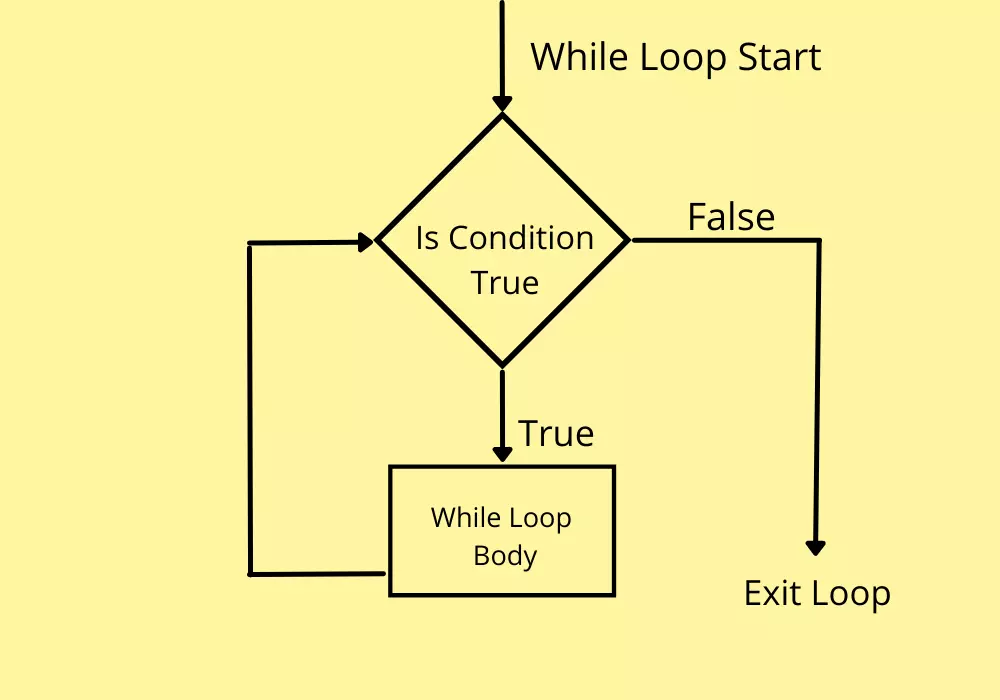
In Python, the iterative statements are also known as looping statements or repetitive statements. The iterative statements are used to execute a part of the program repeatedly as long as a given condition is True.
Python provides the following iterative statements.
- While loops
- For loops
In Python, the while statement is used to execute a set of statements repeatedly. the while statement is also known as entry control loop statement because in the case of the while statement,
first, the given condition is verified then the execution of statements is determined based on the condition result.
The general syntax of while statement in Python is as follows.
while condition:
Statement_1
Statement_2
Statement_3
...
i = 1
while i < 10:
print(i)
i = i + 1
print('Value less than 10')
- break statement
With the break statement we can stop the loop even if the while condition is true:
i = 1
while i < 6:
print(i)
if i == 3:
break
i += 1
- else statement
With the else statement we can run a block of code once when the condition no longer is true:
i = 1
while i < 6:
print(i)
i += 1
else:
print("i is no longer less than 6")
- continue statement
With the continue statement we can stop the current iteration, and continue with the next:
i = 0
while i < 6:
i = i + 1
if i == 3:
continue
print(i)
In Python, the for statement is used to iterate through a sequence like a list, a tuple, a set, a dictionary, or a string. The for statement is used to repeat the execution of a set of statements for every element of a sequence.
The general syntax of for statement in Python is as follows.
for <variable> in <sequence>:
Statement_1
Statement_2
Statement_3
...
#Print each fruit in a fruit list:
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
for x in fruits:
print(x)
- break Statement
With the break statement we can stop the loop before it has looped through all the items:
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
for x in fruits:
print(x)
if x == "banana":
break
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
for x in fruits:
if x == "banana":
break
print(x)
- continue Statement
With the continue statement we can stop the current iteration of the loop, and continue with the next:
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
for x in fruits:
if x == "banana":
continue
print(x)
- range Function
To loop through a set of code a specified number of times, we can use the range() function, The range() function returns a sequence of numbers, starting from 0 by default, and increments by 1 (by default), and ends at a specified number.
for x in range(6):
print(x)
for x in range(2, 6):
print(x)
for x in range(2, 30, 3):
print(x)
- Else in For Loop
The else keyword in a for loop specifies a block of code to be executed when the loop is finished:
for x in range(6):
print(x)
else:
print("Finally finished!")
for x in range(6):
if x == 3: break
print(x)
else:
print("Finally finished!")