This repository contains automation for provisioning 'Docker in Swarm Mode' clusters on your Mac (OSX), Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud Platform. It also has an example proxied web ui, gateway and api (on segregated networks) that you can use to test your deployments.
For local use, there are a number of supporting services that can be used to simulate cloud-native infrastructure such as Docker registries, DNS, load balancers etc:
- private Docker registry (for pushing local images)
- registry mirror (for caching public images)
haproxyload balancer (for hostname to published port mapping)dnsmasqdns server (for.localtld resolution)
The example application has 3 stacks running inside the cluster:
- the swarm visualizer (
servicesstack, deployed usingconfigureutility from theexampledirectory) - the registry ambassador (
swarmstack, deployed by./provisioning/osx/registry.sh) - the web and the api, and their associated reverse proxy and gateway (
appstack, also deployed usingconfigureutility from theexampledirectory)
Incoming requests can hit any node of the swarm and will be routed to an instance of the service (that has published the port) by the swarm's mesh routing.
You can describe stack configurations (published services) in a yaml file which is called _stacks.yml by default, and then use the configuration utility (configure/lib/index.js --help) to write deployable compose-files created by merging multiple compose files (including one for automatic port assignment). Combined with the local dns server and haproxy load balancer, this allows you to access published services by FQDNs in the form http://service.stack.local (in this case http://visualizer.services.local and http://web.app.local). See examples below.
To set up the cluster locally
-
Install the latest VirtualBox and Docker for Mac.
-
There is a script to create a swarm, which provisions 4 local VMs and joins them into a cluster. Take a look at the script to see how straight forward it is. NOTE: this script starts by removing any VMs with the names
mgr1,wkr1,wkr2,wkr3../provisioning/osx/swarm.sh
-
There is a script to run a container with a local dns server (outside the swarm). This is an instance of
dnsmasqand it used to resolve the tld.localtolocalhost. Unfortunately you will needsudoto add a resolver for thelocaltld.sudo mkdir -p /etc/resolver sudo sh -c 'echo "nameserver 127.0.0.1" > /etc/resolver/local' ./provisioning/osx/dns.sh -
There is a script to create containers for a local private Docker registry and a local mirror of Docker hub. It also deploys a registry ambassador inside the swarm to route requests to the registry on the host (
localhost:5000)../provisioning/osx/registry.sh
-
There is a script to run a container with a load balancer (outside the swarm). Note that if the IP addresses of your VMs change, you'll need to run this script again, so that the load balancer points to the correct nodes. (The first time you run this it will use a default config which will be updated when we use the
configure -uutility below)../provisioning/osx/load-balancer.sh
-
Run the
configureutility to generate deployable compose-files with correct ports. This also updates the load balancer in case the ports have changed. It deploys thevisualizer, so that we can see what's going on.Note: you will need to build it (and run tests) before you use it for the first time:
cd configure yarn yarn test cd ..
cd example ../configure/lib/index.js deploy --update services cd ..
-
Build and push the app stack.
cd example export registry=localhost:5000 ../configure/lib/index.js build app ../configure/lib/index.js push app cd ..
-
Create a secret that the
apiservice will use (note we useprintfinstead ofechoto prevent a new-line being added).printf 'sssshhhh!' | on-swarm docker secret create my_secret -
-
Run the
configureutility to deploy theappstack.cd example ../configure/lib/index.js deploy --update app cd ..
-
The following steps use aliases to make it easier to work with local and swarm docker servers (you might want to add them to your
.bash_profile):alias on-local="/path/to/provisioning/osx/on-local.sh" alias on-swarm="/path/to/provisioning/osx/on-swarm.sh" alias to-local="source /path/to/provisioning/osx/point-to-local.sh" alias to-swarm="source /path/to/provisioning/osx/point-to-swarm.sh"
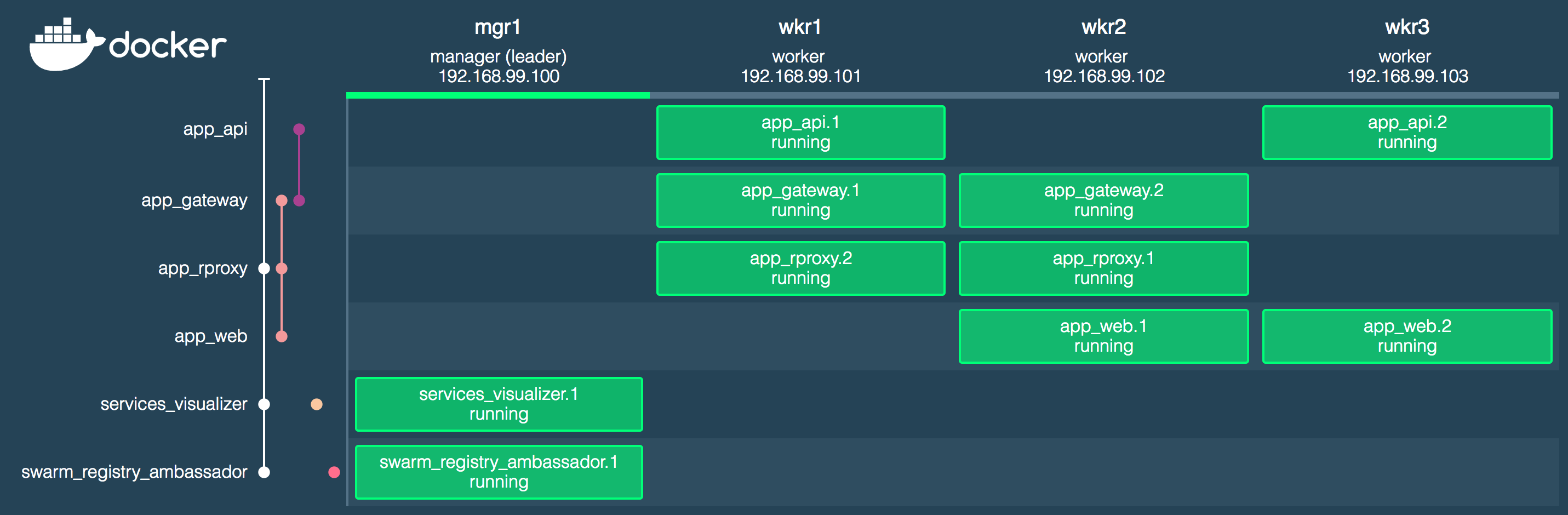
You should wait until all the services in the swarm are running:
on-swarm docker service ls
ID NAME MODE REPLICAS IMAGE PORTS
1yofqh0g1b9b services_visualizer replicated 1/1 charypar/swarm-dashboard:latest *:8000->3000/tcp
fuhipdgtyvvd swarm_registry_ambassador replicated 1/1 svendowideit/ambassador:latest *:5000->5000/tcp
hi21cmf1oi0x app_gateway replicated 2/2 localhost:5000/gateway@sha256:75035764b5ee55c35820aa38b4cf7b4d1742be8e7f47ef5379296978cff87eb5
j3wmx8r2s2kv app_api replicated 2/2 localhost:5000/api@sha256:1b836f221052dace536425e34dc84714440a31a48a8d48594cdff97107121084 *:8002->3000/tcp
ntuo4tmulyel app_web replicated 2/2 localhost:5000/web@sha256:10e40e7311a083371af387fc1d6d505a468e7750e401928a52d2a8aafd217aab
qzxhfbrkp2vz app_rproxy replicated 2/2 localhost:5000/rproxy@sha256:7348f573df6ff4a4623c59ab2453de3cd8ae24d0c150f2373a9521e4117c47a1 *:8001->3000/tcpYou should also have the following local containers running:
on-local docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
73f862aa53c9 haproxy:1.7.8-alpine "/docker-entrypoin..." 22 hours ago Up 22 hours 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp loadbalancer_load_balancer_1
fbff0358c773 andyshinn/dnsmasq "dnsmasq -k -d -A ..." 2 days ago Up 2 days 0.0.0.0:53->53/tcp, 0.0.0.0:53->53/udp dns_dns_1
6e2686acd14a registry:2 "/entrypoint.sh /e..." 3 days ago Up 3 days 0.0.0.0:5001->5000/tcp registry_registry-mirror_1
a578c7c8703c registry:2 "/entrypoint.sh /e..." 3 days ago Up 3 days 0.0.0.0:5000->5000/tcp registry_registry_1When all the services have started, the app should be available at http://web.app.local and the visualizer at http://visualizer.services.local
Note: If you get a 503 Service Unavailable from app_web, you may need to restart app_rproxy (this is probably due to the startup order and it should recover on its own, this needs fixing):
on-swarm docker service update --force app_rproxyCleaning up
./provisioning/osx/local-cleanup.sh
./provisioning/osx/swarm-cleanup.shA note about overlay networks
Be careful of clashes between Boot2Docker's networking and docker swarm's overlay networks
(they both use 10.0.n/24). This is why we change the subnet for the private overlay network in
the compose file (as we ended up looking for a DNS server on the
private network rather than on the host)