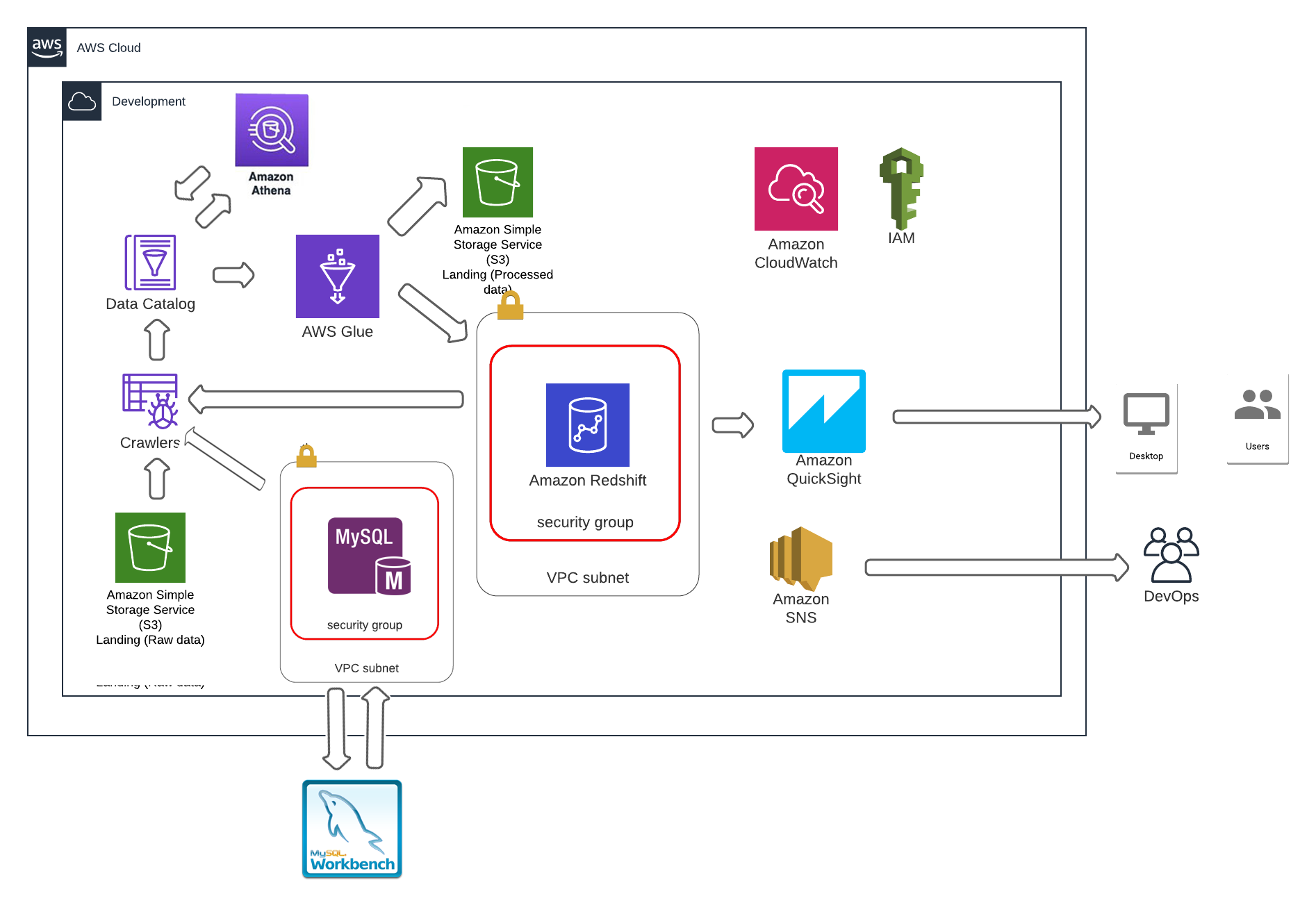
OLPT-to-OLAP-data-analytics on AWS with a use case
Data was not properly formatted in CSV so need to clean some data before crawling.
- Create a bucket with a bucket name for uploading csv datasets.
- Create separated folder of each of the csv files in the bucket and name the folder as the table names that will get the data from the data catalog by aws Athena
A crawler connects to a data store, progresses through a prioritized list of classifiers to determine the schema for your data, and then creates metadata tables in your data catalog.
- Create a csv classifier that determines the schema of data
- Create a IAM role for this job (with read and write access to S3)
- Adding Classifiers to a Crawler
- Create a database to get the data from the data catalog
- This will populate data to AWS Glue Data Catalog
Now we can query and exploring database tables in data catalog using aws Athena
SELECT * FROM "monir-assignar-db"."order" limit 10;SELECT * FROM "monir-assignar-db"."project";- MySQL DB instance in AWS RDS
- Creating appropriate security group for inbound traffic is allowed by default
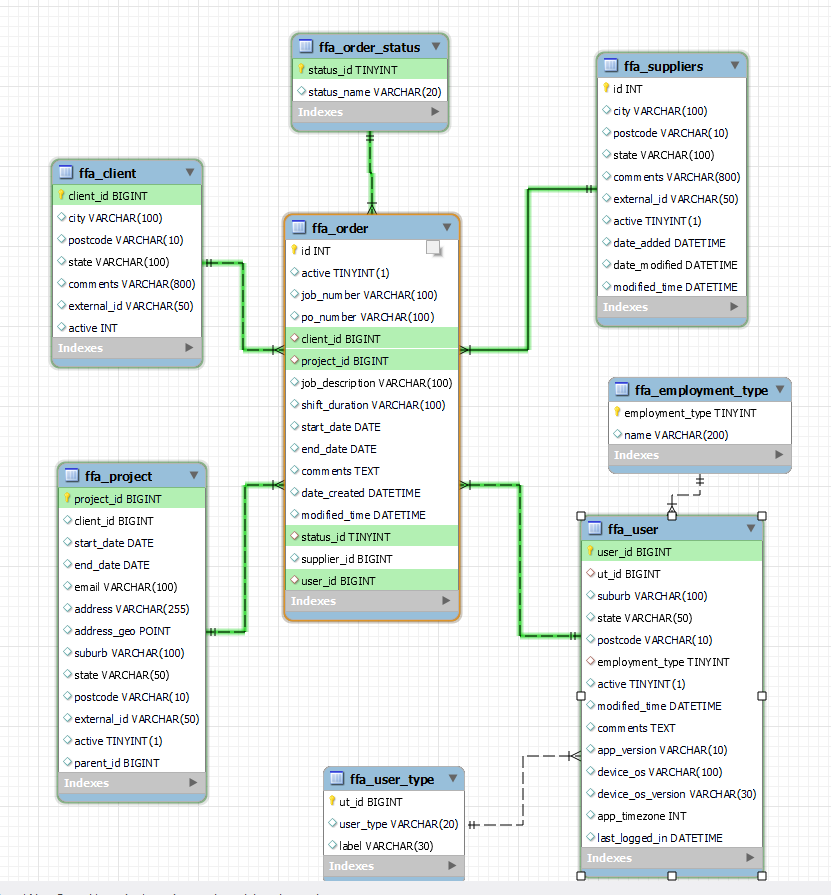
- Create database schema in mysql workbench using the sql script provided in the test
- Create a ERD using the schema by reverse engineering and adding primary and foreign keys
- Create a database schema using the ERD by forward engineering
- Create a RDS-Mysql connection in AWS Glue, add proopiuate IAM role and test the connection
- Create a crawler that crawl the databse schema from MySQL database
- Create a Glue ETL job to load data from glue datacatalogs to RDS Mysql database
MySQL-Workbench-script for creating OLTP scema in AWS RDS MySQL database instance
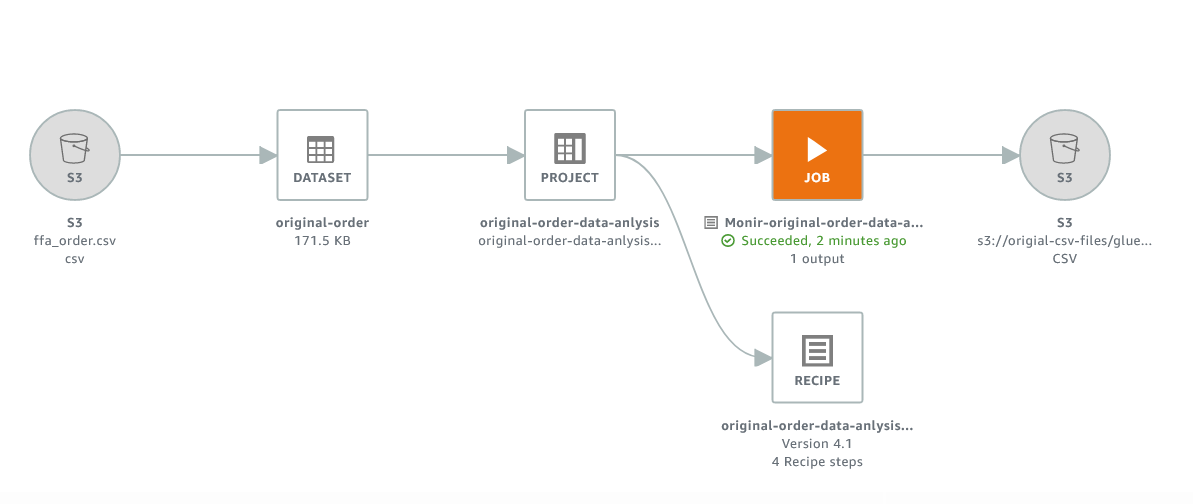
AWS Glue DataBrew job and recipe for data preparation for dimensional modelling
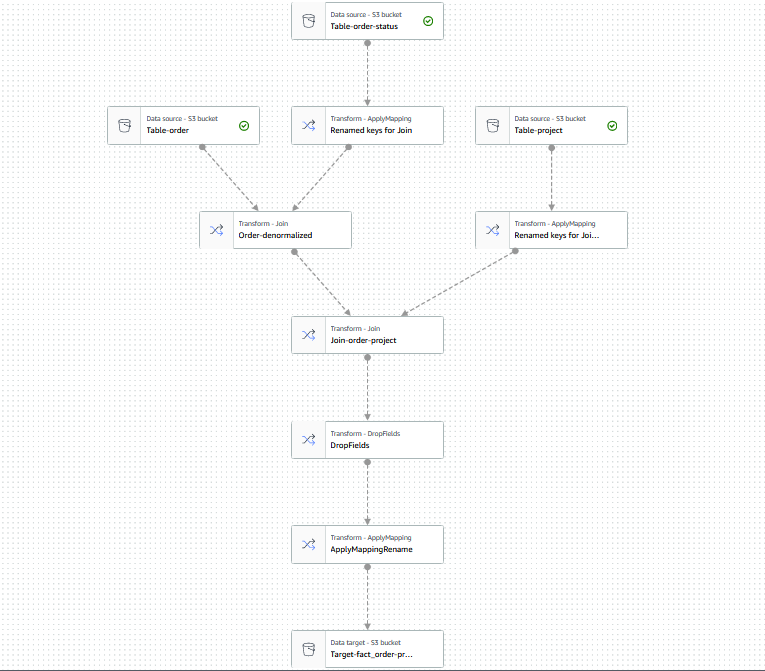
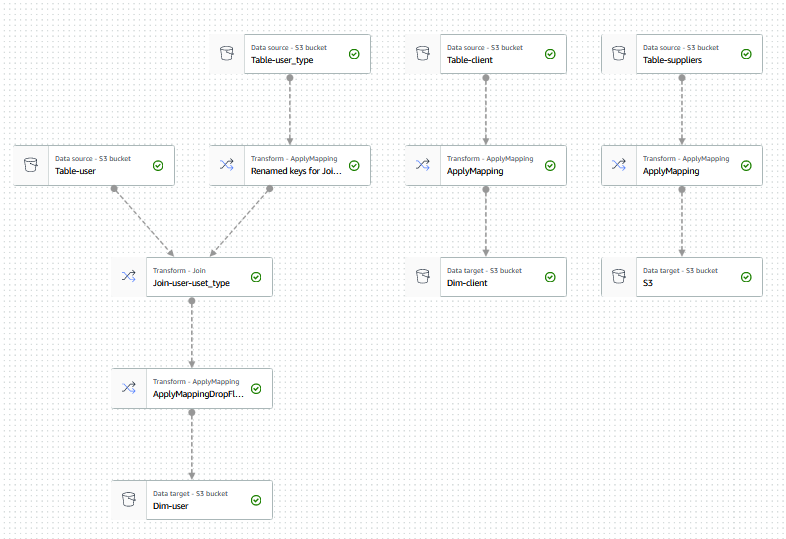
Step 06: AWS Glue jobs to convert this OLTP database structure to OLAP(Star/Snowflake) database structure for BI/Reporting purpose
Following Jobs have been created...
- AWS Glue ETL Job for creating Fact table and updating schema
- AWS Glue ETL Job for creating Dimention tables and updating schemas
AWS Glue ETL Job for creating Fact table and updating schema GlueJob01Code
AWS Glue ETL Job for creating Dimention tables and updating schemas GlueJob02Code
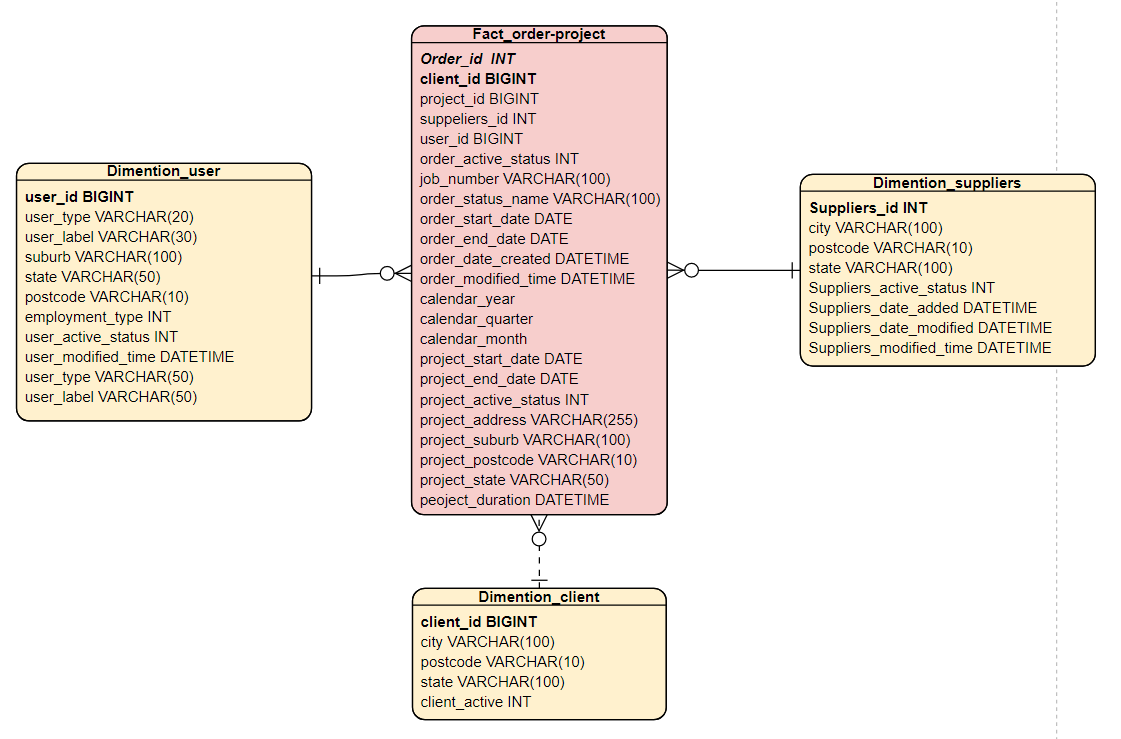
SQL script for creating tables with OLAP STAR SCHEMA in Redshift cluster
- attached the redshift cluster with appropriate IAM role (created)
- create a database schema, database with the SQL file provided in this test. In this case provide primary and foreign key constraints in creating associated tables.
CREATE TABLE assignar_olap_db.fact_order-project
(
order_id INT NOT NULL,
client_id BIGINT,
project_id BIGINT,
suppeliers_id INT,
user_id BIGINT,
order_active_status INT,
job_number VARCHAR(100),
po_number VARCHAR(100),
order_status_name VARCHAR(100),
order_start_date DATE,
order_end_date DATE,
order_date_created DATETIME,
order_modified_time DATETIME,
calendar_year DATETIME,
calendar_quarter DATETIME,
calendar_month DATETIME,
project_start_date DATE,
project_end_date DATE,
project_address VARCHAR(255),
project_address_geo POINT,
project_suburb VARCHAR(100),
project_state VARCHAR(50),
project_postcode VARCHAR(10),
project_active_status INT,
project_duration DATETIME,
PRIMARY KEY(order_id),
FOREIGN KEY(client_id) REFERENCES dimention_client(client_id),
FOREIGN KEY(user_id) REFERENCES dimention_user(user_id),
FOREIGN KEY(suppeliers_id) REFERENCES dimention_suppliers(suppliers_id),
);
CREATE TABLE assignar_olap_db.dimention_user
(
user_id INT NOT NULL,
suburb VARCHAR(100),
state VARCHAR(50),
postcode VARCHAR(10),
employment_type VARCHAR(50),
user_active_status VARCHAR(50),
user_modified_time DATETIME,
user_type VARCHAR(50),
user_label VARCHAR(50),
PRIMARY KEY(user_id)
);
CREATE TABLE assignar_olap_db.dimention_client
(
client_id INT NOT NULL,
city VARCHAR(100),
postcode VARCHAR(10),
state VARCHAR(50),
client_active INT,
PRIMARY KEY(client_id)
);
CREATE TABLE assignar_olap_db.dimention_suppliers
(
suppliers_id INT NOT NULL,
city VARCHAR(100),
postcode VARCHAR(10),
state VARCHAR(50),
suppliers_active_status VARCHAR(50),
suppliers_date_added DATETIME,
suppliers_date_modified DATETIME,
suppliers_modified_time DATETIME,
PRIMARY KEY(suppliers_id)
);- Using the COPY commands to load data from S3 buckets to Redshift created database
copy assignar_oltp_db.ffa_order
from 's3://assignar-test-db-bucket/upload-original-file/fact_order-project/'
iam_role 'arn:aws:iam::166809146462:role/RED'
region 'us-east-1'
delimiter ','
ignoreheader AS 1
DATEFORMAT AS 'dd/mm/yyyy'
TIMEFORMAT AS 'dd/mm/yyyy hh:mi'
csv;- Start analysis data using Redshift Query Editor.
a. How many Dashboard users have created orders in the year of 2020.
SELECT COUNT(user_id)
FROM assignar_olap_db.dimentaion_user
INNER JOIN assignar_olap_db.fact_order-project ON dimentaion_user.user_id = fact_order-project.user_id
WHERE fact_order-project.calendar_year = "2020"
AND dimentaion_user.user_label ="Dashboard User";b. Which project has been worked on the longest.
SELECT fact_order-project.project_id
FROM fact_order-project
WHERE project_duration =
(SELECT max(project_duration) from fact_order-project);c. Which client has the largest Quarter over Quarter growth (number of orders they have completed) in 2020?
SELECT distinct client_id
from
(
SELECT client_id, MAX(COUNT(order_id)) as MXorder
FROM fact_order-project where calendar_year ="2020"
GROUP BY client_id, MXorder
HAVING count(distinct calendar_quarter) = 4
) group by client_id