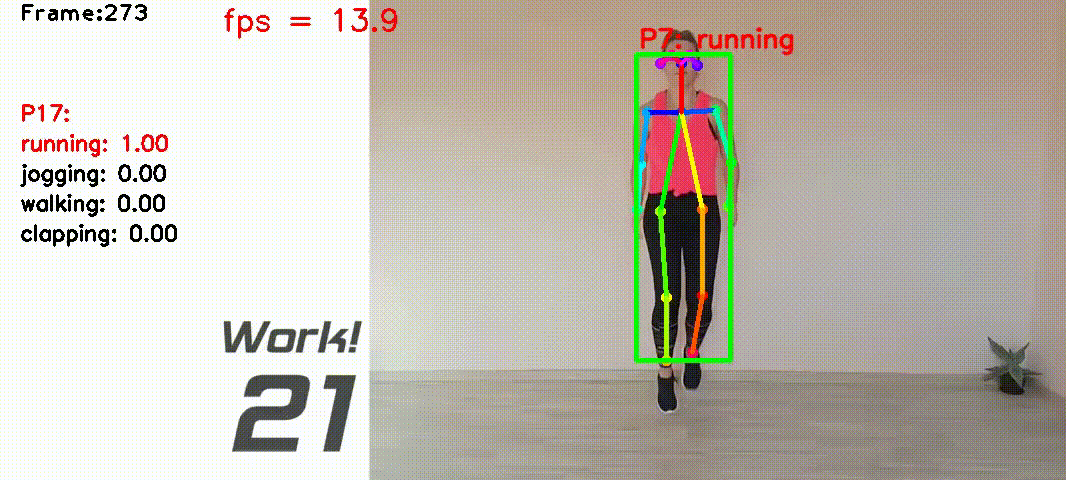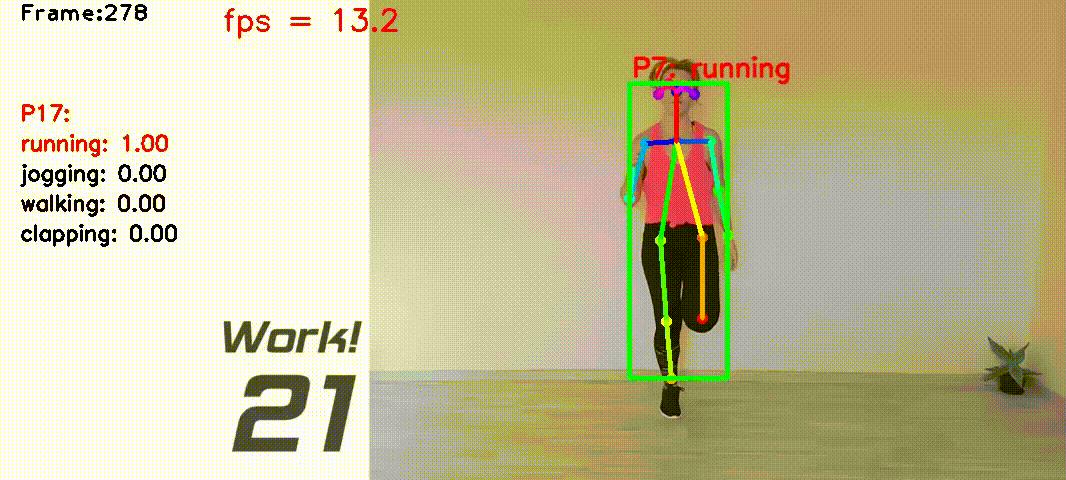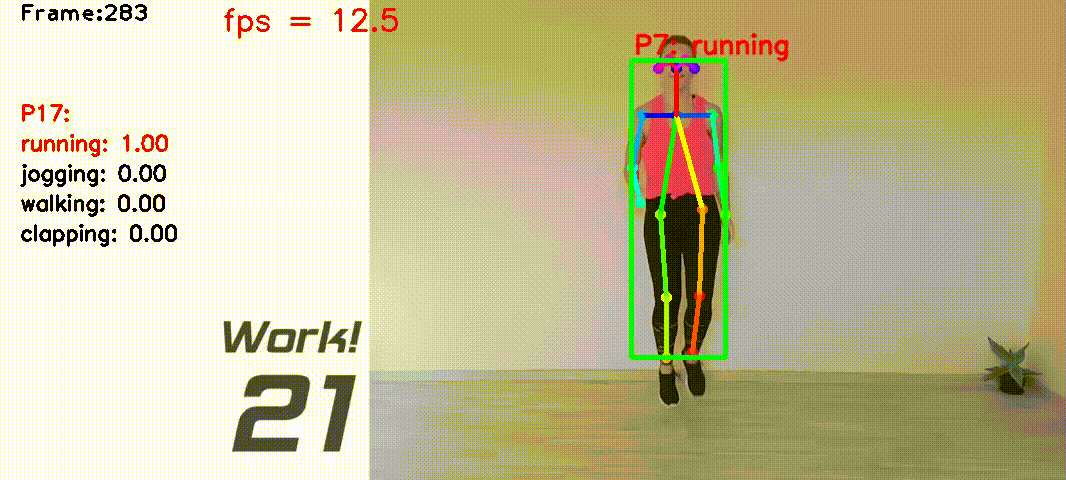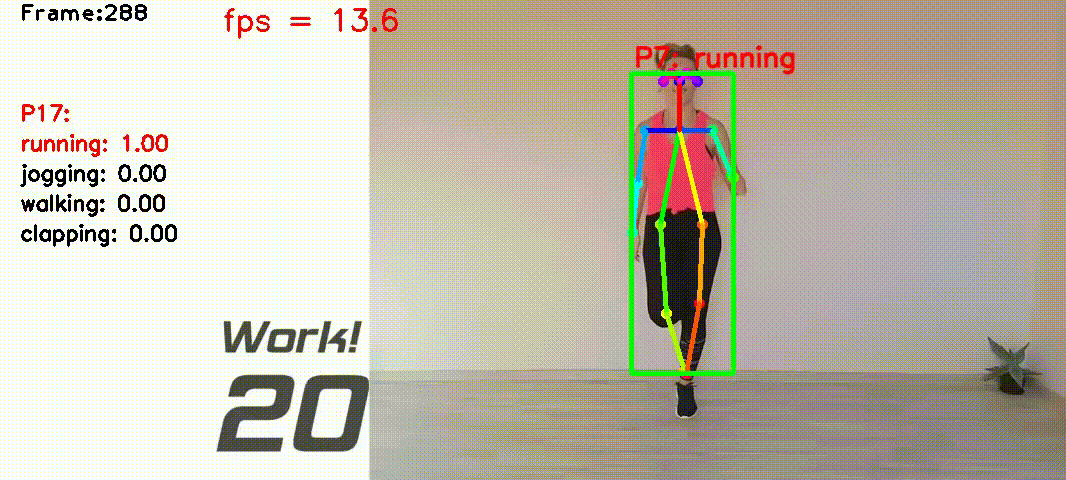
Human action recognition based on video data has diverse applications. For example, it can be used for interactive games where a person's movement is recognized by the computer and used as the input for playing games etc.
Highlights: 4 actions; multiple people (<=5); Real-time and multi-frame based recognition algorithm.
Updates: On 2021-05-10, I refactored the code; added more comments; and put all settings into the config/config.yaml file, including: classes of actions, input and output of each file, OpenPose settings, etc.
Project: This is my final project for human action recognition based on video data has diverse applications in Kocaeli University on May 2021. I worked on is here.
Warning: Since I used the 10 fps video and 0.5s-window for training, you must also limit your video fps to be about 10 fps (7~12 fps) if you want to test my pretrained model on your own video or web camera.
Contents:
- 1. Algorithm
- 2. Install Dependency (OpenPose)
- 3. Program structure
- 4. How to run: Inference
- 5. Training data
- 6. How to run: Training
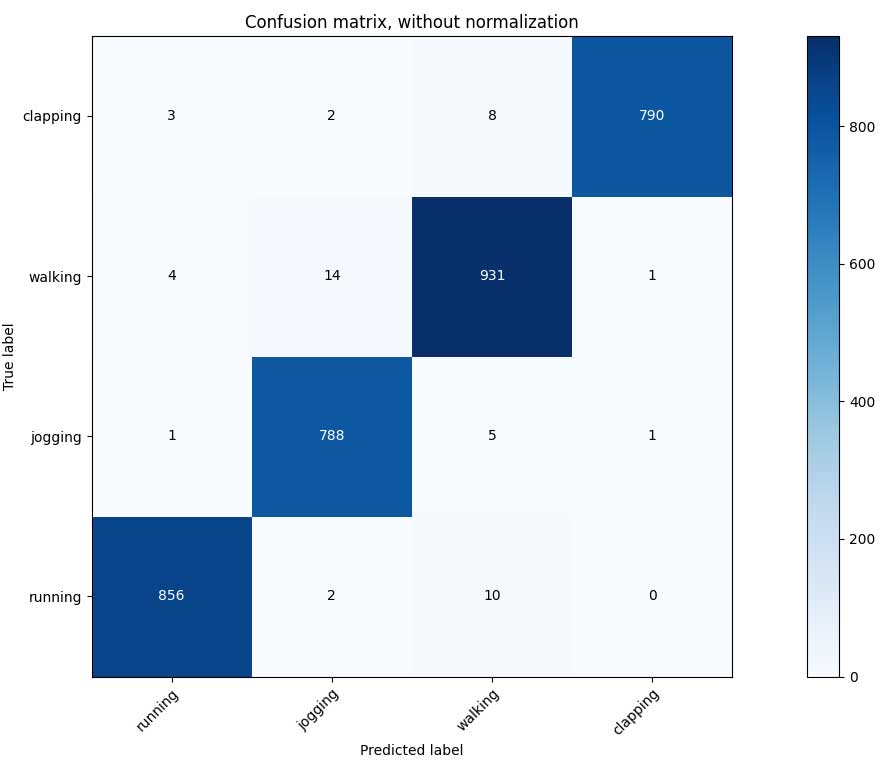
I collected videos of 4 Types of actions: ['running', 'jogging', 'walking', 'clapping']. The total video lengths are about 20 mins, containing about 10000 video frames recorded at 10 frames per second.
The workflow of the algorithm is:
- Get the joints' positions by OpenPose.
- Track each person. Euclidean distance between the joints of two skeletons is used for matching two skeletons.
See
class Trackerin lib_tracker.py - Fill in a person's missing joints by these joints' relative pos in previous frame. See
class FeatureGeneratorin lib_feature_proc.py. So does the following. - Add noise to the (x, y) joint positions to try to augment data.
- Use a window size of 0.5s (5 frames) to extract features.
- Extract features of (1) body velocity and (2) normalized joint positions and (3) joint velocities.
- Apply PCA to reduce feature dimension to 80. Classify by DNN of 3 layers of 50x50x50 (or switching to other classifiers in one line). See
class ClassifierOfflineTrainin lib_classifier.py - Mean filtering the prediction scores between 2 frames. Add label above the person if the score is larger than 0.8. See
class ClassifierOnlineTestin lib_classifier.py
For more details about how the features are extracted, please see my report.
First, Python >= 3.6.
I used the OpenPose from this Github: tf-pose-estimation. First download it:
export MyRoot=$PWD
cd src/githubs
git clone https://github.com/ildoonet/tf-pose-estimation
Follow its tutorial here to download the "cmu" model. As for the "mobilenet_thin", it's already inside the folder.
$ cd tf-pose-estimation/models/graph/cmu
$ bash download.sh
Then install dependencies. I listed my installation steps as bellow:
conda create -n tf tensorflow-gpu
conda activate tf
cd $MyRoot
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install jupyter tqdm
pip install tensorflow-gpu==1.13.1
sudo apt install swig
pip install "git+https://github.com/philferriere/cocoapi.git#egg=pycocotools&subdirectory=PythonAPI"
cd $MyRoot/src/githubs/tf-pose-estimation/tf_pose/pafprocess
swig -python -c++ pafprocess.i && python3 setup.py build_ext --inplace
Make sure you can successfully run its demo examples:
cd $MyRoot/src/githubs/tf-pose-estimation
python run.py --model=mobilenet_thin --resize=432x368 --image=./images/p1.jpg
The 5 main scripts are under src/. They are named under the order of excecution:
src/run1_get_skeletons_from_training_imgs.py
src/run2_put_skeleton_txts_to_a_single_txt.py
src/run3_preprocess_features.py
src/run4_train.py
src/run5_result.py
The input and output of these files as well as some parameters are defined in the configuration file config/config.yaml. I paste part of it below just to provide an intuition:
classes: ['running', 'jogging', 'walking', 'clapping']
image_filename_format: "{:05d}.jpg"
skeleton_filename_format: "{:05d}.txt"
features:
window_size: 5 # Number of adjacent frames for extracting features.
run1_get_skeletons_from_training_imgs.py:
openpose:
model: cmu # cmu or mobilenet_thin. "cmu" is more accurate but slower.
img_size: 656x368 # 656x368, or 432x368, 336x288. Bigger is more accurate.
input:
images_description_txt: data/valid_images.txt
images_folder: data/
output:
images_info_txt: data_skel/raw_skeletons/images_info.txt # This file is not used.
detected_skeletons_folder: &skels_folder data_skel/raw_skeletons/skeleton_res/
viz_imgs_folders: data_skel/raw_skeletons/image_viz/
run2_put_skeleton_txts_to_a_single_txt.py:
input:
# A folder of skeleton txts. Each txt corresponds to one image.
detected_skeletons_folder: *skels_folder
output:
# One txt containing all valid skeletons.
all_skeletons_txt: &skels_txt data_skel/raw_skeletons/skeletons_info.txt
run3_preprocess_features.py:
input:
all_skeletons_txt: *skels_txt
output:
processed_features: &features_x data_skel/features_X.csv
processed_features_labels: &features_y data_skel/features_Y.csv
s4_train.py:
input:
processed_features: *features_x
processed_features_labels: *features_y
output:
model_path: model/trained_classifier.pickleFor how to run the main scripts, please see the Section 4. How to run: Inference and 6. How to run: Training.
The script src/run5_result.py is for doing real-time action recognition.
The classes are set in config/config.yaml by the key classes.
The supported input includes video file, a folder of images, and web camera, which is set by the command line arguments --data_type and --data_path.
The trained model is set by --model_path, e.g.:model/trained_classifier.pickle.
The output is set by --output_folder, e.g.: output/.
The test data (a video, and a folder of images) are already included under the data_videos/ folder.
An example result of the input video "exercise.avi" is:
output/exercise/
├── skeletons
│ ├── 00000.txt
│ ├── 00001.txt
│ └── ...
└── video.avi
Also, the result will be displayed by cv2.imshow().
Example commands are given below:
python src/run5_result.py \
--model_path model/trained_classifier.pickle \
--data_type video \
--data_path data_videos/jogging.mp4 \
--output_folder outputpython src/run5_result.py \
--model_path model/trained_classifier.pickle \
--data_type folder \
--data_path data_videos/testing/ \
--output_folder outputpython src/run5_result.py \
--model_path model/trained_classifier.pickle \
--data_type webcam \
--data_path 0 \
--output_folder outputFollow the instructions in data/download_link.md to download the data. Or, you can create your own. The data and labelling format are described below.
Each data subfolder (e.g. data/running_03-02-12-34-01-795/) contains images named as 00001.jpg, 00002.jpg, etc.
The naming format of each image is defined in config/config.yaml by the sentence: image_filename_format: "{:05d}.jpg".
The images to be used as training data and their label are configured by this txt file: data/valid_images.txt.
A snapshot of this txt file is shown below:
running_03-13-11-27-50-720
52 59
72 79
jogging_03-02-12-34-01-795
54 62
In each paragraph,
the 1st line is the data folder name, which should start with "${class_name}_".
The 2nd and following lines specify the staring index and ending index of the video that corresponds to that class.
Let's take the 1st paragraph of the above snapshot as an example: running is the class, and the frames 52~59 & 72~79 of the video are used for training.
The classes are set in config/config.yaml under the key word classes. No matter how many classes you put in the training data (set by the folder name), only the ones that match with the classes in config.yaml are used for training and inference.
First, you may read
- Section
5. Training data - Section
3. Program structure - config/config.yaml
to know the training data format and the input and output of each script.
Then, follow the following steps to do the training:
- Collect your own data and label them, or use the data. Here is tool to record images from web camera.
- If you are using your data, change the values of
classesandimages_description_txtandimages_folderinside config/config.yaml. - Depend on your need, you may change parameters in config/config.yaml.
- Finally, run the following scripts one by one:
python src/run1_get_skeletons_from_training_imgs.py python src/run2_put_skeleton_txts_to_a_single_txt.py python src/run3_preprocess_features.py python src/run4_train.py
By default, the intermediate data are saved to data_skel/, and the model is saved to model/trained_classifier.pickle.
After training is done, you can run the inference script src/run5_result.py as described in