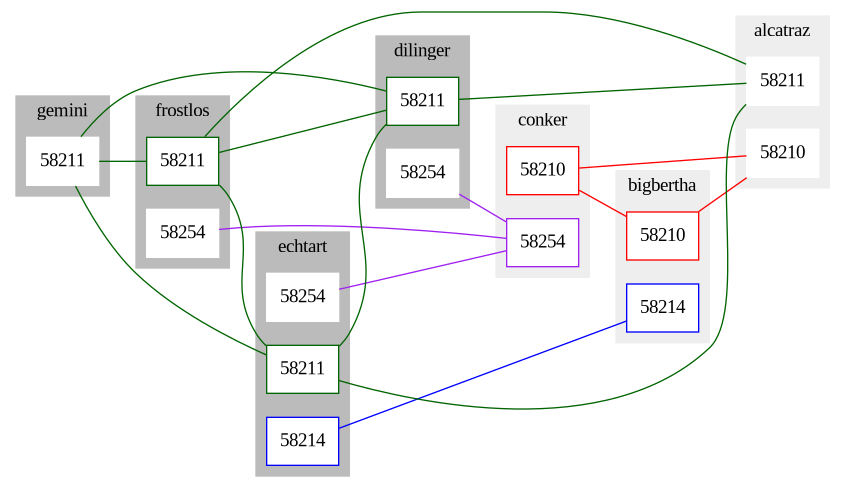
This tool quickly generates config files for multiple Wireguard clients, connected to each other in a way specified in a single table.
| MainIP | wa0 | ha0 | hp0 | gs0 | Public | Desc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Tunnel] | work area | home area | homeproxy | gamestream | |||
| [Port] | 58210 | 58211 | 58214 | 58254 | |||
| [Target] | conker,bigbertha | all,-gemini,-alcatraz | all | conker | |||
| alcatraz | 190.239.111.210 | 10.10.10.1 | 11.11.11.1 | Yes | Work A | ||
| bigbertha | 190.239.111.110 | 10.10.10.2 | 14.14.14.2 | Yes | Work B | ||
| conker | 190.239.111.111 | 10.10.10.3 | 54.54.54.3 | Yes | Home A | ||
| dilinger | 192.168.178.25 | 11.11.11.4 | 54.54.54.4 | No | Home B | ||
| echtart | 192.168.178.11 | 11.11.11.5 | 14.14.14.5 | 54.54.54.5 | No | Something | |
| frostlos | 192.168.178.38 | 11.11.11.6 | 54.54.54.6 | No | Rpi4 | ||
| gemini | 11.11.11.7 | No | Notes |
The table specifies the following pieces of information:
- Wireguard Tunnel as column headers
- The identifier and name of the tunnel (e.g. wa0 and “work area”)
- The listening port of the tunnel to be used on each client
- The target client(s) that all other clients should connect to.
- If some client names are given, then all other clients will specify just these clients as peers
- If “all” is given, then all clients specify all other clients as peers
- If “-” is given before a client name, after an “all” deceleration, then all clients will specify each other barring those with the “-“.
- Client hostnames given as row indexes
- Main stable IP addresses to access the client. Not all clients have these.
- The wireguard address for the client in the respective tunnel
- Whether the client as a public IP or not. If so, it’s endpoint will be specified in client configuration.
With such a table, one can generate a network map along with the corresponding configuration files. This takes care of key generation and peer specification. It also automatically calculates how big your subnet needs to be.
tree outputsoutputs
|-- alcatraz
| |-- ha0.conf
| `-- wa0.conf
|-- bigbertha
| |-- hp0.conf
| `-- wa0.conf
|-- conker
| |-- gs0.conf
| `-- wa0.conf
|-- dilinger
| |-- gs0.conf
| `-- ha0.conf
|-- echtart
| |-- gs0.conf
| |-- ha0.conf
| `-- hp0.conf
|-- frostlos
| |-- gs0.conf
| `-- ha0.conf
`-- gemini
`-- ha0.conf
8 directories, 14 files
You will need to install: wireguard-tools graphviz python-graphviz
This document was written initially in org-mode via Emacs. One needs
to only change the table above and then hit C-c C-c in the Code
section below. A new image will be created, along with output files in
the outputs folder.
These can then be installed on the target machines in a similar manner as that outlined in the Installation section below.
- Create a TSV file with the contents of your client and tunnel configurations, similar to the table above. Call it “mytable.tsv”
- Copy the Code section below into a separate file. Call it “wireguard_config.py”
- Run
python wireguard_config.py mytable.tsv - Copy the outputs to the target clients as outlines in the Installation section
First clear previous outputs
rm -rf outputsThen generate the client configs and network map
from colorsys import hsv_to_rgb
import pandas as pd
from math import floor, log2
import graphviz
from os import popen, makedirs
from sys import argv
if len(argv) > 1:
clients = pd.read_csv(argv[1], sep="\t", header=0, index_col=0)
else:
clients = pd.DataFrame(tab).set_index(0).rename_axis(None).T.set_index("").rename_axis(None).T
class Graph:
color_index = -1
colors = ("red", "darkgreen", "blue", "purple", "black", "brown", "orange", "yellow", "magenta")
edgeAttr = {} ## color
nodes = {}
edges = {}
_PORTSEP = "%%"
_TUNNSEP = "||"
_EDGESEP = "--"
@staticmethod
def _getDistinctColor():
Graph.color_index += 1
return(Graph.colors[Graph.color_index])
@staticmethod
def new_tunnel(tname, port):
Graph.edgeAttr[tname] = {"color": Graph._getDistinctColor()}
@staticmethod
def new_node(A, tport, tname, tport_is_target=False):
tport = str(tport)
if A.name not in Graph.nodes:
Graph.nodes[A.name] = {
"ports": {},
"public": A.is_public
}
if tport not in Graph.nodes[A.name]["ports"]:
tport_col = Graph.edgeAttr[tname]["color"] if tport_is_target else "#ffffff"
Graph.nodes[A.name]["ports"][tport] = tport_col
pid = A.name + Graph._PORTSEP + tport
return(pid)
@staticmethod
def new_edge(nd1, nd2, tname):
key = Graph._EDGESEP.join(sorted([nd1, nd2])) + Graph._TUNNSEP + tname
if key not in Graph.edges:
Graph.edges[key] = True
@staticmethod
def new_connection(A, B, tname, tport,
target_peer=["all"], nontarget_peer=[]):
A_is_target = (A.name in target_peer or target_peer==["all"]) and (A.name not in nontarget_peer)
B_is_target = (B.name in target_peer or target_peer==["all"]) and (B.name not in nontarget_peer)
nd1 = Graph.new_node(A, tport, tname, A_is_target)
nd2 = Graph.new_node(B, tport, tname, B_is_target)
Graph.new_edge(nd1, nd2, tname)
@staticmethod
def render_graph():
g = graphviz.Graph(
engine="dot", filename="wireguard", format="png",
graph_attr={"rankdir":"RL", "compound":"true"},
edge_attr={"labelfontsize" : "6", "labelfloat" : "true"},
node_attr={"shape": "rectangle", "ordering":"out", "style":"filled"}
)
g.attr(compound='true')
for node in Graph.nodes:
ports = Graph.nodes[node]["ports"]
with g.subgraph(name="cluster_"+node) as tmp:
tmp.attr(label=node, style="filled",
color="#eeeeee" if Graph.nodes[node]["public"] else "#bbbbbb")
for pt in ports:
pid = node + Graph._PORTSEP + pt
tmp.node(pid, pt, color=ports[pt], fillcolor="#ffffff")
for edge in Graph.edges:
(nodes, tname) = edge.split(Graph._TUNNSEP)
(nd1, nd2) = nodes.split(Graph._EDGESEP)
g.edge(nd1, nd2,
color=Graph.edgeAttr[tname]["color"])
g.render()
class Tunnel:
def __init__(self, name, title, port, targets=""):
self.name = name
self.title = title
self.listen = port
## Resolve Targets
if len(targets) < 1:
self.target_peer = ["all"]
self.nontarget_peer = []
else:
targs = [x.strip() for x in targets.split(",")]
self.target_peer = [x for x in targs if x[0] != "-"]
self.nontarget_peer = [x[1:] for x in targs if x[0] == "-"]
self.peers = {}
self.peers_resolved = False
Graph.new_tunnel(name, port)
def addPeer(self, client):
assert client.name not in self.peers
self.peers[client.name] = client
def resolvePeers(self):
pnames = [x for x in self.peers.keys()]
for aname in pnames:
## If target clients are given, skip aname until it's a target
if self.target_peer != ["all"]:
if aname not in self.target_peer:
continue
if self.nontarget_peer != []:
if aname in self.nontarget_peer:
continue
for bname in pnames:
if aname != bname:
peera = self.peers[aname]
peerb = self.peers[bname]
peera.addPeer(self.name, peerb)
peerb.addPeer(self.name, peera)
Graph.new_connection(peera, peerb, self.name, self.listen,
self.target_peer, self.nontarget_peer)
self.peers_resolved = True
def generatePeerConfigs(self, output_dir):
if not self.peers_resolved:
self.resolvePeers()
for pname in self.peers:
client_map[pname].generateConfig(self.name, output_dir)
def addClientToTunnel(self, clientname, tunnel_addr):
client_map[clientname].addTunnelToClient(self, tunnel_addr)
class Client:
def __init__(self, name, main_ip, public=False):
self.name = name
self.config_map = {} ## multiple tunnels possible
self.main_ip = main_ip
self.is_public = public
self.generateKeys()
def generateKeys(self):
self.private_key = popen("/usr/bin/wg genkey").read().strip()
self.public_key = popen("echo '" + self.private_key + "' | /usr/bin/wg pubkey").read().strip()
def addTunnelToClient(self, tunnel, address_in_tunnel):
assert tunnel.name not in self.config_map
tunnel.addPeer(self)
self.config_map[tunnel.name] = {"address": address_in_tunnel,
"interface" : "", "peers": []}
def addPeer(self, tunnelname, peer):
if peer not in self.config_map[tunnelname]["peers"]:
self.config_map[tunnelname]["peers"] += [peer]
def determineSubnetMask(self, tunnelname):
npeers = len(self.config_map[tunnelname]["peers"])
return(31 - floor(log2(npeers + 2)))
def generateConfig(self, tunnelname, output_dir):
self.subnetmask = str(self.determineSubnetMask(tunnelname)) ## for network
tunnel = tunnel_map[tunnelname]
tunnel_addr = self.config_map[tunnelname]["address"] + "/" + self.subnetmask
text = '''
[Interface]
# Name, MainIP = %s, %s
Address = %s
ListenPort = %s
PrivateKey = %s''' % (self.name, self.main_ip, tunnel_addr, tunnel.listen, self.private_key)
if tunnelname in self.config_map:
for peer in self.config_map[tunnelname]["peers"]:
text += '''\n
[Peer]
# Name = %s
PublicKey = %s
AllowedIPs = %s''' % (peer.name, peer.public_key, peer.config_map[tunnelname]["address"]+ "/32")
if peer.is_public:
text += "\nEndpoint = %s:%s" % (peer.main_ip, tunnel.listen)
else:
## If stuck behind NAT, then do a keep alive
text += "\nPersistentKeepalive = 60"
dname = output_dir + "/" + self.name
makedirs(dname, exist_ok=True)
with open(dname + "/" + tunnelname + ".conf", "w") as f:
print(text, file=f)
def populateClients():
client_map = {}
## client_map["kaktus"] = Client("kaktus", "132.230.165.150", True)
clmap = clients[["MainIP", "Public"]].filter(regex="^[^[]", axis=0)
for index, row in clmap.iterrows():
client_map[row.name] = Client(row.name, row["MainIP"], row["Public"] == "Yes")
return(client_map)
def populateTunnels():
tunnel_map = {}
##tunnel_map["wb0"] = Tunnel("wb0", "work area", 58210)
tunnels = clients.loc[:, ~clients.columns.isin(["MainIP", "Public", "Desc"])].filter(regex="^\[", axis=0).T
for index, row in tunnels.iterrows():
tunnel_map[row.name] = Tunnel(row.name, row["[Tunnel]"], row["[Port]"], row["[Target]"])
return(tunnel_map)
def addClientsToTunnels():
clmap = clients.loc[:, ~clients.columns.isin(["MainIP", "Public", "Desc"])].filter(regex="^[^[]", axis=0)
## tunnel_map["wb0"].addClientToTunnel("kaktus", "10.10.10.1")
list_tunnels = [x for x in clmap.columns]
for index, row in clmap.iterrows():
for tun in list_tunnels:
if type(row[tun]) == str and len(row[tun]) > 1:
tunnel_map[tun].addClientToTunnel(row.name, row[tun])
def generatePeerConfigs():
outdir = "outputs"
## tunnel_map["wb0"].generatePeerConfigs()
makedirs(outdir, exist_ok=True)
for tunnel in tunnel_map:
tunnel_map[tunnel].generatePeerConfigs(outdir)
client_map = populateClients()
tunnel_map = populateTunnels()
addClientsToTunnels()
generatePeerConfigs()
Graph.render_graph()Check the outputs
tree outputsoutputs
|-- alcatraz
| |-- ha0.conf
| `-- wa0.conf
|-- bigbertha
| |-- hp0.conf
| `-- wa0.conf
|-- conker
| |-- gs0.conf
| `-- wa0.conf
|-- dilinger
| |-- gs0.conf
| `-- ha0.conf
|-- echtart
| |-- gs0.conf
| |-- ha0.conf
| `-- hp0.conf
|-- frostlos
| |-- gs0.conf
| `-- ha0.conf
`-- gemini
`-- ha0.conf
8 directories, 14 files
This part needs to be done outside of emacs. You take every config file, ssh onto your target machine and run:
scp outputs/targetmachine/*.conf targetaddress:/tmp/
ssh targetaddress
sudo su root
## Below as root
mkdir -p /etc/wireguard
cp -v /tmp/*.conf /etc/wireguard
rm /tmp/*.conf
ls /etc/wireguard | xargs -n 1 wg-quick up
## Check status
wg