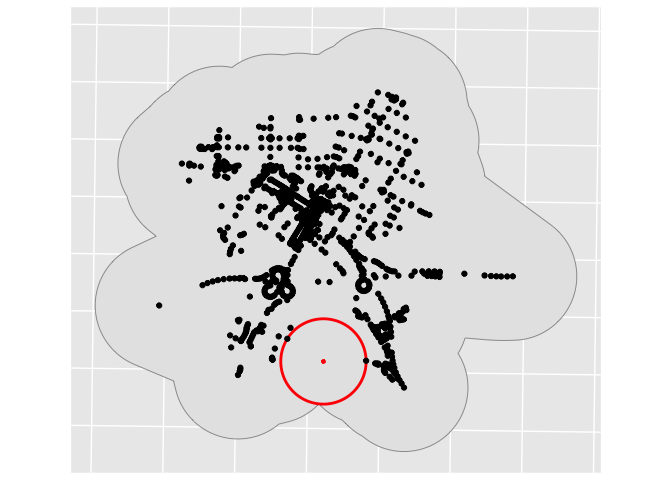
nemo finds the largest empty
circle
in the plane whose interior does not overlap with any given obstacles.
nemo includes ony two functions :
nemo_hullcomputes a concave hull from a set of points and is basically imported from package concaveman brought in R by joelgombinnemo_circlecomputes the larget circle inside a hull and which doesn’t include any point : its center will be the point nemo
You can install the development version from GitHub with:
## install {remotes} if not already
if (!requireNamespace("remotes")) {
install.packages("remotes")
}
## install nemo for github
remotes::install_github("mtmx/nemo")A basic example to find the largest empty circle inside a set of points and its center aka the point nemo :
library(nemo)
data(points)
hull_pts <-
nemo_hull(points = points %>% st_transform(2154),
concavity =2,
length_threshold = 10)
nemo_pts <-
nemo_circle(points = points %>% st_transform(2154),
hull = hull_pts %>% st_buffer(dist=500),
strict_inclusion = T,
nmax_circles = 1)
#> Warning: attribute variables are assumed to be spatially constant
#> throughout all geometries
# mapping output
library(ggplot2)
ggplot() +
geom_sf(data = hull_pts %>% st_buffer(dist=500) , size = 0.2) +
geom_sf(data = nemo_pts ,
size = 1,
fill=NA,
color = "red") +
geom_sf(data = nemo_pts %>% st_centroid() ,
size = 1,
col = "red") +
geom_sf(data=points %>% st_transform(2154))
#> Warning in st_centroid.sf(.): st_centroid assumes attributes are constant
#> over geometries of x