U19-pipeline_python
The python data pipeline defined with DataJoint for U19 projects
The data pipeline is mainly ingested and maintained with the matlab repository: https://github.com/shenshan/U19-pipeline-matlab
This repository is the mirrored table definitions for the tables.
Major schemas
Currently, the main schemas in the data pipeline are as follows:
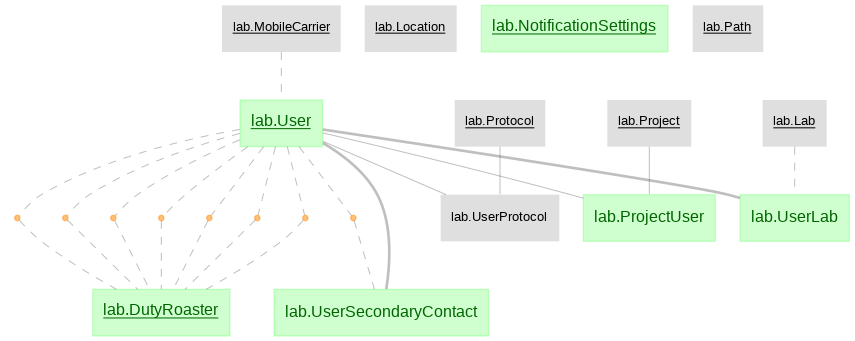
- lab
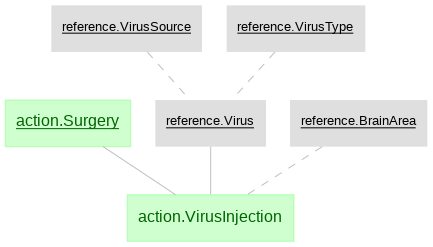
- reference
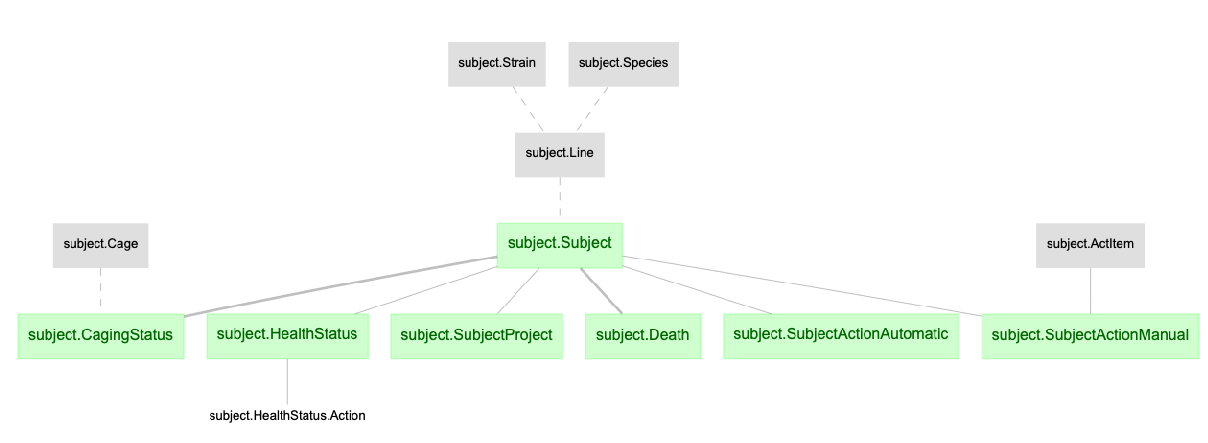
- subject
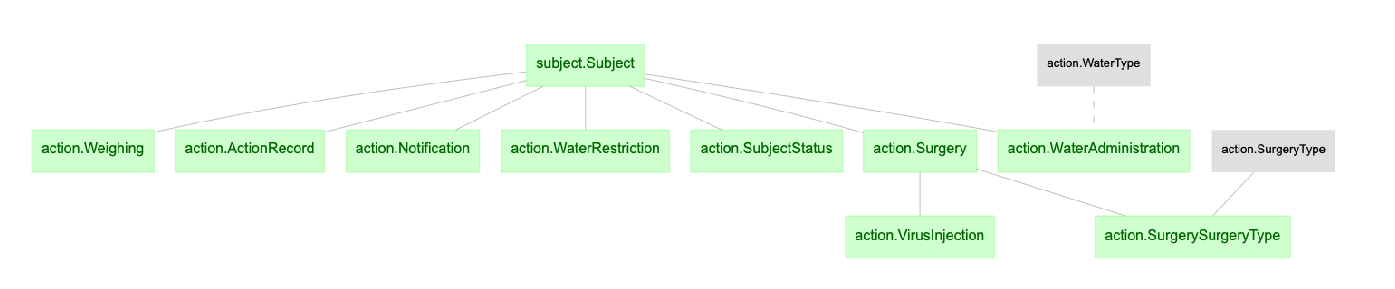
- action
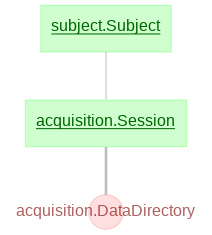
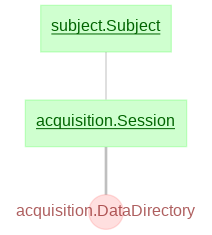
- acquisition
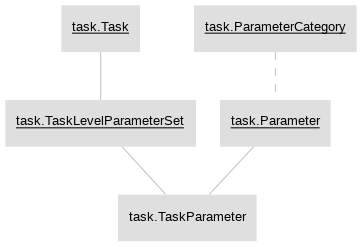
- task
- behavior
Installation of package for usage and development.
To use and contribute to the developement of the package, we recommend either using a Docker setup or creating a virtual environment, as follows:
-
In either way, we first clone the directory
git clone https://github.com/BrainCOGS/U19-pipeline_python -
To use a docker setup, after installing docker, inside this directory, we
- set up the
.envfile, as follows:
DJ_HOST = 'datajoint00.pni.princeton.edu'
DJ_USER = {your_user_name}
DJ_PASSWORD = {your_password}
- run
docker-compose up -d
- Then, we could run
docker exec -it u19_pipeline_python_datajoint_1 /bin/bashThis will provide you a mini environment to work with python.
- To use a virtual environment setup, we could
- install
virtualenvbypip3 install virtualenv
- Create a virtual environment by 'virtualenv princeton_env'
- Activate the virtual environment by
source princeton_env/bin/activate
- With the virtual environment, we could install the package that allows edits:
pip3 install .
Undocumented datajoint features
For all code below, I am assuming datajoint has been imported like:
import datajoint as djUpdate a table entry
dj.Table._update(schema.Table & key, 'column_name', 'new_data')
Get list of all column names in a table (without having to issue a query or fetch)
table.heading.attributes.keys()
This also works on a query object:
schema = dj.create_virtual_module("some_schema","some_schema")
query_object = schema.Sample() & 'sample_name ="test"'
query_object.heading.attributes.keys()The latter case is useful if you are passing the query object between functions or modules and you lose track of the table name.
Use boolean datatype
Example table:
@schema
class Experiment(dj.Manual):
definition = """ # Experiments performed using the light sheet microscope
experiment_id : smallint auto_increment # allowed here are sql datatypes.
----
cell_detection : boolean
"""
It has some counterintuitive properties:
| Inserted_value | Stored_value |
|---|---|
| True | 1 |
| False | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 5* |
| -5 | -5* |
| 5000 | DataError* |
| -5000 | DataError* |
| '10' | 10* |
| '-10' | -10* |
| '0' | 0* |
*Would expect this to be stored as 1 based on the rules of bool in python. See: https://github.com/datajoint/datajoint-docs/issues/222