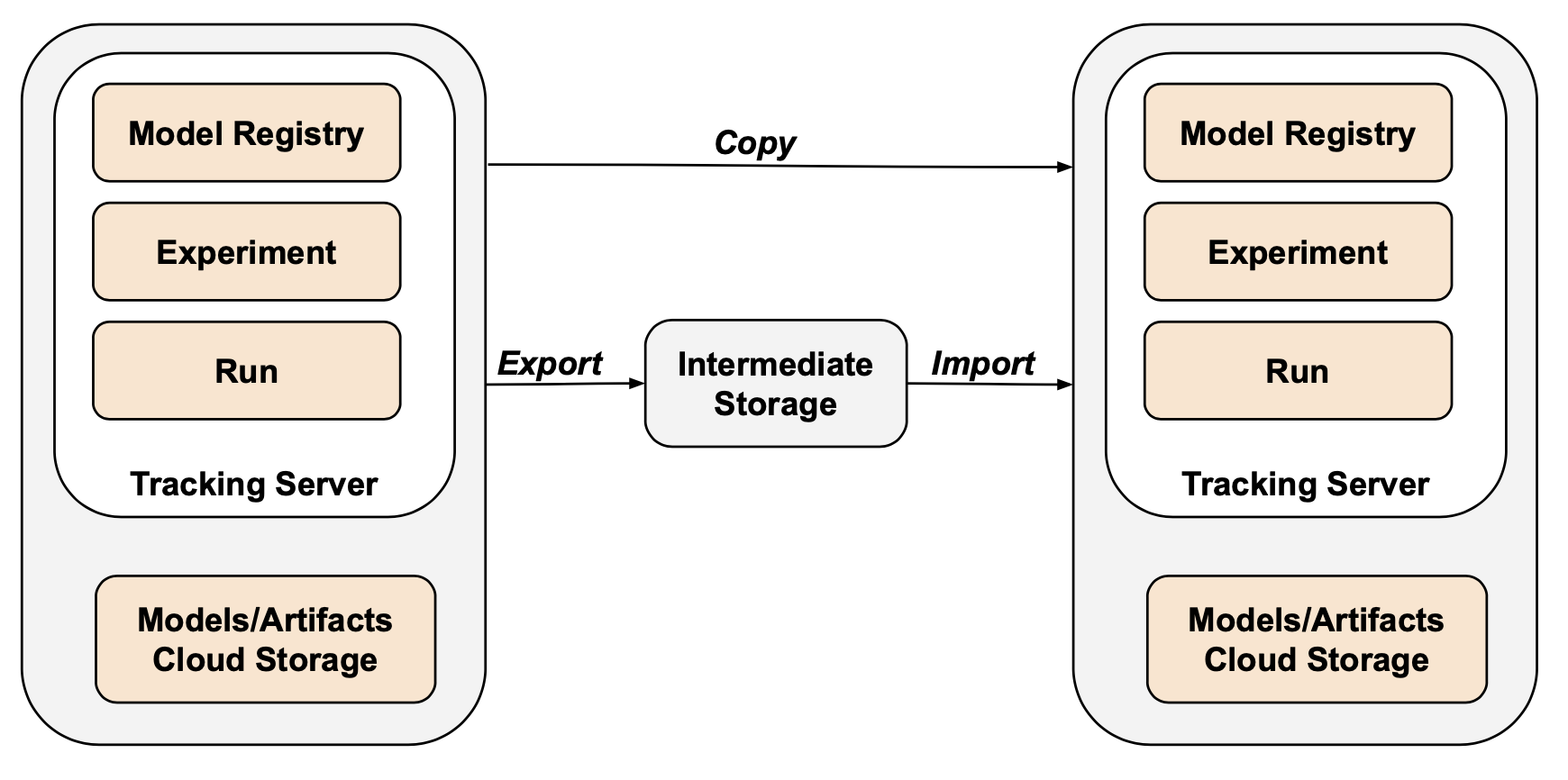
Tools to export and import MLflow runs, experiments or registered models from one tracking server to another.
- Export experiments to a directory.
- Import experiments from a directory.
- Copy an experiment from one tracking server to another.
- Export a run to a directory or zip file.
- Import a run from a directory or zip file.
- Copy a run from one tracking server to another.
- Export a registered model to a directory.
- Import a registered model from a directory.
- List all registered models.
- Nested runs are only supported when you import/copy an experiment. For a run, it is a TODO.
- The Databricks API does not support exporting or importing notebook revision. The workspace/export API endpoint only exports a notebook representing the latest notebook revision.
- Therefore you can only export/import MLflow experiments and runs. The notebook revision associated with a run cannot be exported or imported.
- When you import a run, the link to its source notebook revision ID will appear in the UI but you cannot reach that revision (link is dead).
- For convenience, the export tool exports the latest notebook revision for a notebook-based experiment but again, it cannot be attached to a run when imported.
- Copy tools work only for open source MLflow.
- Copy tools do not work when both the source and destination trackings servers are Databricks MLflow.
- Things get more complicated for the
copyfeature when using a a Databricks tracking server, either as source or destination . - This is primarily because MLflow client constructor only accepts a tracking_uri.
- For open source MLflow this works fine and you can have the two clients (source and destination) in the same program.
- For Databricks MLflow, the constructor is not used to initialize target servers. Environment variables are used to initialize the client, so only one client can exist.
- To copy experiments when a Databricks server is involved, you have to use the the two-stage process of first exporting the experiment and then importing it.
notebook-formats - If exporting a Databricks experiment, the run's notebook (latest revision, not the revision associated with the run) can be saved in the specified formats (comma-delimited argument). Each format is saved as notebook.{format}. Supported formats are SOURCE, HTML, JUPYTER and DBC. See Databricks Export Format documentation.
use-src-user-id - Set the destination user ID to the source user ID. Source user ID is ignored when importing into Databricks since the user is automatically picked up from your Databricks access token.
export-metadata-tags - Creates metadata tags (starting with mlflow_tools.metadata) containing export information. Contains the source mlflow tags in addition to other information. This is useful for provenance and auditing purposes in regulated industries.
Name Value
mlflow_tools.metadata.timestamp 1551037752
mlflow_tools.metadata.timestamp_nice 2019-02-24 19:49:12
mlflow_tools.metadata.experiment_id 2
mlflow_tools.metadata.experiment-name sklearn_wine
mlflow_tools.metadata.run-id 50fa90e751eb4b3f9ba9cef0efe8ea30
mlflow_tools.metadata.tracking_uri http://localhost:5000
Built with python 3.7.6.
python -m venv mlflow-export-import-env
source mlflow-export-import-env/bin/activate
pip install -e .
If you're working with a Databricks-hosted mlflow but still wants to use mlflow-export-import locally, you'll need to set the following environment variables:
export MLFLOW_TRACKING_URI=databricks
export DATABRICKS_HOST=https://mycompany.cloud.databricks.com
export DATABRICKS_TOKEN=<MY_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN>
If you want to run mlflow-export-import scripts directly on Databricks, you need to build a wheel artifact, push it up to DBFS and then install it on your cluster.
python setup.py bdist_wheel
databricks fs cp dist/mlflow_export_import-1.0.0-py3-none-any.whl {MY_DBFS_PATH}
There are two main programs to export experiments:
- export_experiment - exports one experiment
- export_experiment_list - exports a list of experiments
Both accept either an experiment ID or name.
Export one experiment to a directory.
Source: export_experiment.py
Usage
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.experiment.export_experiment --help
Options:
--experiment TEXT Experiment name or ID. [required]
--output-dir TEXT Output directory. [required]
--export-metadata-tags BOOLEAN Export source run metadata tags. [default: False]
--notebook-formats TEXT Notebook formats. Values are SOURCE, HTML,
JUPYTER or DBC. [default: SOURCE]
Export experiment by experiment ID.
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.experiment.export_experiment_list \
--experiment 2 --output-dir out
Export experiment by experiment name.
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.experiment.export_experiment_list \
--experiment sklearn-wine --output-dir out
See the Access the MLflow tracking server from outside Databricks.
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.experiment.export_experiment \
--experiment /Users/me@mycompany.com/SklearnWine \
--output-dir out \
--notebook-formats DBC,SOURCE
The output directory contains a manifest file and a subdirectory for each run (by run ID). The run directory contains a run.json file containing run metadata and an artifact hierarchy.
+-manifest.json
+-441985c7a04b4736921daad29fd4589d/
| +-artifacts/
| +-plot.png
| +-sklearn-model/
| +-model.pkl
| +-conda.yaml
| +-MLmodel
Export several (or all) experiments to a directory.
Source: export_experiment_list.py
Usage
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.experiment.export_experiment_list --help
--experiments TEXT Experiment names or IDs (comma delimited).
'all' will export all experiments. [required]
--output-dir TEXT Output directory. [required]
--export-metadata-tags BOOLEAN Export source run metadata tags. [default: False]
--notebook-formats TEXT Notebook formats. Values are SOURCE, HTML,
JUPYTER or DBC. [default: SOURCE]
Export experiments by experiment ID.
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.experiment.export_experiment_list \
--experiments 2,3 --output-dir out
Export experiments by experiment name.
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.experiment.export_experiment_list \
--experiments sklearn,sparkml --output-dir out
Export all experiments.
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.experiment.export_experiment_list \
--experiments all --output-dir out
The output directory contains a manifest file and a subdirectory for each experiment (by experiment ID).
Each experiment subdirectory in turn contains its own manifest file and a subdirectory for each run. The run directory contains a run.json file containing run metadata and an artifact hierarchy.
In the example below we have two experiments - 1 and 7. Experiment 1 (sklearn) has two runs (f4eaa7ddbb7c41148fe03c530d9b486f and 5f80bb7cd0fc40038e0e17abe22b304c) whereas experiment 7 (sparkml) has one run (ffb7f72a8dfb46edb4b11aed21de444b).
+-manifest.json
+-1/
| +-manifest.json
| +-f4eaa7ddbb7c41148fe03c530d9b486f/
| | +-run.json
| | +-artifacts/
| | +-plot.png
| | +-sklearn-model/
| | | +-model.pkl
| | | +-conda.yaml
| | | +-MLmodel
| | +-onnx-model/
| | +-model.onnx
| | +-conda.yaml
| | +-MLmodel
| +-5f80bb7cd0fc40038e0e17abe22b304c/
| | +-run.json
| +-artifacts/
| +-plot.png
| +-sklearn-model/
| | +-model.pkl
| | +-conda.yaml
| | +-MLmodel
| +-onnx-model/
| +-model.onnx
| +-conda.yaml
| +-MLmodel
+-7/
| +-manifest.json
| +-ffb7f72a8dfb46edb4b11aed21de444b/
| | +-run.json
| +-artifacts/
| +-spark-model/
| | +-sparkml/
| | +-stages/
| | +-metadata/
| +-mleap-model/
| +-mleap/
| +-model/
Top-level manifest.json for experiments.
{
"info": {
"mlflow_version": "1.11.0",
"mlflow_tracking_uri": "http://localhost:5000",
"export_time": "2020-09-10 20:23:45"
},
"experiments": [
{
"id": "1",
"name": "sklearn"
},
{
"id": "7",
"name": "sparkml"
}
]
}
Experiment manifest.json.
{
"experiment": {
"experiment_id": "1",
"name": "sklearn",
"artifact_location": "/opt/mlflow/server/mlruns/1",
"lifecycle_stage": "active"
},
"export_info": {
"export_time": "2020-09-10 20:23:45",
"num_runs": 2
},
"run-ids": [
"f4eaa7ddbb7c41148fe03c530d9b486f",
"f80bb7cd0fc40038e0e17abe22b304c"
],
"failed_run-ids": []
}
Run manifest.json: see below.
Import experiments from a directory. Reads the manifest file to import expirements and their runs.
The experiment will be created if it does not exist in the destination tracking server. If the experiment already exists, the source runs will be added to it.
There are two main programs to import experiments:
- import_experiment - imports one experiment
- import_experiment_list - imports a list of experiments
Imports one experiment.
Source: import_experiment.py
Usage
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.experiment.import_experiment --help \
Options:
--input-dir TEXT Input path - directory [required]
--experiment-name TEXT Destination experiment name [required]
--just-peek BOOLEAN Just display experiment metadata - do not import
--use-src-user-id BOOLEAN Set the destination user ID to the source
user ID. Source user ID is ignored when
importing into Databricks since setting it
is not allowed.
--import-mlflow-tags BOOLEAN Import mlflow tags
--import-metadata-tags BOOLEAN Import mlflow_export_import tags
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.experiment.import_experiment \
--experiment-name imported_sklearn \
--input-dir out
export MLFLOW_TRACKING_URI=databricks
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.experiment.import_experiment \
--experiment-name /Users/me@mycompany.com/imported/SklearnWine \
--input-dir exported_experiments/3532228
Import a list of experiments.
Source: import_experiment_list.py
Usage
python -m mlflow_export_import.experiment.import_experiment_list --help
Options:
--input-dir TEXT Input directory. [required]
--experiment-name-prefix TEXT If specified, added as prefix to experiment name.
--use-src-user-id BOOLEAN Set the destination user ID to the source
user ID. Source user ID is ignored when
importing into Databricks since setting it
is not allowed. [default: False]
--import-mlflow-tags BOOLEAN Import mlflow tags. [default: True]
--import-metadata-tags BOOLEAN Import mlflow_tools tags. [default: False]
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.experiment.import_experiment_list \
--experiment-name-prefix imported_ \
--input-dir out
Copies an experiment from one MLflow tracking server to another.
Source: copy_experiment.py
In this example we use:
- Source tracking server runs on port 5000
- Destination tracking server runs on 5001
Usage
python -m mlflow_export_import.experiment.copy_experiment --help
Options:
Options:
--src-uri TEXT Source MLflow API URI. [required]
--dst-uri TEXT Destination MLflow API URI. [required]
--src-experiment TEXT Source experiment ID or name. [required]
--dst-experiment-name TEXT Destination experiment name. [required]
--use-src-user-id BOOLEAN Set the destination user ID to the source
user ID. Source user ID is ignored when
importing into Databricks since setting it
is not allowed. [default: False]
--export-metadata-tags BOOLEAN Export source run metadata tags. [default: False]
Run example
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.experiment.copy_experiment \
--src-experiment sklearn_wine \
--dst-experiment-name sklearn_wine_imported \
--src-uri http://localhost:5000 \
--dst-uri http://localhost:5001
Export run to directory or zip file.
Source: export_run.py
Usage
python -m mlflow_export_import.run.export_run --help
Options:
--run-id TEXT Run ID. [required]
--output TEXT Output directory or zip file. [required]
--export-metadata-tags BOOLEAN Export source run metadata tags. [default: False]
--notebook-formats TEXT Notebook formats. Values are SOURCE, HTML,
JUPYTER or DBC. [default: SOURCE]
Run examples
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.run.export_run \
--run-id 50fa90e751eb4b3f9ba9cef0efe8ea30 \
--output out
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.run.export_run \
--run-id 50fa90e751eb4b3f9ba9cef0efe8ea30 \
--output run.zip
Produces a directory with the following structure:
run.json
artifacts
plot.png
sklearn-model
MLmodel
conda.yaml
model.pkl
Sample run.json
{
"info": {
"run-id": "50fa90e751eb4b3f9ba9cef0efe8ea30",
"experiment_id": "2",
...
},
"params": {
"max_depth": "16",
"max_leaf_nodes": "32"
},
"metrics": {
"mae": 0.5845562996214364,
"r2": 0.28719674214710467,
},
"tags": {
"mlflow.source.git.commit": "a42b9682074f4f07f1cb2cf26afedee96f357f83",
"mlflow.runName": "demo.sh",
"run_origin": "demo.sh",
"mlflow.source.type": "LOCAL",
"mlflow_tools.metadata.tracking_uri": "http://localhost:5000",
"mlflow_tools.metadata.timestamp": 1563572639,
"mlflow_tools.metadata.timestamp_nice": "2019-07-19 21:43:59",
"mlflow_tools.metadata.run-id": "130bca8d75e54febb2bfa46875a03d59",
"mlflow_tools.metadata.experiment_id": "2",
"mlflow_tools.metadata.experiment-name": "sklearn_wine"
}
}
Imports a run from a directory or zip file.
Source: import_run.py
Usage
python -m mlflow_export_import.run.import_run --help
Options:
--input TEXT Input path - directory or zip file. [required]
--experiment-name TEXT Destination experiment name. [required]
--use-src-user-id BOOLEAN Set the destination user ID to the source
user ID. Source user ID is ignored when
importing into Databricks since setting it
is not allowed. [default: False]
--import-mlflow-tags BOOLEAN Import mlflow tags. [default: True]
--import-metadata-tags BOOLEAN Import mlflow_tools tags. [default: False]
Directory out is where you exported your run.
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.run.import_run \
--run-id 50fa90e751eb4b3f9ba9cef0efe8ea30 \
--input out \
--experiment-name sklearn_wine_imported
export MLFLOW_TRACKING_URI=databricks
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.run.import_run \
--run-id 50fa90e751eb4b3f9ba9cef0efe8ea30 \
--input out \
--experiment-name /Users/me@mycompany.com/imported/SklearnWine \
Copies a run from one MLflow tracking server to another.
Source: copy_run.py
In this example we use
- Source tracking server runs on port 5000
- Destination tracking server runs on 5001
Usage
Options:
python -m mlflow_export_import.run.copy_run --help
--input TEXT Input path - directory or zip file.
[required]
--experiment-name TEXT Destination experiment name. [required]
--use-src-user-id BOOLEAN Set the destination user ID to the source
user ID. Source user ID is ignored when
importing into Databricks since setting it
is not allowed. [default: False]
--import-mlflow-tags BOOLEAN Import mlflow tags. [default: True]
--import-metadata-tags BOOLEAN Import mlflow_tools tags. [default: False]
Run example
export MLFLOW_TRACKING_URI=http://localhost:5000
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.run.copy_run \
--src-run-id 50fa90e751eb4b3f9ba9cef0efe8ea30 \
--dst-experiment-name sklearn_wine \
--src-uri http://localhost:5000 \
--dst-uri http://localhost:5001
Export a registered model to a directory.
Source: export_model.py.
Usage
python -m mlflow_export_import.model.export_model --help
Options:
--model TEXT Registered model name. [required]
--output-dir TEXT Output directory. [required]
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.model.export_model --model sklearn_wine --output-dir out
Output export directory example
+-749930c36dee49b8aeb45ee9cdfe1abb/
| +-artifacts/
| +-plot.png
| +-sklearn-model/
| | +-model.pkl
| | +-conda.yaml
| | +-MLmodel
| |
+-model.json
model.json
{
"registered_model": {
"name": "sklearn_wine",
"creation_timestamp": "1587517284168",
"last_updated_timestamp": "1587572072601",
"description": "hi my desc",
"latest_versions": [
{
"name": "sklearn_wine",
"version": "1",
"creation_timestamp": "1587517284216",
. . .
Import a registered model from a directory.
Source: import_model.py.
Usage
Options:
python -m mlflow_export_import.model.import_model --help
--input-dir TEXT Input directory produced by export_model.py.
[required]
--model TEXT New registered model name. [required]
--experiment-name TEXT Destination experiment name - will be created if it
does not exist. [required]
--delete-model BOOLEAN First delete the model if it exists and all its
versions. [default: False]
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.model.import_model \
--model sklearn_wine \
--experiment-name sklearn_wine_imported \
--input-dir out \
--delete-model True
Model to import:
Name: sklearn_wine
Description: my model
2 latest versions
Deleting 1 versions for model 'sklearn_wine_imported'
version=2 status=READY stage=Production run-id=f93d5e4d182e4f0aba5493a0fa8d9eb6
Importing latest versions:
Version 1:
current_stage: None:
Run to import:
run-id: 749930c36dee49b8aeb45ee9cdfe1abb
artifact_uri: file:///opt/mlflow/server/mlruns/1/749930c36dee49b8aeb45ee9cdfe1abb/artifacts
source: file:///opt/mlflow/server/mlruns/1/749930c36dee49b8aeb45ee9cdfe1abb/artifacts/sklearn-model
model_path: sklearn-model
run-id: 749930c36dee49b8aeb45ee9cdfe1abb
Importing run into experiment 'scratch' from 'out/749930c36dee49b8aeb45ee9cdfe1abb'
Imported run:
run-id: 03d0cfae60774ec99f949c42e1575532
artifact_uri: file:///opt/mlflow/server/mlruns/13/03d0cfae60774ec99f949c42e1575532/artifacts
source: file:///opt/mlflow/server/mlruns/13/03d0cfae60774ec99f949c42e1575532/artifacts/sklearn-model
Version: id=1 status=READY state=None
Waited 0.01 seconds
Calls the registered-models/list API endpoint and creates the file registered_models.json.
Source: list_registered_models.py.
Usage
python -u -m mlflow_export_import.model.list_registered_models
cat registered_models.json
{
"registered_models": [
{
"name": "keras_mnist",
"creation_timestamp": "1601399113433",
"last_updated_timestamp": "1601399504920",
"latest_versions": [
{
"name": "keras_mnist",
"version": "1",
"creation_timestamp": "1601399113486",
"last_updated_timestamp": "1601399504920",
"current_stage": "Archived",
"description": "",
"source": "file:///opt/mlflow/server/mlruns/1/9176458a78194d819e55247eee7531c3/artifacts/keras-model",
"run_id": "9176458a78194d819e55247eee7531c3",
"status": "READY",
"run_link": ""
},