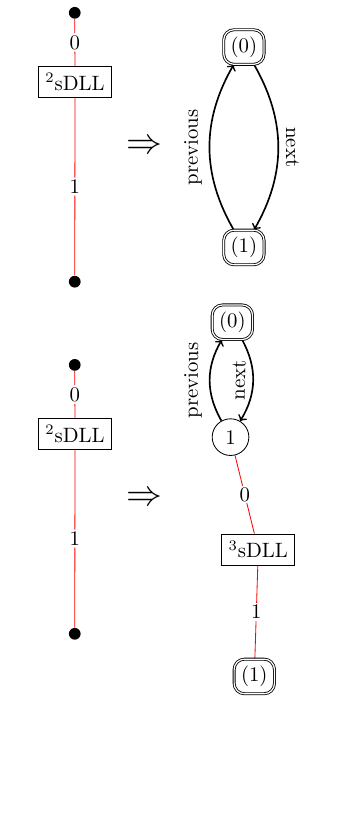
representation of our input grammar ./sDLL.json can be seen in the image below.
Determines the provided path as a common prefix for all other paths provided in command line options. More precisely, affected options whose arguments are concatenated with prefix PATH are:
Specifies a name for the grammar as TEXT. Does not have any technical purpose, other than displaying the name on the report.
Loads a user-supplied graph grammar from the provided GRAMMAR_FILE.
Please confer syntax for graph grammars for further details on writing custom graph grammars.
If --root-path (link) is set then the common root path is added as a prefix to the grammar file.
Loads a user-supplied system of inductive predicate definitions (SID) written in a fragment of symbolic heap separation logic. The SID will internally be converted into a graph grammar. Please confer the syntax for inductive predicate definitions for further details on writing custom predicate definitions.
If --root-path (link) is set then the common root path is added as a prefix to the input file.
Adds a predefined graph grammar with the provided name to the grammars. The predefined grammars are:
- SLList
- DLList
- BT
For more information, also confere the specification of predefined graph grammars.
Uses the completion algorithm specified by NAME.
Available completion algorithms are:
completionAbstractionBlockingaddRulesNewNonterminalHeuristicjoinGeneratedNonterminalssingleNonterminalRuleAddingHeuristicruleRestrictiononlyRuleAddingonlyRuleAddingNotLocalConcretizablecombinedAlgorithm1combinedAlgorithm1NoLocalConcretizabilityCheckcombinedAlgorithm2combinedAlgorithm2NoLocalConcretizabilityCheck
Adds the completion heuristics with names in the list LIST_OF_NAMES to the completion algorithm. The list is structured as the list of names seperated by commans. If no completion algorithm is specified, a default algorithm with no heuristics is used.
Available completion heuristics are:
AddRulesNewNonterminalCompletionAbstractionBlockingCompletionRuleRestrictionJoinGeneratedNonterminalsSingleNonTerminalRuleAdding
For more information, also see the specification of the heuristics.
Exports the graph grammar after completion. The exported grammar is written to the directory PATH.
If --root-path (link) is set then the common root path is added as a prefix to the input file.
Exports the latex output as a tikz visualization for critical pairs before completion and the not strongly-joinable critical pairs after completion, as well as the grammar before completion and after completion in the directory PATH.
If --root-path (link) is set then the common root path is added as a prefix to the input file.
Suppresses all output generated by the logger.
Generate additional logging output that does not require knowledge about implementation details.
Generate additional logging output that may require deep knowledge about implementation details.