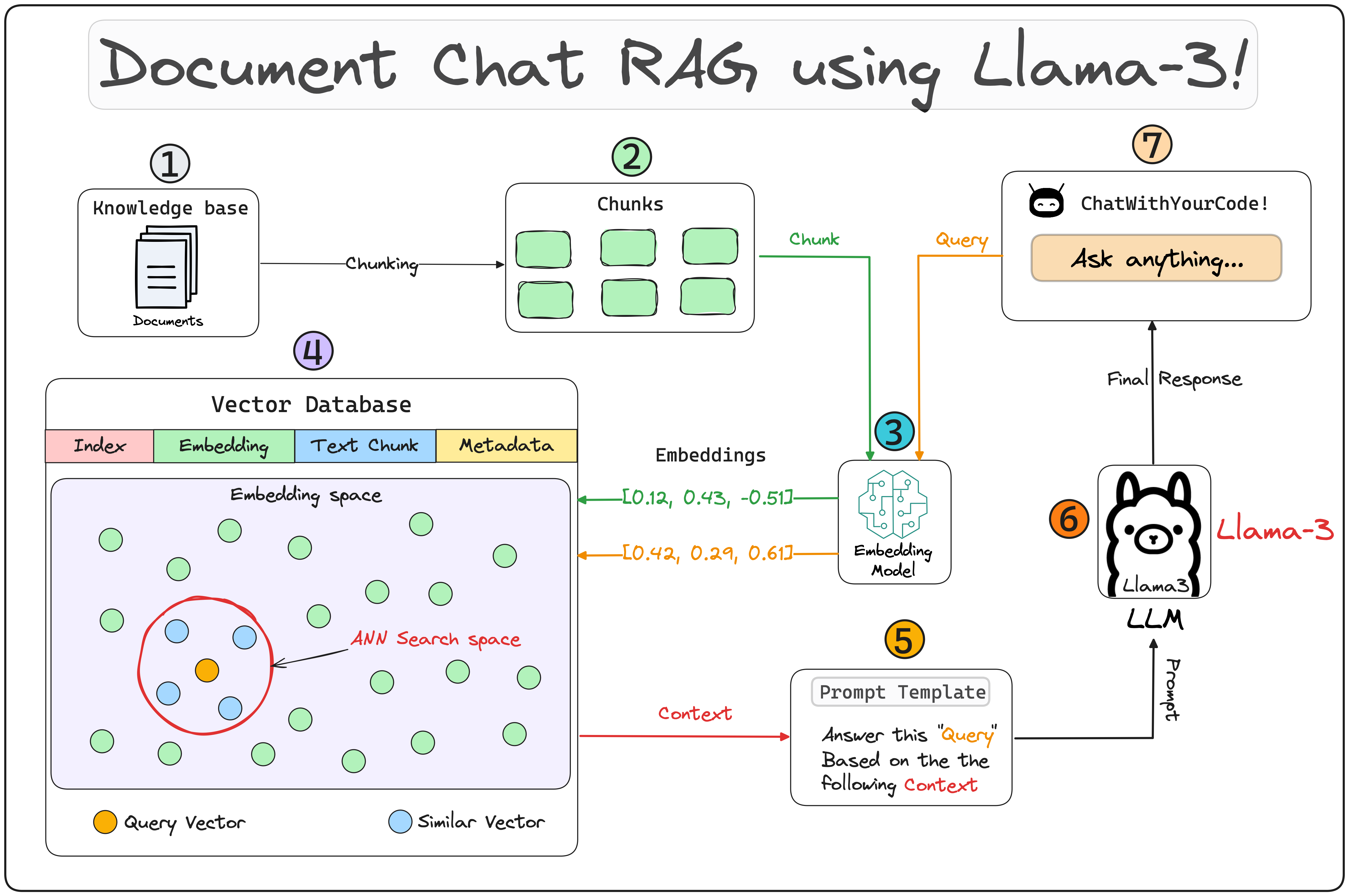
- 📚 Chat with your documents using advanced RAG technology
- 🧠 Powered by Meta AI's Llama3 model
- 🚀 Fast and efficient retrieval using vector databases
- 🎨 User-friendly Streamlit interface
Click to expand the interactive architecture diagram
graph TD
A[Custom Knowledge Base] -->|Indexing| B[Embeddings Model]
B -->|Vector Creation| C[Vector Database]
D[User Chat Interface] -->|Query| E[Query Engine]
C -->|Retrieval| E
E -->|Prompt| F[LLM - Llama3]
F -->|Response| D
G[Prompt Template] -->|Refinement| E
style A fill:#f9d5e5,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style B fill:#eeac99,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style C fill:#e06377,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style D fill:#5b9aa0,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style E fill:#d6cbd3,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style F fill:#b6b4c2,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style G fill:#c8ad7f,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
1. 📚 Custom Knowledge Base
A collection of relevant and up-to-date information that serves as a foundation for RAG. In this case, it's a PDF provided by you that will be used as a source of truth to provide answers to user queries.
from llama_index.core import SimpleDirectoryReader
# load data
loader = SimpleDirectoryReader(
input_dir = input_dir_path,
required_exts=[".pdf"],
recursive=True
)
docs = loader.load_data()2. 🧠 Embeddings Model
A technique for representing text data as numerical vectors, which can be input into machine learning models.
from llama_index.embeddings.huggingface import HuggingFaceEmbedding
embed_model = HuggingFaceEmbedding(model_name="BAAI/bge-large-en-v1.5", trust_remote_code=True)3. 🗄️ Vector Databases
A collection of pre-computed vector representations of text data for fast retrieval and similarity search.
from llama_index.core import Settings
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex
# Create vector store and upload indexed data
Settings.embed_model = embed_model
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(docs)4. 💬 User Chat Interface
A user-friendly interface built with Streamlit that allows users to interact with the RAG system. The code for it can be found in app.py.
5. 🔍 Query Engine
The query engine fetches relevant context and sends it along with the query to the LLM to generate a final natural language response.
from llama_index.llms.ollama import Ollama
from llama_index.core import Settings
# setting up the llm
llm = Ollama(model="llama3", request_timeout=120.0)
# Setup a query engine on the index previously created
Settings.llm = llm
query_engine = index.as_query_engine(streaming=True, similarity_top_k=4)6. ✏️ Prompt Template
A custom prompt template used to refine the response from LLM & include the context:
qa_prompt_tmpl_str = (
"Context information is below.\n"
"---------------------\n"
"{context_str}\n"
"---------------------\n"
"Given the context information above I want you to think step by step to answer the query in a crisp manner, incase case you don't know the answer say 'I don't know!'.\n"
"Query: {query_str}\n"
"Answer: "
)
qa_prompt_tmpl = PromptTemplate(qa_prompt_tmpl_str)
query_engine.update_prompts({"response_synthesizer:text_qa_template": qa_prompt_tmpl})This application requires significant computational resources. A standard GPU may not suffice to run it locally; a more advanced environment is recommended. You can explore the functionality using LightningAi workspace, Streamlit Cloud or other cloud-based solutions. Check this out to try out on hand https://lightning.ai/lightning-ai/studios/rag-using-llama-3-1-by-meta-ai