Capabilities, benefits, and best practices
Date: 1/18/17
Presenter: Vyom Nagrani
- Working with AWS Lambda
- development and testing
- deployment and alm
- security and scaling
- debugging and operations
- Q & A
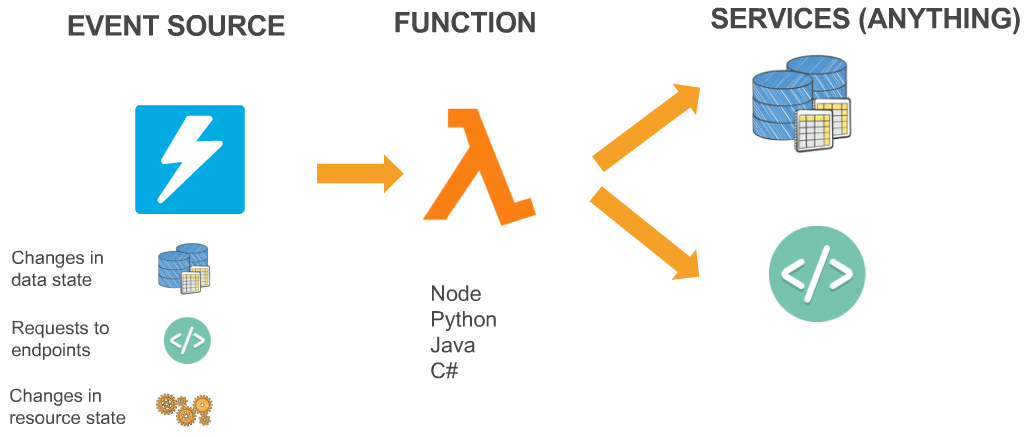
- productivity-focused compute platform to build powerful, dynamic, modular applications in the cloud
- no infrastructure to manage
- cost-effective and efficient
- bring your own code
- Amazon S3
- Amazon DynamoDB
- Amazon Kinesis
- Amazon Cognito
- Amazon Alexa
- Amazon API Gateway
- AWS IoT
- AWS CloudFormation
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS CodeCommit
- Amazon CloudWatch
- Amazon SES
- Amazon SNS
- Amazon Cron events
- stateless processing of discrete or streaming updates to your data-store or message bus
- execute server side backend logic for web, mobile, device, or voice user interactions
- customize responses and response workflows to state and data changes within AWS
- Node.js 4.3, Java 8, Python 2.7, C#
- select power rating from 128 MB to 1.5 GB
- CPU and network allocated proportionately
- synchronous or asynchronous
- integrated with other AWS services
- Persist data using external storage
- no affinity or access to underlying infrastructure
- the method in your code where AWS Lambda begins execution
- Pre-defined object format for AWS integrations & events
- Java & C# support simplet data types, POJOs/POCOs, and Stream input/output
- use methods and properties like
getRemainingTimeInMillis(),identity,awsRequestId,invokedFunctionArn,clientContext,logStreamName
- enables private communication with other resources within your VPC
- provide EC2 security group and subnets, auto-creates ENIs
- Internet access can be added through NAT Gateway
- failed events sent to your SQS queue / SNS topic
- redrive messages that Lambda could not process
- Currently available for asynchronous invocations only
- Add custom key/value pairs as part of configuration
- reuse code across different setups or passwords
- encrypted with specified KMS key on server, decrypted at container init
- declarations in your Lambda function code outside handler()
- disk content in /tmp
- Background processes or callbacks
- make use of container reuse opportunistically, e.g.
- load additional libraries
- cache static data
- database connections
- time to set up a new container ad do necessary bootstrapping when a Lambda function is invoked for the first time or after it has been updated
- Ways to reduce cold start latency
- more memory = faster performance, lower startup time
- smaller function ZIP loads faster
- Node.js and Python start execution faster than Java and C#
- public Amazon Linux AMI version (amen-ami-hvm-)
- Linux kernel version
- Compile native binaries against this environment - can be used to bring your own runtime!
- Changes over time, always check the latest versions supported here http://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/current-supported-versions.html
- ImageMagick (node.js wrapper and native binary)
- OpenJDK 1.8, .NET Core 1.0.1
- AWS SDK for javascript
- .zip file consisting of your code and any dependencies
- use npm/pip to install libraries
- all dependencies must be at root level
- either .zip file with all code/dependencies or standalone jar
- AWS Serverless Application Model - extension optimized for Serverless
- New Serverless resources - APIs, Functions, Tables
- Open specification (Apache 2.0)
- Python serverless micro-framework
- Quickly create and deploy applications
- Set up AWS Lambda and Amazon API Gateway endpoint
- https://github.com/awslabs/chalice
- Serverless Framework http://serverless.com
- Apex Serverless Architecture http://apex.run
- DEEP Framework by Mitoc Group https://github.com/MitocGroup/deep-framework
- versions = immutable copies of code + configuration
- aliases = mutable pointers to versions
- development against $LATEST version
- each version/alias gets its own ARN
- enables rollbacks, staged promotions, "locked" behavior for client
- permissions you grant to your Lambda function determine which service or event source can invoke your function
- resource policies make it easy to grant cross-account permissions to invoke your Lambda function
- Permissions you grant to this role determine what your AWS Lambda function can do
- If event source is...
- For stream-based event sources: number of shards per stream is the unit of concurrency
- For all other event sources: Request rate and duration drives concurrency (concurrency = requests per second * duration)
- For stream-based event sources: automatically retried until data expires
- For Asynchronous invocations: automatically retried for up to six hours with delays between retries
- For synchronous invocations:: Invoking application receives a 429 error and is responsible for retries
- remember, a throttle is NOT an error!
- if you expect sudden large spikes in demand, consider async invocations to Lambda
- proactively engage AWS Support to increase your throttling limits
- build retries/backoff in client apps
- make sure your downstream setup keeps up
- limit concurrency when connecting to relational dbs
- 4xx Client Error: can be fixed by developer
- 5xx Server Error: Most can be fixed by admin, e.g. EC2 ENI management errors (502)
- For stream-based event sources: Automatically retried until data expires
- For Asynchronous invocations: Automatically retried 2 extra times, then published to dead-letter queue
- For Synchronous invocations: Invoking application receives an error code
- collects data about requests that your application serves
- visibility into the AWS Lambda service (dwell time, number of retries, latency, and errors)
- detailed breakdown of your function's performance, including calls made to downstream services and endpoints
- capture calls made to AWS Lambda API; deliver log files to Amazon S3
- tracks the request made to AWS Lambda, the source IP address form which the request was made, who made the request, when it was made
- All control plane APIs can be tracked ...
- every invocation generates START, END, and REPORT entries in CloudWatch Logs
- User logs included
- Default (free) Metrics: Invocations, Duration, Throttles, Errors - available as CloudWatch Metrics
- Additional Metrics: Create custom metrics for tracking health/status
- Function code vs log-filters
- ops-centric vs. business-centric
Key Takeaway
AWS Lambda is one of the core components of the platform AWS provides to develop serverless applications