Project to demonstrate the usage of Apache Spark within a Jupyter notebook within ArcGIS Pro.
Oct 25, 2022 - Updated to support upcoming Pro 3.1. See SparkGeo2 notebook for integration with Apache Arrow :-)
Apr 12, 2022 - Running PySpark in Pro 2.9 requires the PYSPARK_PYTHON environment variable to be set. It should point to the python.exe executable of your active conda environment, e.g., C:\Users\%USERNAME%\AppData\Local\ESRI\conda\envs\spark_esri\python.exe. Defining CONDA_DEFAULT_ENV is neither sufficient and nor necesary.
Dec 16, 2021 - Added check for env var SPARK_HOME to override built-in spark. See instructions below.
Oct 30, 2021 - Pro 2.8 relies on the Windows registry to find the active conda environment. The registry key is HKEY_CURRENT_USER/SOFTWARE/ESRI/ArcGISPro/PythonCondaEnv. The value of this key is used to set the required os environment variable PYSPARK_PYTHON for PySpark to work correctly in a Pro notebook.
As of this writing, the order to detect the active conda environment is as follows:
- look for env var
CONDA_DEFAULT_ENV. - look for
%LOCALAPPDATA%/ESRI/conda/envs/proenv.txt, in case of an older Pro version. - look for
HKEY_CURRENT_USER/SOFTWARE/ESRI/ArcGISPro/PythonCondaEnv.
Oct 27, 2021 - Pro 2.8.3 removed the reliance and existence of the file %LOCALAPPDATA%/ESRI/conda/envs/proenv.txt. It now depend on env var CONDA_DEFAULT_ENV to determine the activate conda env.
Sep 16, 2021 - Perform the following as a patch for Pro 2.8.3
cd c:\
git clone https://github.com/kontext-tech/winutils
Define a system environment variable HADOOP_HOME with value C:\winutils\hadoop-3.3.0 and add to system variable PATH the %HADOOP_HOME%/bin value.
NOTE: This works in Pro 2.6 ONLY. There is a small "issue" with Pro 2.7 and pyarrow. The folks in Redlands have a fix that will be in 2.8 :-(
If you do not wish to use Pro's built-in Spark, you can download and install Spark 3.x separately. For example, download spark-3.2.1-bin-hadoop3.2.tgz and set the environment variable SPARK_HOME to the folder where you extracted the archive. It's best to avoid spaces in the folder path.
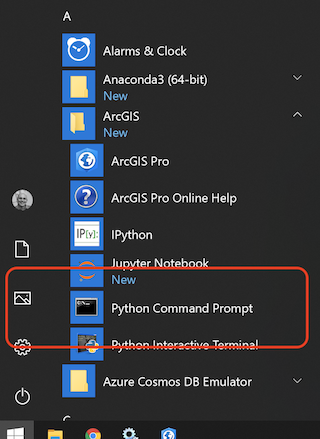
Start a Python Command Prompt:
Note: You might need to add proxy settings to .condarc located in C:\Program Files\ArcGIS\Pro\bin\Python.
conda config --set proxy_servers.http http://username:password@host:port
conda config --set proxy_servers.https https://username:password@host:port
The above will produce something like the below:
ssl_verify: true
proxy_servers:
http: http://domainname\username:password@host:port
https: http://domainname\username:password@host:port
Create a new conda environment:
proswap arcgispro-py3
conda remove --yes --all --name spark_esri
conda create --yes --name spark_esri --clone arcgispro-py3
proswap spark_esri
Optional:
pip install fsspec==2021.8.1 boto3==1.18.35 s3fs==0.4.2 pyarrow==1.0.1
conda install --yes -c esri -c conda-forge -c default^
"numba=0.53.*"^
"pandas=1.2.*"^
"pyodbc=4.0.*"^
"gcsfs=0.7.*"
Install the Esri Spark module.
Note: You might need to install Git for Windows.
git clone https://github.com/mraad/spark-esri.git
cd spark-esri
python setup.py install
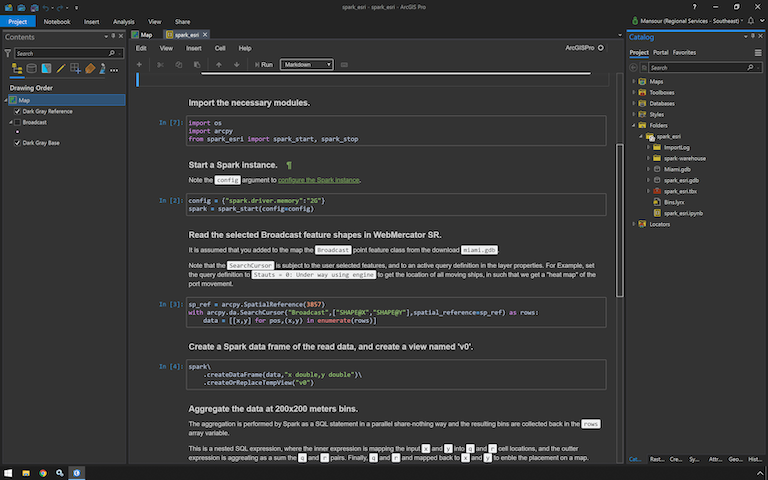
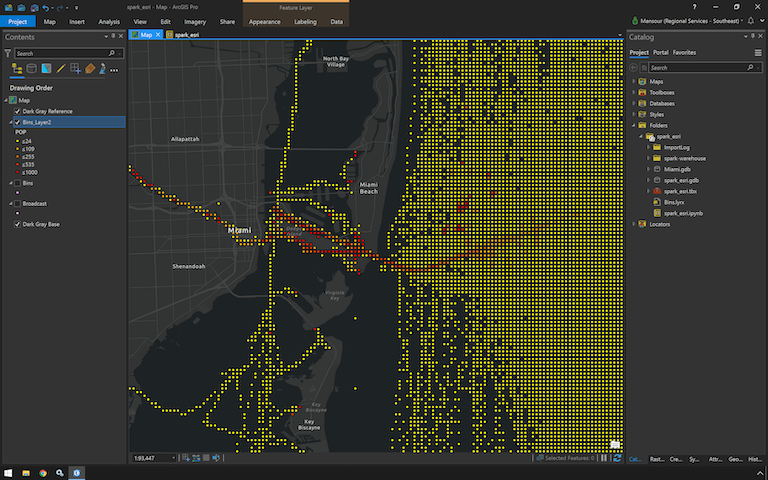
Spatial Binning Notebook
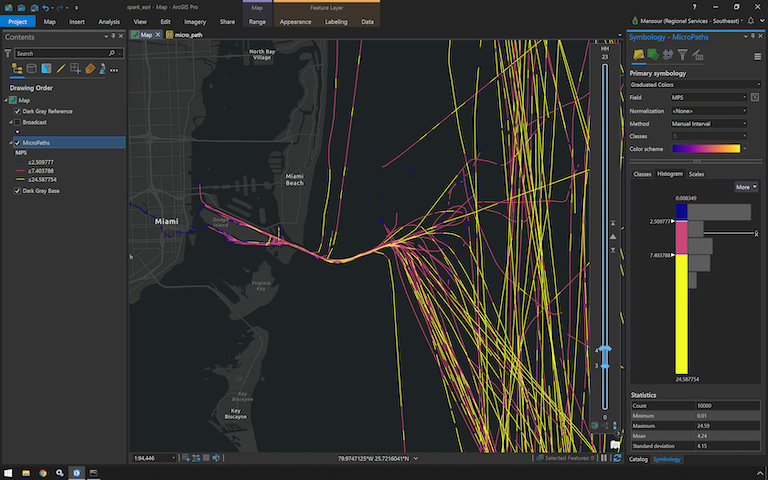
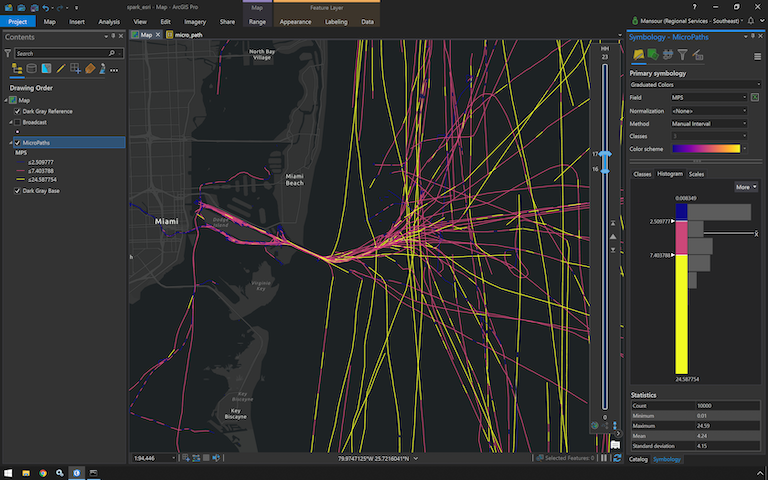
MicroPathing Notebook
Please note the usage of the range slider on the map to filter the micropaths between a user defined hour of day.
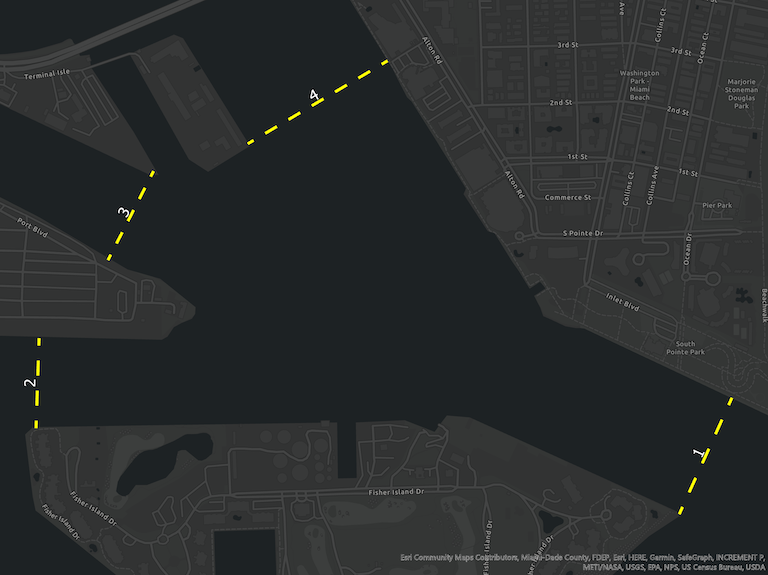
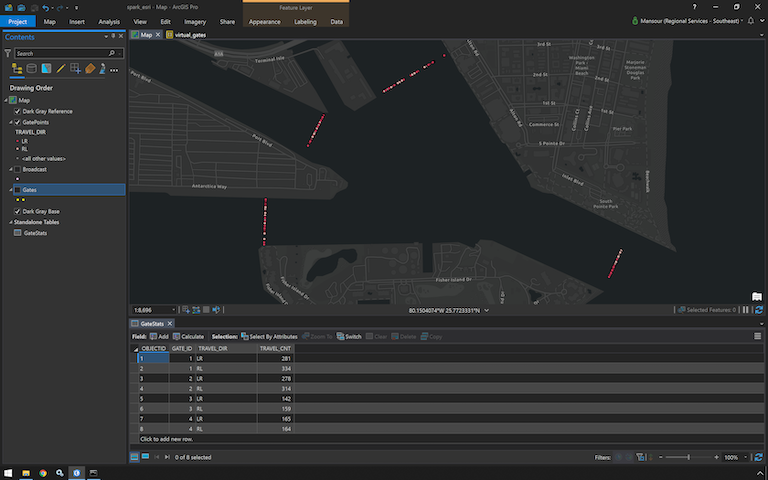
Virtual Gate Crossings Notebook
The following is the resulting crossing points and gates statistics.
- Unify spark_esri and spark_dbconnect python modules.
- https://github.com/kontext-tech/winutils
- https://github.com/cdarlint/winutils
- https://github.com/steveloughran/winutils
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/check-if-two-given-line-segments-intersect/
- https://www.kite.com/python/answers/how-to-check-if-two-line-segments-intersect-in-python
- https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/development/extending.html
- https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/style.html
- https://www.esri.com/arcgis-blog/products/arcgis-pro/health/use-proximity-tracing-to-identify-possible-contact-events/
- https://marinecadastre.gov/ais/
- https://www.movable-type.co.uk/scripts/latlong.html
- https://www.kaggle.com/c/nyc-taxi-trip-duration/data
- https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/utilities/polylinealgorithm
- https://nvidia.github.io/spark-rapids
- https://github.com/nvidia/spark-rapids
- https://github.com/quantopian/qgrid
- https://gist.github.com/rkaneko/dd2fae35149a29405d5e287ccd62677f Put parquet file on MinIO (S3 compatible storage) using pyarrow and s3fs
- https://towardsdatascience.com/installing-apache-pyspark-on-windows-10-f5f0c506bea1