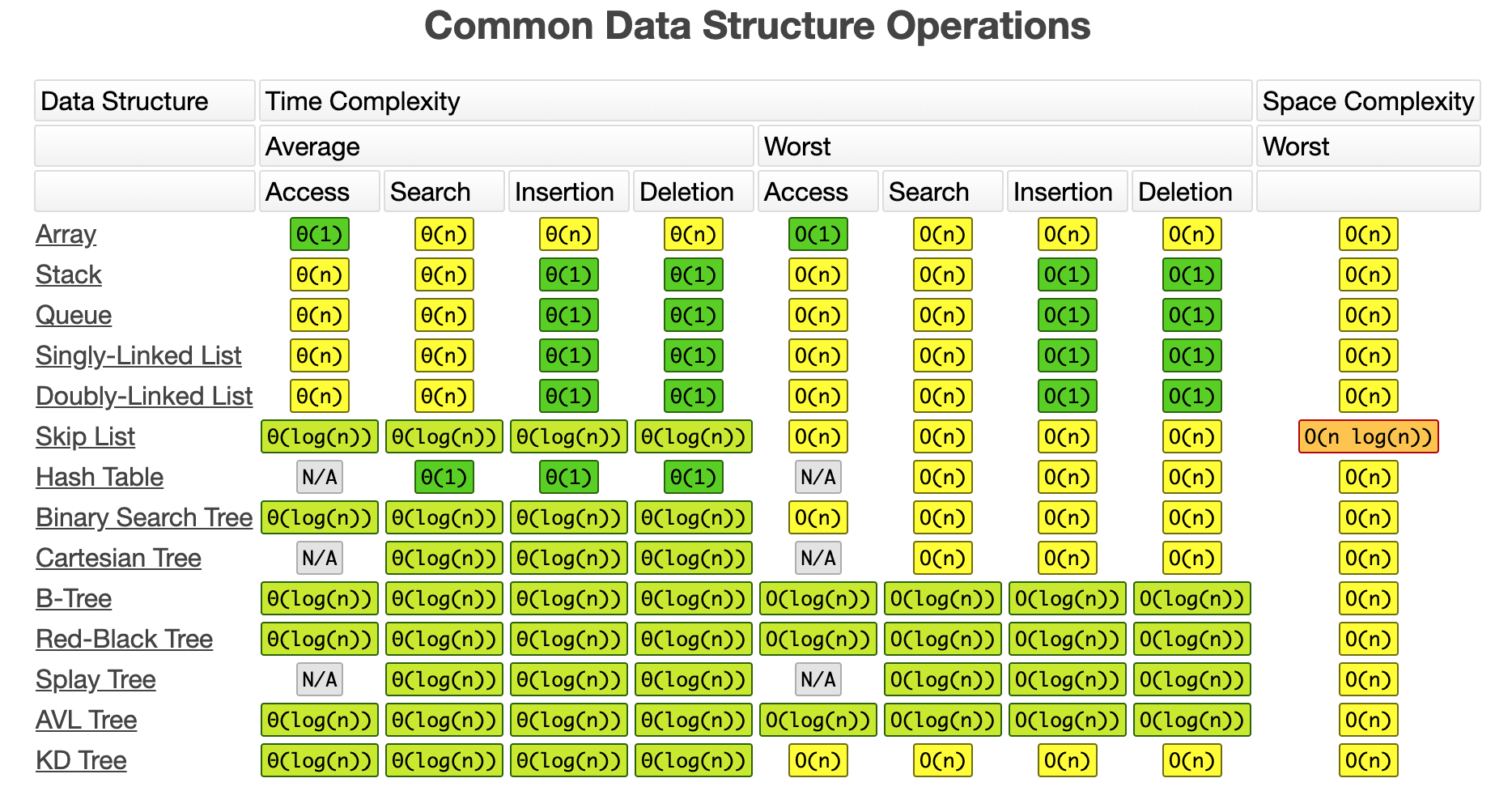
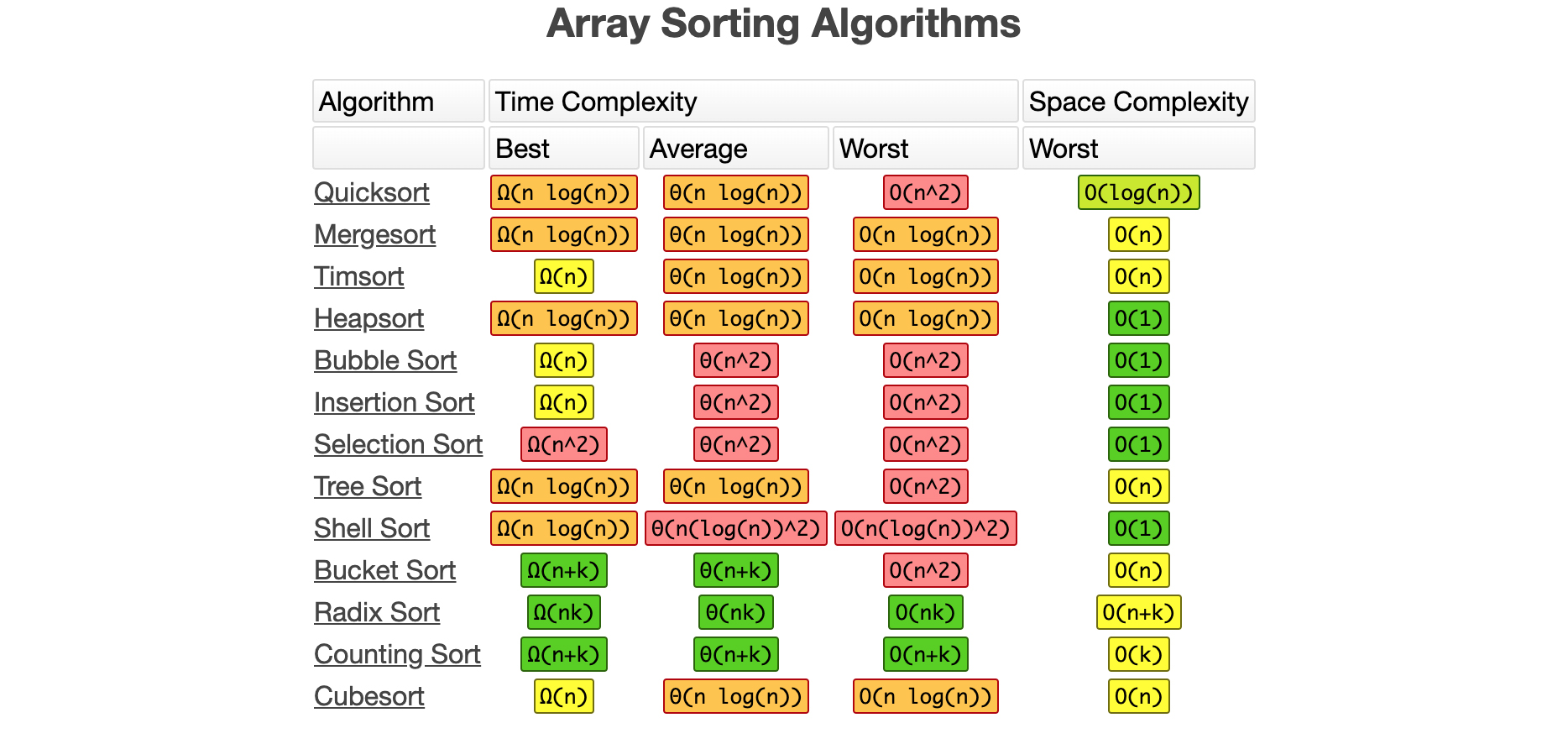
Data Structure and Algorithm practice
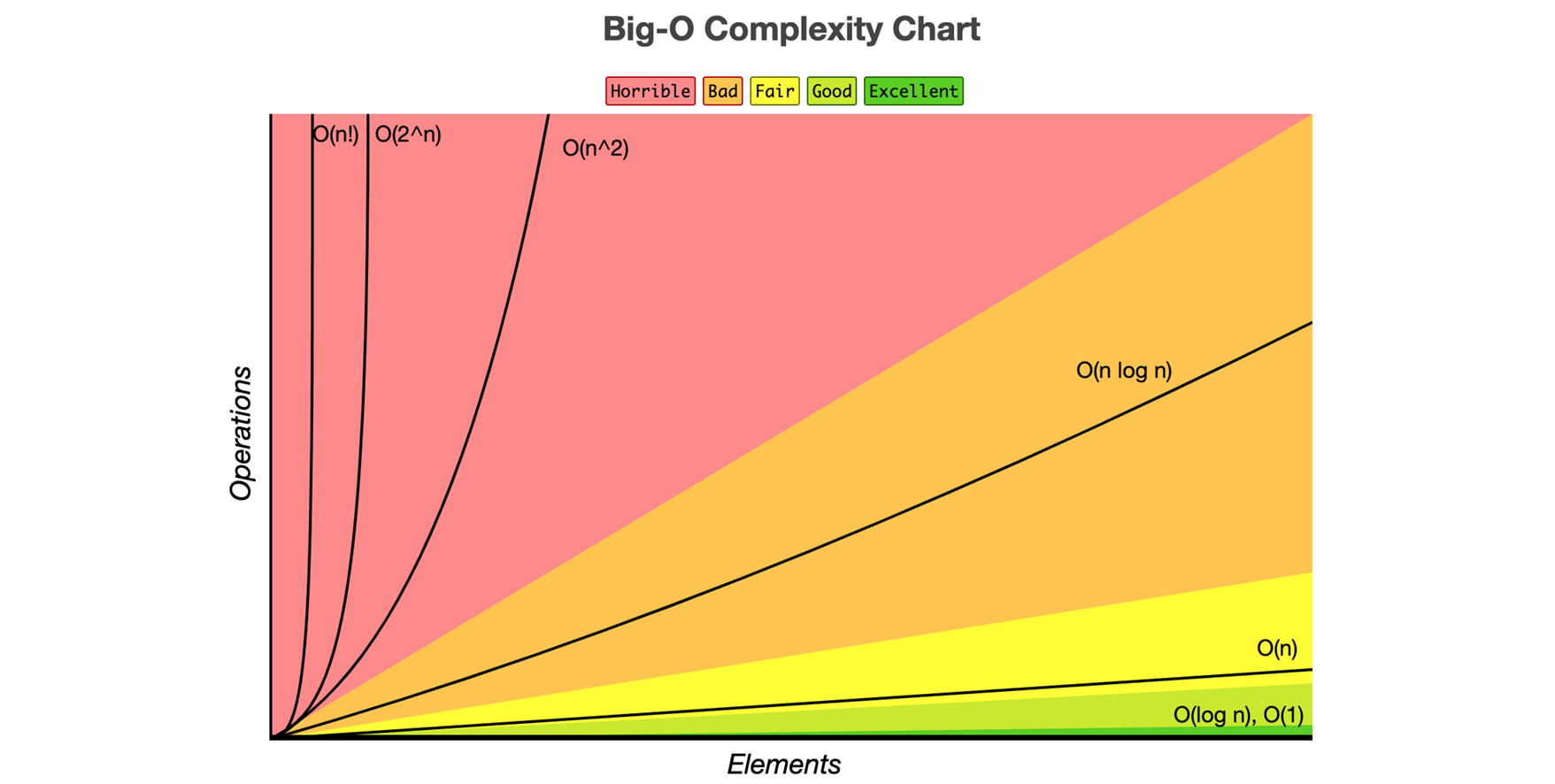
- Logarithmic algorithm – O(logn): Runtime grows logarithmically in proportion to n.
- Linear algorithm – O(n): Runtime grows directly in proportion to n.
- Superlinear algorithm – O(nlogn): Runtime grows in proportion to n.
- Polynomial algorithm – O(n^c): Runtime grows quicker than previous all based on n.
- Exponential algorithm – O(c^n): Runtime grows even faster than polynomial algorithm based on n.
- Factorial algorithm – O(n!): Runtime grows the fastest, becomes quickly unusable for even small values of n.