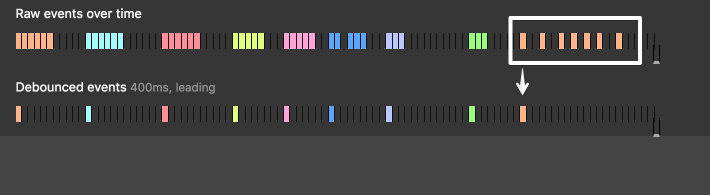Check wiki pages for more info - https://github.com/muni2explore/javascript-docs/wiki
Grouping a sudden burst of events (like keystrokes) into a single one.
Guaranteeing a constant flow of executions every X milliseconds. Like checking every 200ms your scroll position to trigger a CSS animation.
a throttle alternative. When your function recalculates and renders elements on screen and you want to guarantee smooth changes or animations. Note: no IE9 support.
var obj = {};
//which is equivalent to this
var obj = new Object();function addEvent(evnt, elem, func) {
if (elem.addEventListener) // W3C DOM
elem.addEventListener(evnt, func, false);
else if (elem.attachEvent) { // IE DOM
elem.attachEvent("on" + evnt, func);
} else { // No much to do
elem[evnt] = func;
}
}- Factory function
var createObj = function(name) {
return {
name: name,
sayHello: function() {
console.log("Hello "+this.name);
}
}
}
var muni = createObj("muni");
console.log(muni.sayHello()); // Hello muni
var sasi = createObj("sasi");
console.log(sasi.sayHello()); // Hello Sasi- Constructor function
var CreateObj = function(name) {
this.name = name;
this.sayHello = function() {
console.log("Hello "+this.name);
}
}
var muni = new CreateObj("muni");
console.log(muni.sayHello()); // Hello muni
var sasi = new CreateObj("sasi");
console.log(sasi.sayHello()); // Hello Sasivar makeReuest = function(url,cb){
var data = 30;
cb(data);
}
var obj = {
amt: 50,
loadData: function(data){
var sum = this.amt + data;
console.log(sum);
},
prepareRequest: function(){
var url = "http://example.com";
makeReuest(url, this.loadData.bind(this));
}
};
obj.prepareRequest();- Data Descriptor (value)
- Accessor Descriptor (get & set)
var obj = new Object();
Object.defineProperty(objectName, "propertyName", {
value: "somevalue" //Object descriptor object either Data/Accessor Object
writable: true //default false
})Example
var fruitObj = function(name) {
var fruit = {};
Object.defineProperty(fruit, "name", {
value: name,
writable: false
});
return fruit;
};
var apple = fruitObj("Apple");
console.log(apple.name); //Apple
apple.name = "Orange";
console.log(apple.name); //AppleExample : Writable True
var fruitObj = function(name) {
var fruit = {};
Object.defineProperty(fruit, "name", {
value: name,
writable: true
});
return fruit;
};
var apple = fruitObj("Apple");
console.log(apple.name); //Apple
apple.name = "Orange";
console.log(apple.name); //Orangevar createPerson = function(firstName, lastName) {
var person = {};
Object.defineProperties(person, {
firstName: {
value: firstName,
writable: true
},
lastName: {
value: lastName,
writable: true
},
fullName: {
get: function() {
return this.firstName+" "+this.lastName;
},
set: function(val) {
this.firstName = val;
this.lastName = val;
}
}
});
return person;
}
var muniAyothi = createPerson("muni", "ayothi");
console.log( muniAyothi.fullName ) // 'muni ayothi'
muniAyothi.fullName = 'sasi'
console.log( muniAyothi.fullName )// 'sasi sasi'configurable:true property which enable to redefine the particular property
var createPerson = function(firstName, lastName) {
var person = {};
Object.defineProperties(person, {
firstName: {
value: firstName
},
lastName: {
value: lastName
},
fullName: {
get: function() {
return this.firstName+" "+this.lastName;
},
configurable: false // default false
}
});
return person;
}
var muniAyothi = createPerson("muni", "ayothi");
Object.defineProperty(muniAyothi, "fullName", {
get: function() {
return this.lastName +" "+this.firstName;
}
} );
console.log(muniAyothi.fullName);Note: Script snippet #1:21 Uncaught TypeError: Cannot redefine property: fullName at Function.defineProperty () at :21:8
var createPerson = function(firstName, lastName) {
var person = {};
Object.defineProperties(person, {
firstName: {
value: firstName,
enumerable: true
},
lastName: {
value: lastName,
enumerable: true
},
fullName: {
get: function() {
return this.firstName+" "+this.lastName;
},
enumerable: true // default false
}
});
return person;
}
var muniAyothi = createPerson("muni", "ayothi");
Object.keys(muniAyothi); //['firstName', 'lastName', 'fullName']Directly accessing other object properties and combining with it's own properties.
var createPerson = function(firstName, lastName) {
var person = {
firstName: firstName,
lastName: lastName
};
Object.defineProperty(person, "fullName", {
get: function() {
return this.firstName+" "+this.lastName;
},
enumerable: true, // default false
configurable: true
});
return person;
}
var createEmployee = function(firstName, lastName, position) {
var person = createPerson(firstName, lastName);
person.position = position;
var fullName = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(person, "fullName");
var fullNameFunction = fullName.get.bind(person);
Object.defineProperty(person, "fullName",{
get: function(){
return fullNameFunction() +", "+ this.position;
}
});
return person;
}
var emp1 = createEmployee("Muni", "Ayothi", "Senior Webdeveloper");
console.log(emp1.fullName); //Muni Ayothi, Senior Webdeveloper
emp1.firstName = "Sasi";
console.log(emp1.fullName); //Sasi Ayothi, Senior Webdevelopervar createPerson = function(firstName, lastName) {
var person = {
firstName: firstName,
lastName: lastName,
sayHello: function(){
return "Hi there.."
}
};
Object.defineProperty(person, "fullName", {
get: function() {
return this.firstName+" "+this.lastName;
},
enumerable: true, // default false
configurable: true
});
return person;
}
var createEmployee = function(firstName, lastName, position) {
var person = createPerson(firstName, lastName);
person.position = position;
var fullName = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(person, "fullName");
var fullNameFunction = fullName.get.bind(person);
Object.defineProperty(person, "fullName",{
get: function(){
return fullNameFunction() +", "+ this.position;
}
});
var sayHelloFn = person.sayHello.bind(person);
person.sayHello = function() {
return sayHelloFn() + " My name is " + this.fullName
}
return person;
}
var emp1 = createEmployee("Muni", "Ayothi", "Senior Webdeveloper");
console.log(emp1.fullName); //Muni Ayothi, Senior Webdeveloper
emp1.firstName = "Sasi";
console.log(emp1.fullName); //Sasi Ayothi, Senior Webdeveloper
console.log(emp1.sayHello()); //Hi there.. My name is Sasi Ayothi, Senior Webdevelopervar Person = function(firstName, lastName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
Person.prototype.sayHello = function(){
return "Hi there..";
}
Object.defineProperty(Person.prototype, "fullName", {
get: function(){
return this.firstName+" "+this.lastName;
},
enumerable: true
});
var p1 = new Person("muni", "ayothi");
console.log(p1.firstName); //muni
console.log(p1.fullName); //muni ayothivar Person = function(firstName, lastName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
Object.defineProperties(Person.prototype, {
sayHello:{
value: function() {
return "Hi there..";
}
},
fullName:{
get: function(){
return this.firstName+" "+this.lastName;
},
enumerable: true
}
});
var p1 = new Person("muni", "ayothi");
console.log(p1.firstName); //muni
console.log(p1.fullName); //muni ayothi
console.log(p1.sayHello()); //Hi there..all = div.getElementByTagName('i'); //live nodelist
document.querySelectorAll('i'); //Static nodelistvar person = {
firstName: 'Muni',
lastName: 'Ayothi'
}
Object.defineProperties(person, {
fullName:{
get: function(){
return this.firstName+" "+this.lastName;
},
enumerable: true
}
});
var employee = Object.create(person);
console.log( employee.fullName ); //Muni AyothiWhen you create using Object.create() method, actually it's create new Object and assign that Object property in the newly created Object prototype.
employee.__proto__ === person //truevar person = {
firstName: 'Muni',
lastName: 'Ayothi'
}
Object.defineProperties(person, {
fullName:{
get: function(){
return this.firstName+" "+this.lastName;
},
enumerable: true
}
});
var employee = Object.create(person);
console.log( employee.fullName ); //Muni Ayothi
console.log( employee.__proto__ === person ); //true;
person.sayHi = function() {
return "hi there";
}
console.log( employee.sayHi() ); //hi there
employee.sayHi = function() {
return this.__proto__.sayHi.call(this)+" my name is "+this.fullName;
}
console.log( employee.sayHi() ); //hi there. my name is Muni Ayothi
console.log( person.sayHi() ); //hi thereWe can pass data descriptor when we creating new Object using Object.create() method.
var person = {
firstName: 'Muni',
lastName: 'Ayothi'
}
Object.defineProperties(person, {
fullName:{
get: function(){
return this.firstName+" "+this.lastName;
},
enumerable: true
}
});
var employee = Object.create(person, {
sayHi:{
value: function() {
return this.__proto__.sayHi.call(this)+" my name is "+this.fullName;
},
enumerable: true,
writable: false
}
});
console.log( employee.fullName ); //Muni Ayothi
console.log( employee.__proto__ === person ); //true;
person.sayHi = function() {
return "hi there";
}
console.log( employee.sayHi() ); //hi there. my name is Muni Ayothi
console.log( person.sayHi() ); //hi therevar Person = function(firstName, lastName){
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
Object.defineProperties(Person.prototype, {
fullName:{
get: function(){
return this.firstName+" "+this.lastName;
},
enumerable: true
},
sayHi: {
value: function() {
return "Hi there..";
}
}
});
var Employee = function(firstName, lastName, position){
Person.call(this, firstName, lastName);
this.position = position;
}
var emp1 = new Employee('Muni', 'Ayothi', 'Senior Webdeveloper');
emp1.firstName; //Muni
console.log(emp1.fullName); //undefinedWhere Person.call(this, firstName, lastName); actually attaches firstName and lastName property to the Employee Object directly. But that is not linked Person prototype properties to the Employee Object.
Here we have linked Person prototype properties to the Employee prototype properties by Object.create() method
var Person = function(firstName, lastName){
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
Object.defineProperties(Person.prototype, {
fullName:{
get: function(){
return this.firstName+" "+this.lastName;
},
enumerable: true
},
sayHi: {
value: function() {
return "Hi there..";
}
}
});
var Employee = function(firstName, lastName, position){
Person.call(this, firstName, lastName);
this.position = position;
}
Employee.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype, {
fullName:{
get: (function(){
var desc = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(Person.prototype, "fullName").get;
return function(){
return desc.call(this)+", "+this.position;
}
})(),
enumerable: true
},
sayHi: {
value: function() {
return Person.prototype.sayHi.call(this)+" My Name is "+this.fullName;
}
}
});
var emp1 = new Employee('Muni', 'Ayothi', 'Senior Webdeveloper');
console.log(emp1.firstName); //Muni
console.log(emp1.fullName); //Muni Ayothi, Senior Webdeveloper
console.log(emp1.sayHi()); //Hi there.. My Name is Muni AyothiWhere
emp1.__proto__.__proto__.sayHi === Person.prototype.sayHi; //true
emp1.__proto__.__proto__.__proto__.toString === Object.prototype.toString; //true
emp1.__proto__.__proto__.__proto__.hasOwnProperty('toString'); //true