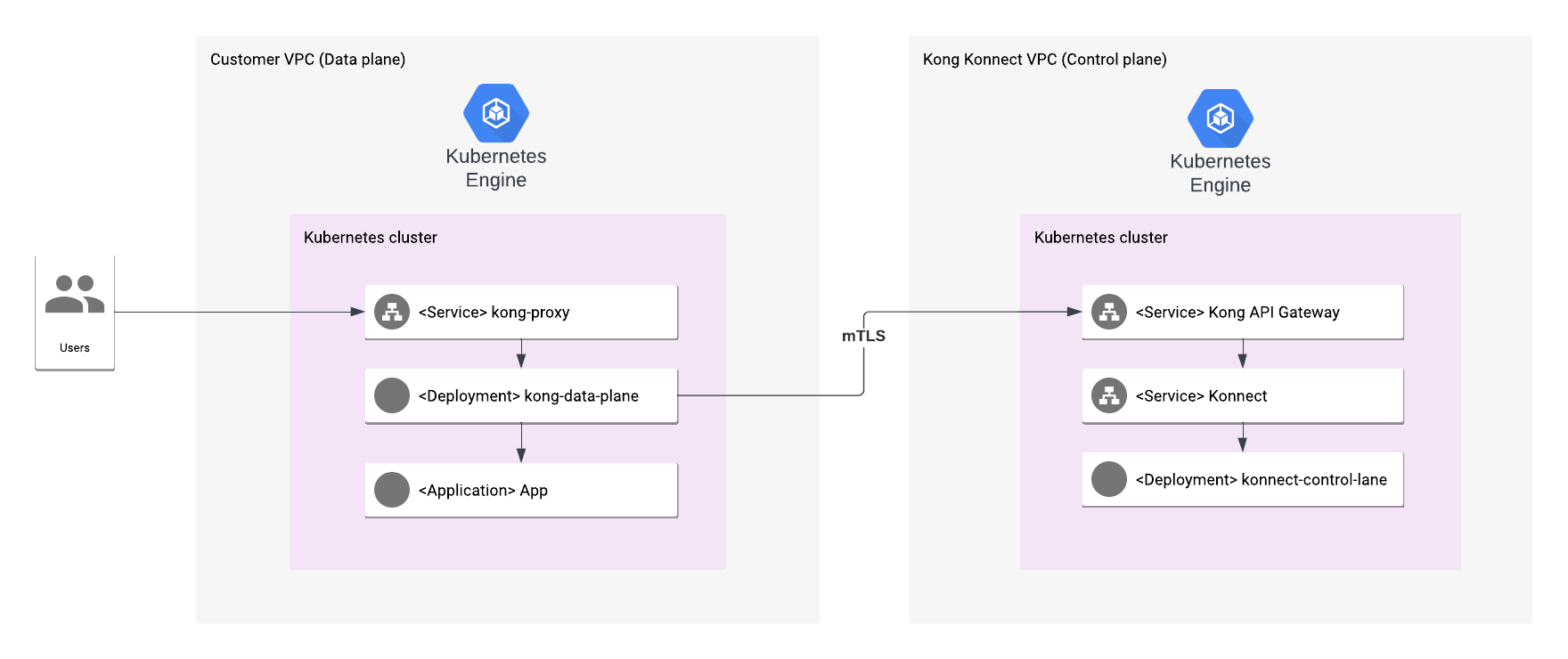
Konnect is an API lifecycle management platform designed from the ground up for the cloud native era and delivered as a service. This platform lets you build modern applications better, faster, and more securely. The management plane is hosted in the cloud by Kong, while the runtime engine, Kong Gateway — Kong’s lightweight, fast, and flexible API gateway — is managed by you within your preferred network environment.
To learn more about Kong Konnect, see the Kong Konnect.
The Kong Konnect platform provides a cloud control plane (CP), which manages all service configurations. It propagates those configurations to all runtime nodes, which use in-memory storage. These nodes can be installed anywhere, on-premise or in the cloud.
This application is pre-configured with an SSL certificate. While you are installing the application using the steps below, you must replace the certificate with your own valid SSL certificate.
Popular open stacks on Kubernetes packaged by Google.
Runtime instances, acting as data planes, listen for traffic on the proxy port 443 by default. The Konnect data plane evaluates incoming client API requests and routes them to the appropriate backend APIs. While routing requests and providing responses, policies can be applied with plugins as necessary.
For example, before routing a request, the client might be required to authenticate. This delivers several benefits, including:
The service doesn’t need its own authentication logic since the data plane is handling authentication. The service only receives valid requests and therefore cycles are not wasted processing invalid requests. All requests are logged for central visibility of traffic.
Kong Gateway data planes proxy service traffic. With Konnect Cloud working as the control plane, a runtime doesn’t need a database to store configuration data. Instead, configuration is stored in-memory on each node, and you can easily update multiple runtimes from one Konnect account with a few clicks.
Kong Gateway data planes proxy service traffic.
-
From the left navigation menu, open runtimes icon Runtime Manager.
-
Select the default runtime group.
-
Every account starts with one group named default. If you have an Enterprise subscription, you can create additional custom groups.
-
Click Add runtime instance.
The page opens to a runtime configuration form with the Docker tab selected. Here you will find variables that you would need to use on the next steps.
Get up and running with a few clicks! Install this Konnect app to a Google Kubernetes Engine cluster using Google Cloud Marketplace. Follow the on-screen instructions.
You can use Google Cloud Shell or a local workstation to complete the following steps.
You'll need the following tools in your development environment. If you are
using Cloud Shell, gcloud, kubectl, Docker, and Git are installed in your
environment by default.
Configure gcloud as a Docker credential helper:
gcloud auth configure-dockerCreate a new cluster from the command line:
export CLUSTER=konnect-cluster
export ZONE=us-west1-a
gcloud container clusters create "$CLUSTER" --zone "$ZONE"Configure kubectl to connect to the new cluster.
gcloud container clusters get-credentials "$CLUSTER" --zone "$ZONE"Clone this repo and the associated tools repo.
git clone --recursive https://github.com/Kong/konnect-gcp-marketplace.gitAn Application resource is a collection of individual Kubernetes components, such as Services, Deployments, and so on, that you can manage as a group.
To set up your cluster to understand Application resources, run the following command:
kubectl apply -f "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/marketplace-k8s-app-tools/master/crd/app-crd.yaml"You need to run this command once.
The Application resource is defined by the Kubernetes SIG-apps community. The source code can be found on github.com/kubernetes-sigs/application.
Choose the instance name and namespace for the app:
export APP_INSTANCE_NAME=konnect-gcp
export NAMESPACE=defaultOn the Konnect UI, Create New Runtime Instance, you need to pull these variables.
export CLUSTER_CP=""
export SERVER_NAME=""
export TELEMETRY_ENDPOINT=""
export TELEMETRY_SERVER_NAME=""On the Konnect UI, Create New Runtime Instance you will be able to generate the certificates.
-
Set
TLS_CERTIFICATE_KEYandTLS_CERTIFICATE_CRTvariables:export TLS_CERTIFICATE_KEY="$(cat /tmp/tls.key | base64)" export TLS_CERTIFICATE_CRT="$(cat /tmp/tls.crt | base64)"
Set up the image tag:
It is advised to use stable image reference which you can find on Marketplace Container Registry. Example:
export TAG="<BUILD_ID>"Configure the container images:
export IMAGE_KONG_REPO="marketplace.gcr.io/konghq-public/konnect"
export IMAGE_POSTGRES="marketplace.gcr.io/konghq-public/konnect/postgresql:${TAG}"If you use a different namespace than default, run the command below to create
a new namespace:
kubectl create namespace "$NAMESPACE"Use helm template to expand the template. We recommend that you save the
expanded manifest file for future updates to the application.
helm template "$APP_INSTANCE_NAME" chart/konnect-dp \
--namespace "$NAMESPACE" \
--set kong.image.repository="$IMAGE_KONG_REPO" \
--set kong.image.tag="$TAG" \
--set kong.postgresql.image="$IMAGE_POSTGRES" \
--set kong.env.cluster_control_plane="${CLUSTER_CP}" \
--set kong.env.cluster_server_name="${SERVER_NAME}" \
--set kong.env.cluster_telemetry_endpoint="$TELEMETRY_ENDPOINT" \
--set kong.env.cluster_telemetry_server_name="$TELEMETRY_SERVER_NAME" \
--set tls.base64EncodedPrivateKey="$TLS_CERTIFICATE_KEY" \
--set tls.base64EncodedCertificate="$TLS_CERTIFICATE_CRT" \
> "${APP_INSTANCE_NAME}_manifest.yaml"Use kubectl to apply the manifest to your Kubernetes cluster:
kubectl apply -f "${APP_INSTANCE_NAME}_manifest.yaml" --namespace "${NAMESPACE}"To get the GCP Console URL for your app, run the following command:
echo "https://console.cloud.google.com/kubernetes/application/${ZONE}/${CLUSTER}/${NAMESPACE}/${APP_INSTANCE_NAME}"To view your app, open the URL in your browser.
You can get the IP addresses for your Konnect solution either from the command line, or from the Google Cloud Platform Console.
In the GCP Console, do the following:
- Open the Kubernetes Engine Services page.
- Identify the Konnect solution using its name (typically
konnect-*-svc) - From the Endpoints column, note the IP addresses for ports 80 and 443.
If you are using the command line, run the following command:
kubectl get svc -l app.kubernetes.io/name=$APP_INSTANCE_NAME --namespace "$NAMESPACE"This command shows the internal and external IP address of your Konnect service.
Konnect Cloud deployments run in hybrid mode, which means that there is a separate control plane attached to one or more data plane nodes. These planes must communicate with each other to receive and send configuration. If communication is interrupted and either side can’t send or receive config, data plane nodes still continue proxying traffic to clients.
Data travelling between control planes and data planes is secured through a mutual TLS handshake.
Normally, the data plane maintains a persistent connection with the control plane. The data plane sends a heartbeat to the control plane every 30 seconds to keep the connection alive. If it receives no answer, it tries to reconnect to the control plane node after a 5-10 second random delay.
These steps assume that you have a new image for the Konnect container available
to your Kubernetes cluster. The new image is used in the following commands as
[NEW_IMAGE_REFERENCE].
kubectl set image deployment "$APP_INSTANCE_NAME-kong" \
--namespace "$NAMESPACE" proxy=[NEW_IMAGE_REFERENCE]where [NEW_IMAGE_REFERENCE] is the new image.
You can delete the Konnect application using the Google Cloud Platform Console, or using the command line.
-
In the GCP Console, open Kubernetes Applications.
-
From the list of applications, click Konnect.
-
On the Application Details page, click Delete.
-
Run the
kubectl deletecommand:kubectl delete -f ${APP_INSTANCE_NAME}_manifest.yaml --namespace $NAMESPACE
Optionally, if you don't need the deployed application or the Kubernetes Engine cluster, delete the cluster using this command:
gcloud container clusters delete "$CLUSTER" --zone "$ZONE"