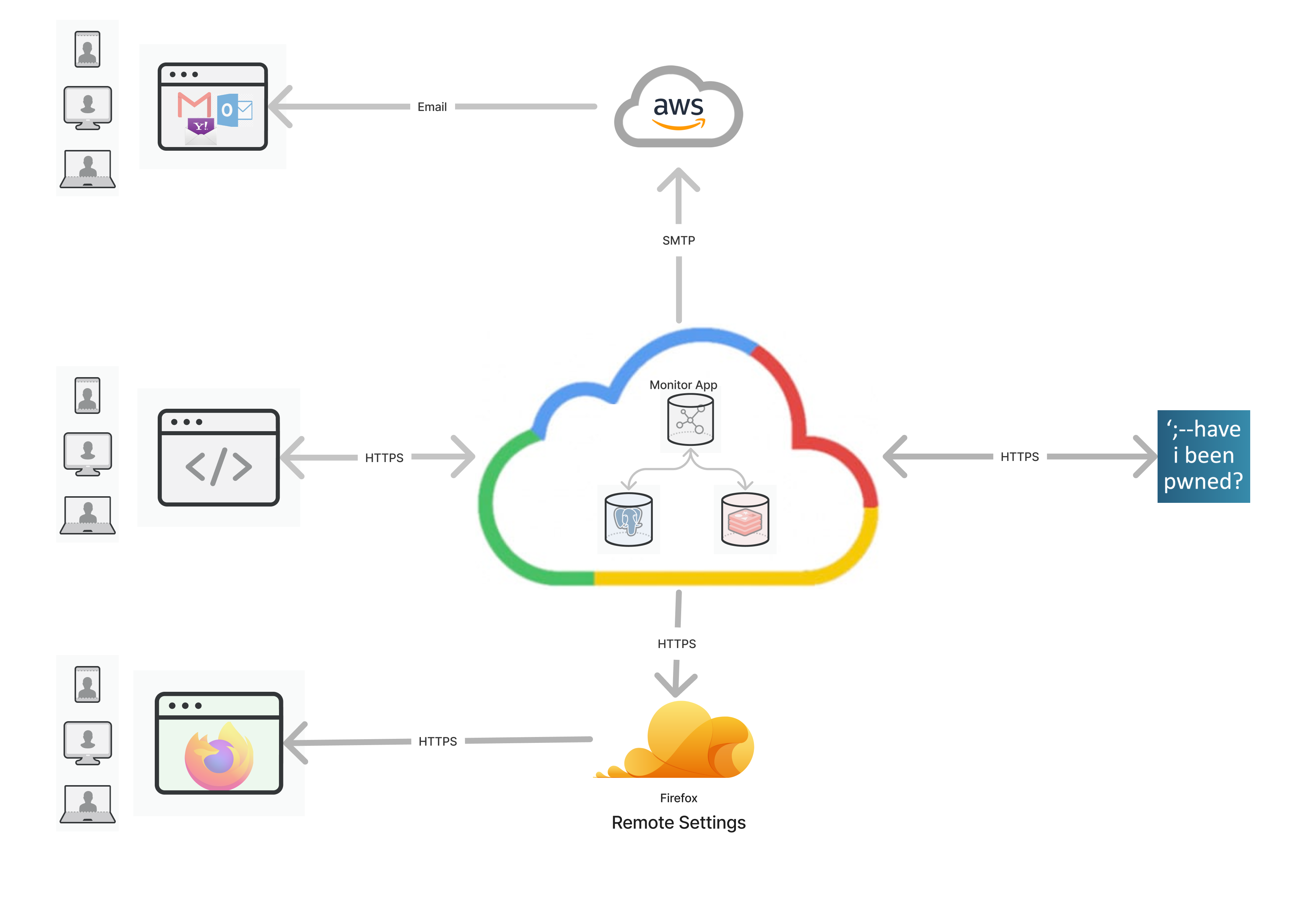
Firefox Monitor notifies users when their credentials have been compromised in a data breach.
This code is for the monitor.mozilla.org service & website.
Breach data is powered by haveibeenpwned.com.
See the Have I Been Pwned about page for the "what" and "why" of data breach alerts.
- Volta (installs the correct version of Node and npm)
- Postgres | Note: On a Mac, we recommend downloading the Postgres.app instead.
- Python | With Homebrew
- k6 | k6 load testing tool
Linting and formatting is enforced via ESLint and Stylelint for JS and CSS. Both are installed as dev-dependencies and can be run with npm run lint. A push to origin will also trigger linting.
ESLint rules are based on eslint-config-standard. To fix all auto-fixable problems, run npx eslint . --fix
Stylelint rules are based on stylelint-config-standard. To fix all auto-fixable problems, run npx stylelint public/css/ --fix
We track commits that are largely style/formatting via .git-blame-ignore-revs. This allows Git Blame to ignore the format commit author and show the original code author. In order to enable this in GitLens, add the following to VS Code settings.json:
"gitlens.advanced.blame.customArguments": [
"--ignore-revs-file",
".git-blame-ignore-revs"
],
To create the database tables ...
-
Create the
blurtsdatabase:createdb blurts createdb test-blurts # for tests -
Update the
DATABASE_URLvalue in your.env.local(see step 3 under "Install") file with your local db credentials:DATABASE_URL="postgres://<username>:<password>@localhost:<port>/blurts" -
Run the migrations:
npm run db:migrate
-
Clone and change to the directory:
git clone https://github.com/mozilla/blurts-server.git cd blurts-server -
Install dependencies:
npm install
-
Copy the
.env.local.examplefile to.env.local:cp .env.local.example .env.local
-
Install fluent linter (requires Python)
pip install -r .github/requirements.txt OR pip3 install -r .github/requirements.txt
-
Generate required Glean files (needs re-ran anytime Glean
.yamlfiles are updated):npm run build-glean
-
Generate required Nimbus files (needs re-ran anytime Nimbus'
config/nimbus.yamlfile is updated):npm run build-nimbus
-
Create location data: Running the script manually is only needed for local development. The location data is being used in the onboarding exposures scan for autocompleting the “City and state” input.
npm run create-location-data
-
Ensure that you have the right
envvariables/keys set in your.env.localfile. You can retrieve the variables from the Firefox Monitor 1Password Vault, or through Magic-Wormhole, by asking one of the our engineers.
-
To run the server similar to production using a build phase, which includes minified and bundled assets:
npm start
OR
Run in "dev mode" with:
npm run dev
-
You may receive the error
Required environment variable was not set. If this is the case, get the required env var(s) from another team member or ask in #fx-monitor-engineering. Otherwise, if the server started successfully, navigate to localhost:6060
Monitor uses GCP PubSub for processing incoming breach data, this can be tested locally using an emulator: https://cloud.google.com/pubsub/docs/emulator
gcloud beta emulators pubsub start --project=your-project-name(Set your-project-name as the value for GCP_PUBSUB_PROJECT_ID in your .env.local.)
$(gcloud beta emulators pubsub env-init)
npm run devcurl -d '{ "breachName": "000webhost", "hashPrefix": "test", "hashSuffixes": ["test"] }' \
-H "Authorization: Bearer unsafe-default-token-for-dev" \
http://localhost:6060/api/v1/hibp/notifyThis emulates HIBP notifying our API that a new breach was found. Our API will then add it to the (emulated) pubsub queue.
This pubsub queue will be consumed by this cron job, which is responsible for looking up and emailing impacted users:
NODE_ENV="development" npm run dev:cron:breach-alertsMonitor generates multiple emails that get sent to subscribers. To preview or test-send these emails see documentation here.
The repo comes with a development FxA oauth app pre-configured in .env, which
should work fine running the app on http://localhost:6060. You'll need to get
the OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET value from a team member or someone in #fxmonitor-engineering.
The unit test suite can be run via npm test.
At the beginning of a test suite run, the test-blurts database will be populated with test tables and seed data found in src/db/seeds/
At the end of a test suite, coverage info will be sent to Coveralls to assess coverage changes and provide a neat badge. To upload coverage locally, you need a root .coveralls.yml which contains a token – get this from another member of the Monitor team.
End-to-End tests use Playwright and can be run via npm run e2e. E2E-How-To for more info.
TODO: the following functionality is disabled but the instructions are left here for posterity.
Firefox's internal about:protections page ("Protections Dashboard") fetches and displays breach stats for Firefox users who are signed into their FXA.
To test this part of Monitor:
- Set a Firefox profile to use the staging Firefox Accounts server.
- In the same profile, go to about:config and replace all
https://monitor.firefox.comvalues withhttp://localhost:6060 - Restart Firefox with that profile.
- Go to
about:protections - Everything should be using your localhost instance of Monitor.
k6 is used for load testing.
To test the HIBP breach alerts endpoint, use:
export SERVER_URL=...
export HIBP_NOTIFY_TOKEN=...
npm run loadtest:hbibp-webhookYou can customise the number of requests to send in parallel ("virtual users") by setting the
K6_VUS environment
variable (default 1000), and for how long to send those requests by setting the
K6_DURATION
environment variable (default 30s).
You can also enforce the alert being sent for a specific email address via the
LOADTEST_BREACHED_EMAIL environment variable.
See https://grafana.com/docs/k6/latest/get-started/running-k6/ for more information.
All text that is visible to the user is defined in Fluent files inside /locales/en/ and /locales-pending/. After strings get added to files in the former directory on our main branch, they will be made available to our volunteer localizers via Pontoon, Mozilla's localization platform. Be sure to reference the localization documentation for best practices. It's best to only move the strings to /locales/en/ when they are more-or-less final and ready for localization. Your PR should be automatically tagged with a reviewer from the Mozilla L10n team to approve your request.
You can check translation status via the Pontoon site. After strings have been localized, a pull request with the updated strings is automatically opened against our repository. Please be mindful that Mozilla localizers are volunteers, and translations come from different locales at different times – usually after a week or more.
To use the strings in code, you need to obtain a ReactLocalization instance, which selects the right version of your desired string for the user. How to do that depends on where your code runs: in tests, in a cron job, in a server component, or on the client-side. Generally, you will import a getL10n function from one of the modules in /src/app/functions/l10n/, except for Client Components, which use the useL10n hook. Look at existing code for inspiration.
We use GCP Cloudrun for dev review – official stage and production apps are built by the Dockerfile and Github Actions. Everything that is merged into main will deploy automatically to stage. The ADR for preview deployment can be found here
TODO: add full deploy process similar to Relay
TODO: consider whether we can re-enable Heroku Review Apps