Copyright (c) 2022 Maximilian W. Hofer & Kenneth A. Younge.
Repo maintainer: Maximilian W. Hofer (maximilian.hofer@epfl.ch)
AUTHOR: Maximilian W. Hofer
SOURCE: https://github.com/mxhofer/OrgSim-RL
LICENSE: Access to this code is provided under an MIT License.
The OrgSim-RL platform is a reinforcement learning simulation tool to model organizational returns to specialization.
- dyna-q/: dyna-Q algorithm
- vm/: virtual machine scripts
- .streamlit/: Streamlit authentication
- config.yaml: all parameter configurations
- dashboard.py: Streamlit dashboard
Create your own copy of the repository to freely experiment with OrgSim-RL.
git clone https://github.com/mxhofer/OrgSim-RL.git
pip install -r requirements.txt
You will need to enable the following services:
- BigQuery
- AppEngine (make sure you have deployment rights)
- Container Registry
- IAM (make sure you have permission to create a new service account)
- Create a VM with a disk (e.g. 200GB)
- Add to the disk:
- vm/rpc.sh script
- When you stop this first VM, keep the disk around so you can re-use copies of the disk for future VMs
- Stop the VM
- Create a new image from the disk. Future VMs will use a copy of this image.
- Update VM configurations in vm/vm.py:
- GitHub URL
- Format:
https://<username>:<token>@<github_url>
- Format:
- Project name
- Image name
- Compute zone
- GitHub URL
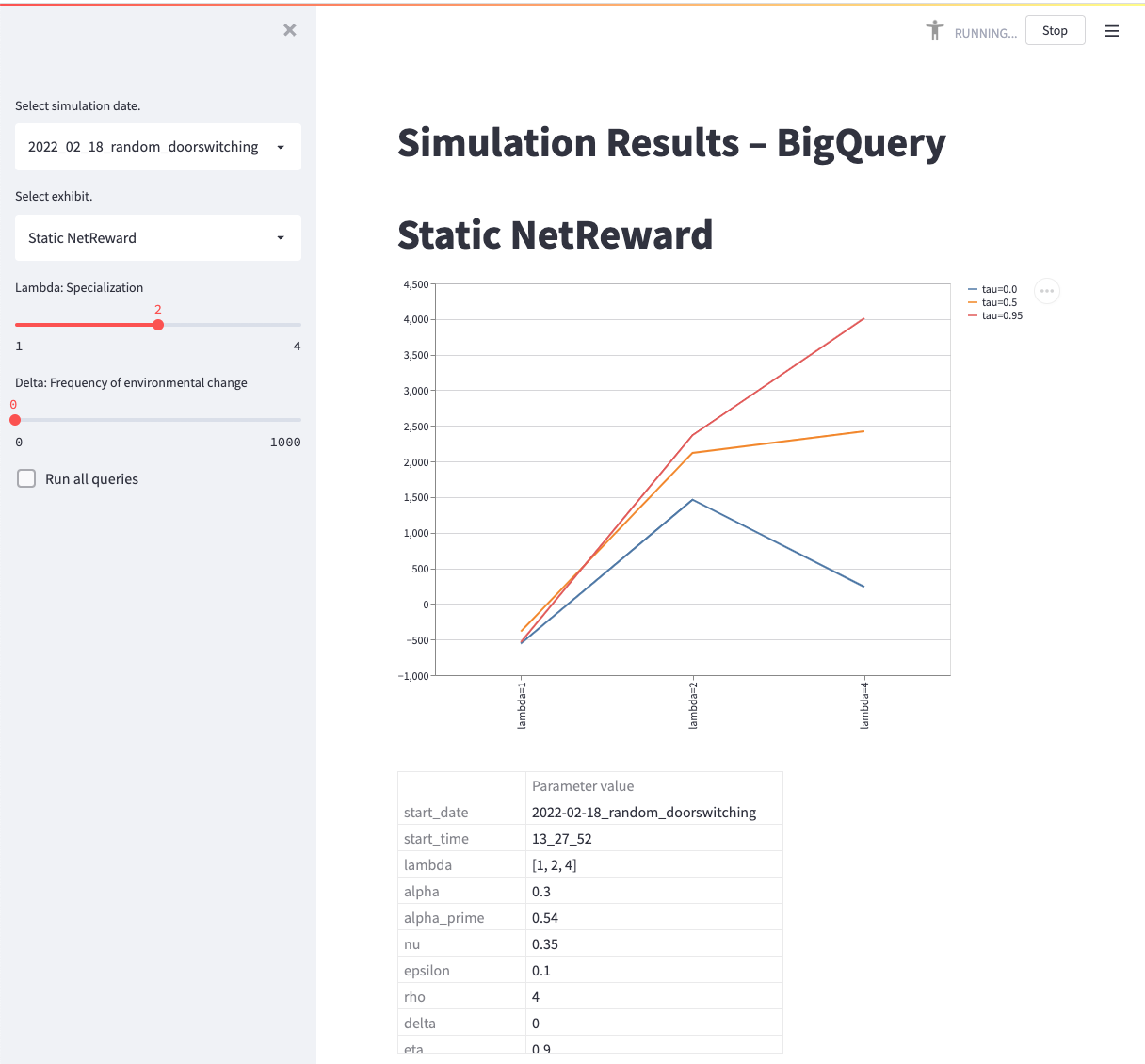
The config.yaml file contains all parameter values. The parameter values for specializaiton (lambda), automation (tau), environmental change (delta) are passed through the command line.
Beware: the simulation with default parameters takes > 12 hours to complete on an M1 MacBook Pro.
-
In your terminal, navigate to the dyna-q/ directory.
-
Run the simulation:
python dynaQ.py lambda <par_val> tau <par_val> delta <par_val> -
Review results in
dyna-q/outputs/results/<simulation_date>/
The vm/vm.py file starts VMs and overwrites parameter values for specializaiton (lambda), automation (tau), environmental change (delta).
- Set parameters in config.yaml
- Set a value for the
TAGvariable at the top of dyna-q/dynaQ.py to identify the simulation run. - Push repository to GitHub
- Set parameter ranges in vm/vm.py
- Run vm/vm.py
- Go to Google Cloud / Compute Engine / VM instances
- Click on a VM
- Open
Serial Port 1 (console)to check stdout log
- Check Google Cloud / Cloud Storage / Browser for simulation ouputs:
- Check bucket
simulation-output/results/
- Check bucket
- Validate outputs
- Use the
validate_outputsfunction in vm/vm.py
- Use the
- Follow the general guide on ingesting .csv files into BigQuery here
- Data set ID: date + TAG
- Create table from: select a .csv output file in the appropriate bucket. Then edit the filename to
*.csvto ingest all files in that bucket. - Table name:
results(hard requirement as the SQL queries expect this table name!) - Schema: Auto detect.
- Cluster by
delta, lambdato speed up querying performance. - In Advanced Options. Header rows to skip: 1
- Create table.
- Validate number of rows in table
- Click on the table name
- Navigate to
Details - Check
Number of rows. Number of rows should equal:- # of values for lambda x # of values for tau x # of values lambda x # episodes x # runs
- On Google Cloud:
- Create a service account with Viewer permissions. See details here.
- Create a key.
- Download the key as a JSON.
- Save the key file in .streamlit/
- Update the path to the key file in dashboard.py
- Add the key file to .gitignore
- Test that the dashboard is running locally:
streamlit run dashboard.py --server.port=8080 --server.address=0.0.0.0- Running the dashboard will write .csv files of the outputs to disk in dyna-q/outputs
- Test that the dashboard is running locally in a Docker container:
docker build . -t dashboarddocker run -p 8080:8080 dashboard
- Deploy dashboard:
gcloud app deploy dashboard.yaml- Click on the URL of the deployed service
Your deployed Streamlit dashboard is ready to use!